Racism remains a pervasive issue affecting societies worldwide, manifesting in various forms such as systemic discrimination, prejudiced attitudes, and unequal opportunities. This infographic visually presents key statistics, historical context, and the ongoing impact of racism on different communities. Understanding these elements is crucial for fostering awareness and promoting social justice.
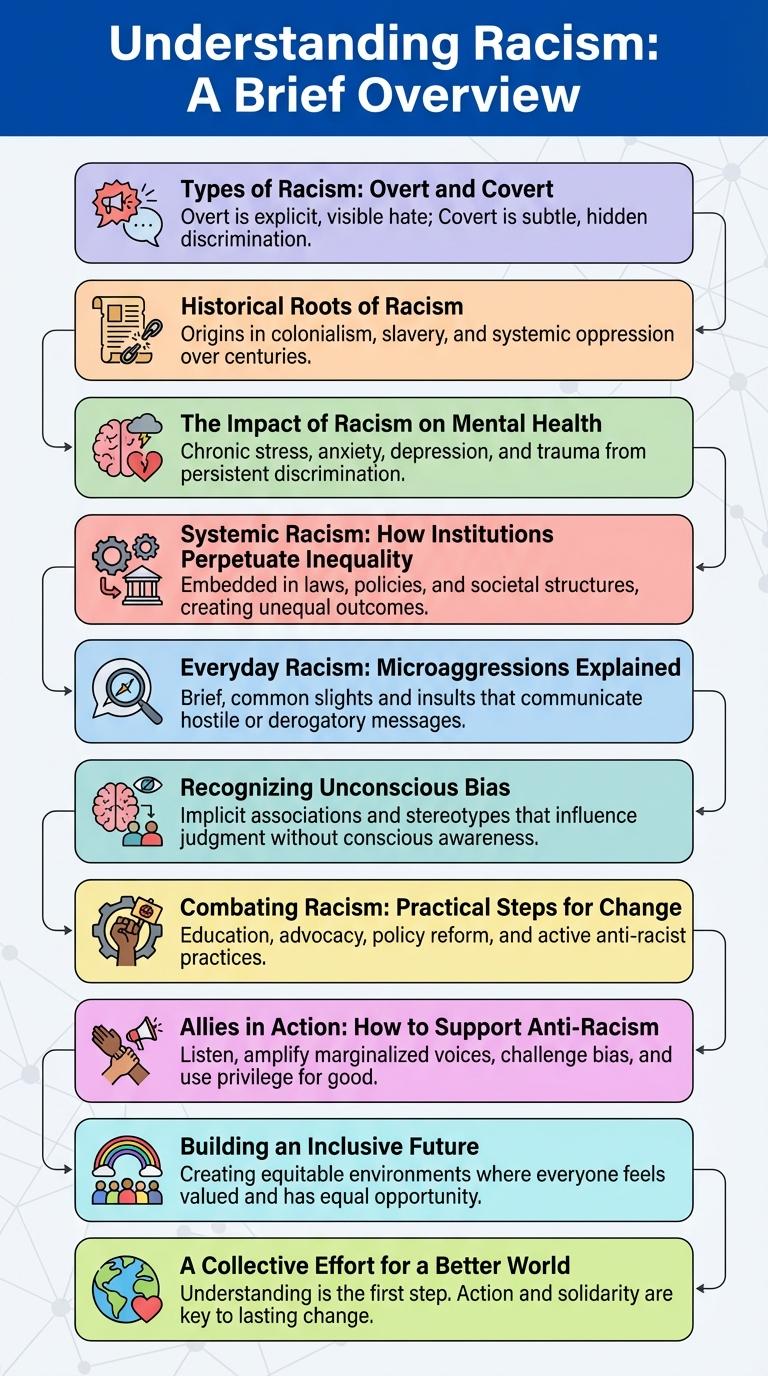
Understanding Racism: A Brief Overview
Racism is the belief that different races possess distinct characteristics, abilities, or qualities that can determine superiority or inferiority. It leads to discrimination and prejudice, impacting individuals and society on multiple levels.
Understanding racism requires recognizing both individual biases and systemic inequalities embedded in institutions. Awareness and education are essential steps toward fostering equality and social justice.
Types of Racism: Overt and Covert
| Type of Racism | Description |
|---|---|
| Overt Racism | Explicit actions or statements that openly express racial bias or discrimination. |
| Covert Racism | Hidden or subtle behaviors, policies, or attitudes that indirectly perpetuate racial inequality. |
| Examples of Overt Racism | Racial slurs, hate crimes, discriminatory laws, and open racial segregation. |
| Examples of Covert Racism | Microaggressions, racial profiling, employment biases, and unequal resource distribution. |
Historical Roots of Racism
Racism has deep historical roots that have shaped societies worldwide. Understanding these origins is crucial to addressing systemic inequality.
- Colonialism - European colonial powers imposed racial hierarchies to justify exploitation and control of indigenous populations.
- Slavery - The transatlantic slave trade institutionalized racial discrimination by dehumanizing African people for economic gain.
- Pseudoscience - 19th-century scientific racism used flawed theories to falsely categorize races and legitimize prejudice.
Recognizing these historical foundations helps dismantle persistent racial biases and promotes equity.
The Impact of Racism on Mental Health
Racism significantly affects mental health by increasing stress, anxiety, and depression among marginalized groups. Experiences of discrimination and social exclusion contribute to long-term psychological trauma and diminished well-being. Addressing racism is essential for promoting equitable mental health care and reducing health disparities.
Systemic Racism: How Institutions Perpetuate Inequality
Systemic racism refers to the policies and practices ingrained in institutions that result in unequal outcomes for racial groups. It creates barriers that limit access to resources, opportunities, and justice for marginalized communities.
- Education Disparities - Schools in predominantly minority neighborhoods often receive less funding, limiting quality education and resources.
- Criminal Justice Bias - Minority groups face disproportionately high rates of arrests, convictions, and harsher sentencing.
- Housing Inequality - Historical redlining and discriminatory lending have restricted access to homeownership for people of color.
Everyday Racism: Microaggressions Explained
Everyday racism often manifests through microaggressions, subtle and often unintentional discriminatory comments or actions. These microaggressions can undermine the dignity and sense of belonging of marginalized individuals.
Common examples include assumptions about intelligence, language ability, or cultural background based on race. Such interactions perpetuate stereotypes and contribute to systemic inequality.
Recognizing Unconscious Bias
What is unconscious bias and how does it affect our perceptions? Unconscious bias refers to the automatic, implicit judgments we make about others based on background, race, or ethnicity. These biases influence behavior without our conscious awareness, shaping interactions and decisions unknowingly.
How can recognizing unconscious bias reduce racism? Awareness of unconscious bias allows individuals to actively challenge stereotypes and prejudices ingrained in social systems. This awareness promotes equitable treatment and supports diversity and inclusion efforts in communities and workplaces.
What are common signs of unconscious bias in daily life? Examples include making assumptions based on race, favoring people who look similar, or interpreting behaviors through stereotypical lenses. Identifying these signs helps in creating unbiased responses and fairer social environments.
Which methods effectively reveal unconscious biases? Tools such as Implicit Association Tests (IAT) and reflective practices increase self-awareness of hidden prejudices. Regular training sessions and open discussions encourage ongoing recognition and correction of unconscious biases.
Why is addressing unconscious bias crucial for combating racism? Unchecked biases perpetuate systemic inequalities and social exclusion. Confronting these biases leads to more inclusive attitudes, fostering equality and respect across diverse racial and ethnic groups.
Combating Racism: Practical Steps for Change
Racism remains a pervasive issue impacting societies worldwide. Combating it requires conscious efforts to promote equality and respect for all individuals.
Education plays a crucial role in dismantling stereotypes and fostering understanding. Encouraging open conversations about race helps raise awareness and challenges prejudices. Supporting policies that promote diversity and inclusion creates lasting social change.
Allies in Action: How to Support Anti-Racism
Allies play a vital role in the fight against racism by actively supporting marginalized communities. Taking tangible steps helps create an inclusive society where equality thrives.
Supporting anti-racism involves continuous learning, speaking out against injustice, and amplifying underrepresented voices.
- Educate Yourself - Engage with books, documentaries, and workshops to understand systemic racism and its impacts.
- Listen and Amplify - Prioritize listening to experiences of people of color and share their stories to raise awareness.
- Challenge Racism - Speak up against racist remarks and behaviors in personal and professional environments.
- Support Inclusive Policies - Advocate for equitable laws and workplace practices that promote diversity and inclusion.
- Participate in Community Actions - Join protests, support minority-owned businesses, and volunteer for anti-racism organizations.
