Infographics about gender roles visually present the societal expectations and stereotypes associated with different genders, highlighting disparities in areas such as work, education, and family life. They provide clear, concise data illustrating how traditional roles impact opportunities and behaviors across cultures. This visual format helps increase awareness and fosters discussions on gender equality and social change.
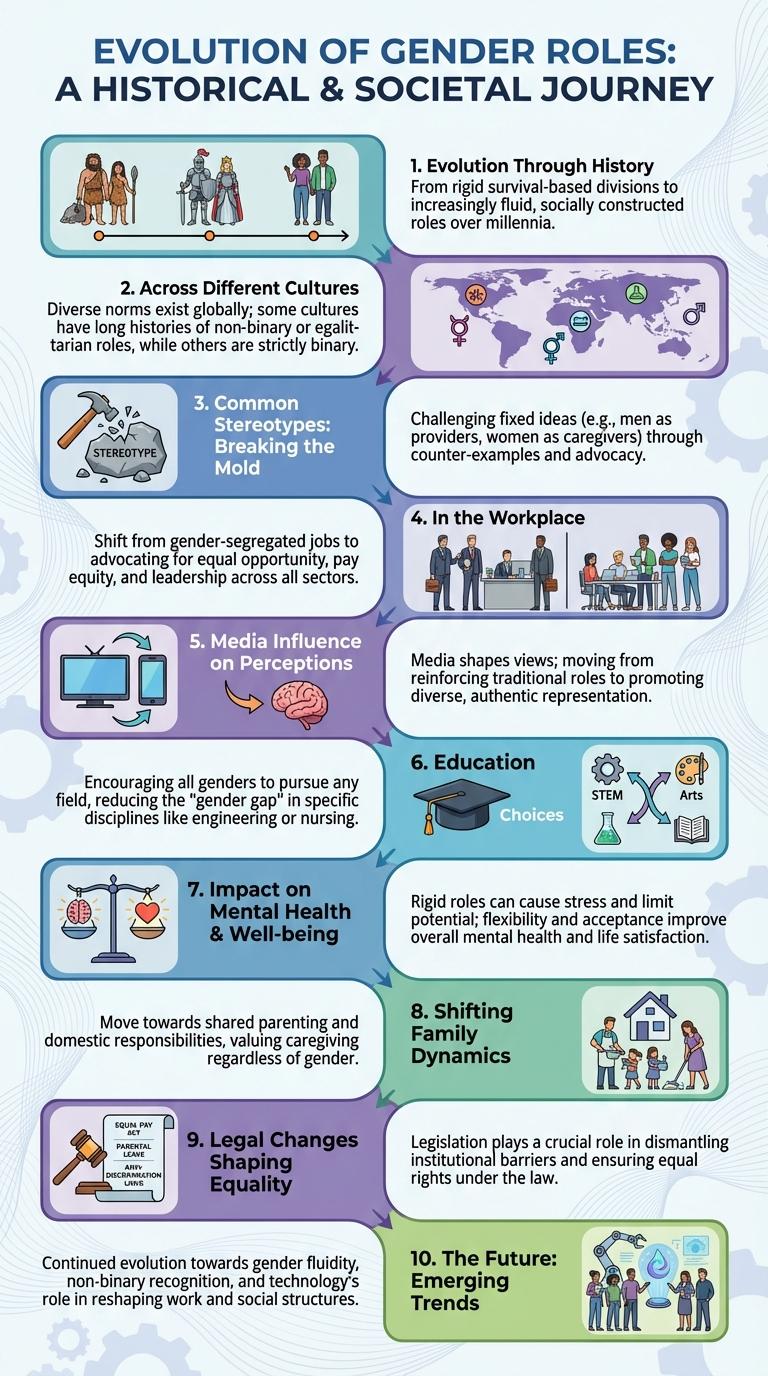
Evolution of Gender Roles Through History
The evolution of gender roles reflects significant social, economic, and cultural changes throughout history. Traditionally, many societies assigned distinct roles to men and women, often centered around labor divisions and family responsibilities. Over time, movements for gender equality and shifts in workforce participation have transformed these roles into more fluid and diverse expressions of identity and capability.
Gender Roles Across Different Cultures
How do gender roles vary across different cultures? Gender roles define societal expectations for behaviors and responsibilities based on gender. These roles differ significantly depending on cultural, historical, and social contexts, influencing family dynamics, work, and education.
| Culture | Traditional Gender Roles |
|---|---|
| Western | Emphasis on gender equality; shared responsibilities in career and home life. |
| Middle Eastern | Distinct roles; men as providers, women as caregivers with increasing female workforce participation. |
| East Asian | Strong family hierarchy; men as primary earners, women balancing domestic duties and work. |
| Indigenous | Varied roles; some tribes practice gender fluidity and equal contribution in community tasks. |
| Latin American | Traditional machismo influences male dominance; women often manage household and family care. |
Common Stereotypes: Breaking the Mold
Common gender stereotypes often depict men as assertive and women as nurturing, limiting individual expression and opportunities. These rigid roles influence career choices, behavior expectations, and social interactions in diverse cultures.
Breaking the mold means challenging these norms by promoting equality and embracing diverse identities. Encouraging open dialogue and education helps dismantle stereotypes, fostering an inclusive society where everyone can thrive.
Gender Roles in the Workplace
Gender roles in the workplace shape expectations about behavior, responsibilities, and career paths for men and women. These roles influence hiring decisions, job assignments, and professional development opportunities.
Studies reveal that women often face challenges such as wage gaps and underrepresentation in leadership roles. Men are typically expected to occupy positions requiring physical strength or technical expertise, reinforcing occupational stereotypes.
Media Influence on Gender Perceptions
Media significantly shapes societal views on gender roles, often reinforcing traditional stereotypes. Exposure to gendered content influences individual perceptions of appropriate behaviors and identities.
- Television Portrayals - TV shows frequently depict men and women in conventional roles, affecting audience expectations.
- Advertising Impact - Advertisements use gender-specific imagery and messages that emphasize stereotypical traits.
- Social Media Influence - Social media platforms amplify gender norms through curated content and influencer presentations.
Gender Roles and Education Choices
Gender roles significantly influence education choices, shaping career paths and academic interests from an early age. Societal expectations often lead to gendered preferences in fields such as STEM for males and humanities for females.
Studies reveal that girls tend to pursue education in arts, literature, and social sciences, while boys gravitate towards science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). This trend reflects persistent stereotypes and cultural norms affecting self-perception and confidence in certain subjects. Encouraging diversity in education can help break down these gender biases and expand opportunities for all students.
Impact on Mental Health and Well-being
Gender roles shape individuals' behaviors and expectations, influencing mental health and overall well-being. Restrictive norms often create stress, limiting emotional expression and access to support.
- Increased Anxiety and Depression - Conforming to rigid gender roles correlates with higher rates of anxiety and depression due to societal pressure and lack of emotional outlets.
- Limited Emotional Expression - Men facing norms to suppress emotions risk unresolved stress, while women may experience guilt over nonconformity, affecting mental health.
- Reduced Access to Support - Stigma around mental health in gendered expectations leads to reluctance in seeking help, worsening psychological well-being.
Shifting Family Dynamics and Gender
Gender roles within families are undergoing significant changes influenced by societal progress and cultural shifts. These evolving dynamics impact responsibilities, expectations, and relationships among family members.
- Increased Shared Parenting - More households are embracing equal division of childcare and household duties between partners.
- Rise of Dual-Income Families - Economic factors contribute to both parents actively participating in the workforce.
- Redefinition of Masculinity and Femininity - Traditional gender expectations are challenged, allowing for diverse expressions within family roles.
Understanding these transformations helps promote balanced and inclusive family environments.
Legal Changes Shaping Gender Equality
Legal changes have played a crucial role in shaping gender equality by establishing rights and protections against discrimination. Laws such as the Equal Pay Act and Title IX have addressed disparities in workplaces and educational institutions. Recent legislation continues to advance gender equality by promoting equal opportunities and safeguarding against gender-based violence.
