Juvenile delinquency remains a critical issue affecting communities worldwide, reflecting the challenges faced by young individuals in various social environments. Understanding the factors contributing to youth crime, such as family dynamics, peer influence, and socioeconomic status, is essential for developing effective prevention strategies. Visualizing these elements through an infographic offers a clear and impactful way to grasp the scope and causes of juvenile delinquency.
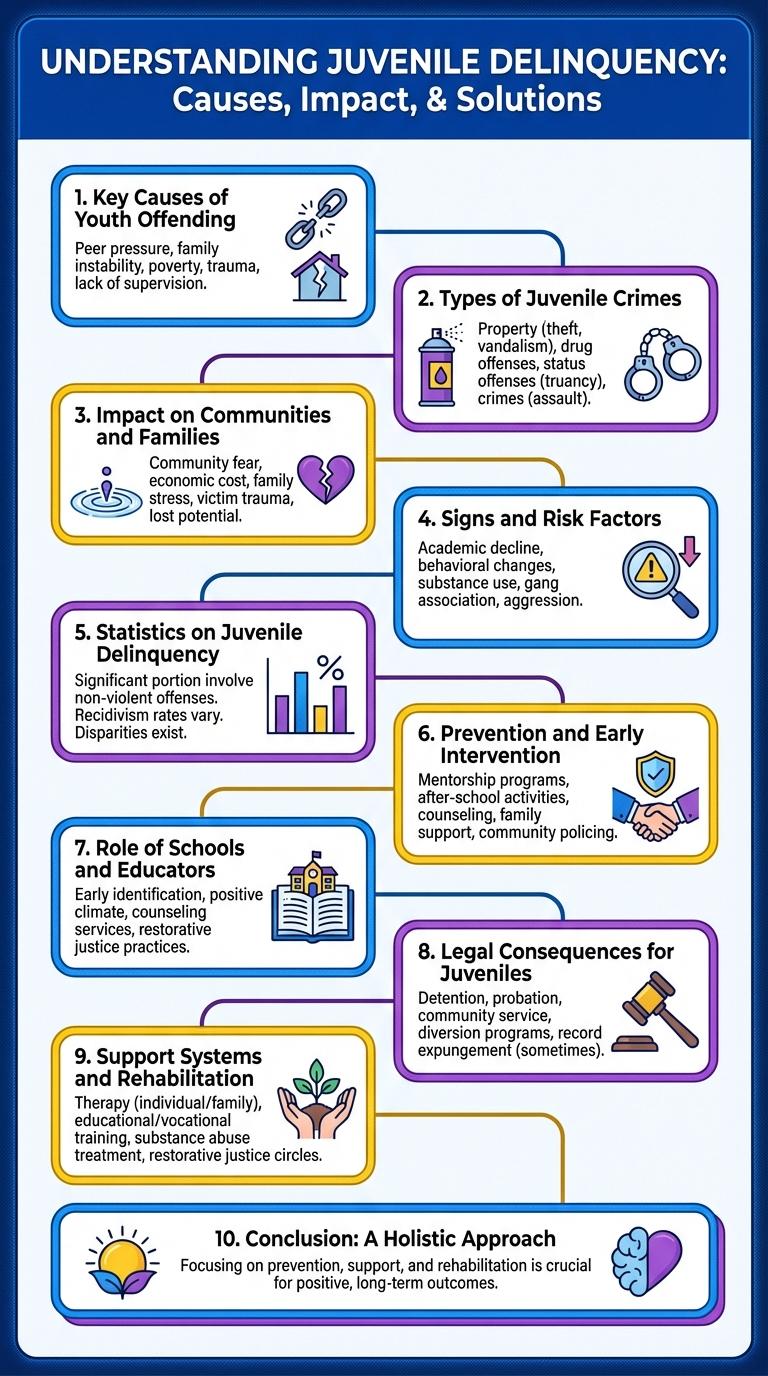
Understanding Juvenile Delinquency
Juvenile delinquency refers to illegal or antisocial behavior by individuals under the age of 18. Understanding its causes and patterns is essential for effective prevention and intervention.
Multiple factors contribute to juvenile delinquency, including family environment, peer influence, and socioeconomic status.
- Risk Factors - Exposure to violence, lack of parental supervision, and substance abuse increase the likelihood of delinquent behavior.
- Common Offenses - Theft, vandalism, and drug-related crimes are prevalent among juveniles involved in delinquency.
- Prevention Strategies - Early intervention programs, counseling, and community support reduce juvenile delinquency rates.
Key Causes of Youth Offending
Youth offending stems from multiple interconnected factors that influence behavior during critical developmental stages. Understanding these causes helps in designing effective prevention and intervention programs.
Family environment, including parental neglect and domestic violence, plays a significant role in juvenile delinquency. Peer pressure and the need for social acceptance often drive young individuals toward criminal activities.
Types of Juvenile Crimes
Juvenile delinquency encompasses various types of offenses committed by individuals under the age of 18. Understanding these types helps in addressing the root causes and implementing preventive measures.
Types of juvenile crimes vary widely, reflecting different social and behavioral issues among youth.
- Status Offenses - Acts that are only considered violations due to the offender's age, such as truancy or curfew violations.
- Property Crimes - Involves theft, vandalism, or burglary committed by juveniles.
- Violent Crimes - Includes assault, robbery, and other offenses causing physical harm.
Impact on Communities and Families
| Impact Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Community Safety | Increased juvenile delinquency leads to higher crime rates, causing fear and reduced quality of life for residents. |
| Economic Costs | Communities face expenses related to law enforcement, legal proceedings, and rehabilitation programs for youth offenders. |
| Family Strain | Families experience emotional distress, financial burdens, and breakdowns in relationships due to juvenile behaviors. |
| Educational Disruption | Delinquent youth often face school suspensions or dropouts, impacting future employment opportunities and community growth. |
| Social Stigma | Communities and families associated with juvenile offenders may encounter social exclusion and discrimination, limiting support networks. |
Signs and Risk Factors
Juvenile delinquency often manifests through signs such as frequent truancy, aggressive behavior, and sudden changes in social circles. Risk factors include family instability, peer pressure, and exposure to violence or substance abuse. Early identification of these signs and risk factors can help in implementing effective interventions to prevent further delinquent behavior.
Statistics on Juvenile Delinquency
Juvenile delinquency refers to illegal or antisocial behavior by individuals under 18 years old. It remains a significant concern in many countries, impacting communities and legal systems globally.
Statistics reveal that approximately 1.3 million youth arrests were made in the United States in 2022, with theft, vandalism, and assault being the most common offenses. Studies indicate that male juveniles are more likely to engage in delinquent acts compared to females. Recidivism rates show that nearly 50% of youths reoffend within a year after their initial offense.
Prevention and Early Intervention
What are effective strategies for preventing juvenile delinquency? Early intervention programs targeting at-risk youth reduce the likelihood of offending by addressing underlying social and emotional challenges. Community-based initiatives focusing on family support and education improve long-term outcomes for children.
How does early intervention impact juvenile delinquency rates? Studies show that counseling and mentorship help youth develop positive decision-making skills and resilience. Structured afterschool activities keep children engaged and away from harmful influences.
Role of Schools and Educators
Juvenile delinquency significantly affects community safety and youth development. Schools and educators are pivotal in identifying risk factors and fostering positive behavioral changes.
- Early Identification - Educators can recognize warning signs of delinquency through changes in attendance, behavior, or academic performance.
- Preventive Programs - Schools implement social-emotional learning and conflict resolution curricula to reduce the likelihood of delinquent behavior.
- Supportive Environment - Teachers and staff create inclusive, supportive spaces that encourage healthy peer relationships and discourage antisocial activities.
Effective school-based interventions contribute to lowering juvenile delinquency rates and promoting long-term youth success.
Legal Consequences for Juveniles
Juvenile delinquency refers to illegal or antisocial behavior committed by individuals under the age of 18. Legal consequences for juveniles often include rehabilitative measures like counseling, community service, or probation instead of harsh penalties. Severity of consequences depends on the offense, with serious crimes potentially resulting in detention in juvenile facilities or transfer to adult court.
