Gender-based violence (GBV) remains a critical global issue affecting millions of individuals regardless of age or background. This infographic poster highlights key statistics, types, and prevention strategies to raise awareness and promote action. Visual elements convey the urgent need for education and community support to combat GBV effectively.
Understanding Gender-Based Violence (GBV)
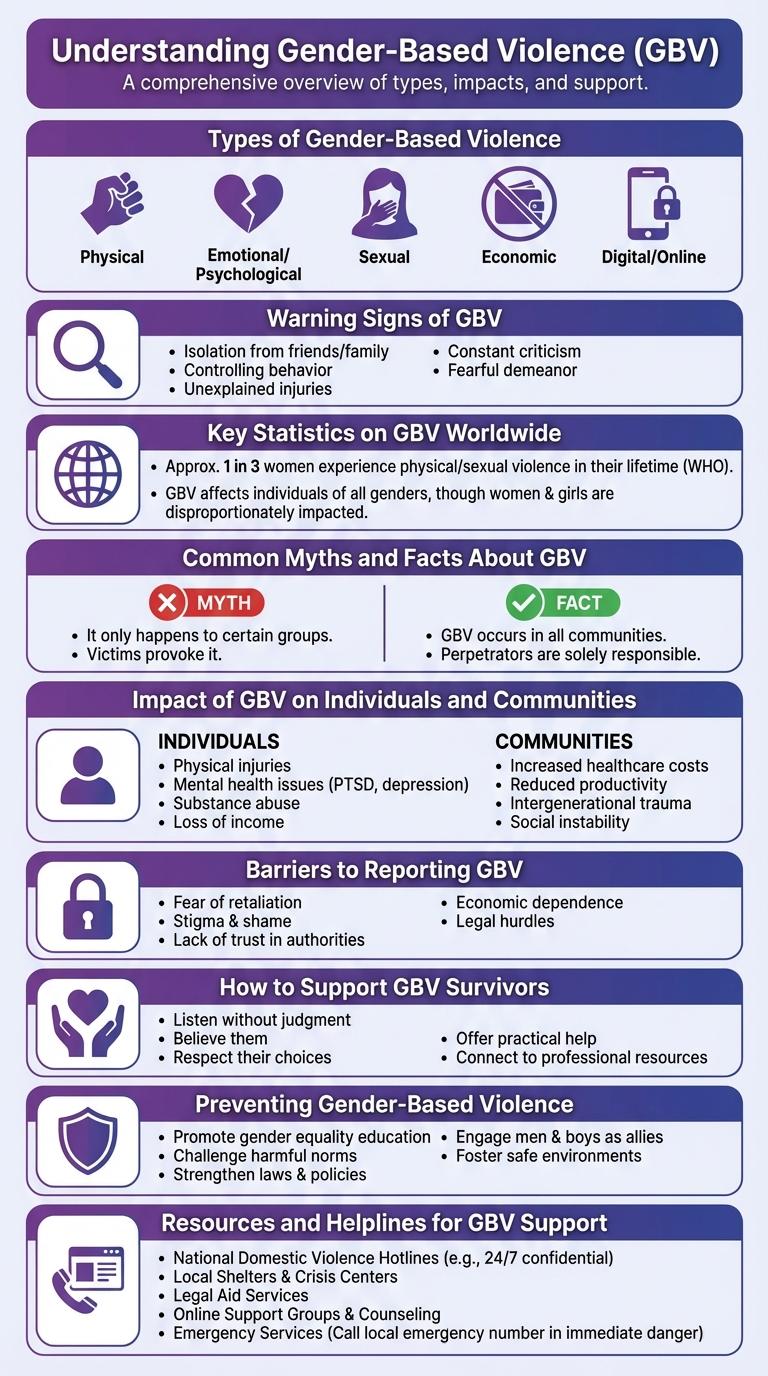
Gender-Based Violence (GBV) is a critical human rights issue affecting individuals worldwide. It involves harmful acts directed at people based on their gender identity or roles.
- Definition of GBV - GBV includes physical, sexual, psychological, and economic harm inflicted due to gender disparities and power imbalances.
- Prevalence - One in three women globally experience some form of GBV during their lifetime, highlighting its widespread impact.
- Consequences - GBV causes severe physical injuries, mental health issues, and socio-economic disadvantages for survivors.
Types of Gender-Based Violence
Gender-Based Violence (GBV) encompasses various harmful acts directed at individuals based on their gender. Understanding the different types of GBV is crucial for prevention and support.
GBV manifests in physical, emotional, sexual, and economic forms, affecting millions worldwide regardless of age or background.
- Physical Violence - Acts causing bodily harm such as hitting, slapping, or other forms of assault.
- Sexual Violence - Unwanted sexual acts including rape, harassment, and exploitation.
- Emotional and Psychological Violence - Behaviors that harm emotional well-being including intimidation, threats, and humiliation.
- Economic Violence - Controlling or restricting access to financial resources to limit independence.
- Early and Forced Marriage - Marrying individuals against their will, often leading to further abuse and deprivation of rights.
Warning Signs of GBV
Gender-based violence (GBV) affects millions worldwide, impacting physical and emotional well-being. Recognizing early warning signs can help prevent escalation and provide timely support.
- Unexplained Injuries - Frequent bruises or cuts may indicate physical abuse.
- Isolation from Friends and Family - Abusers often control social interactions to exert power.
- Changes in Behavior - Sudden withdrawal, anxiety, or depression may signal distress.
Awareness of these warning signs is crucial for intervention and protection against GBV.
Key Statistics on GBV Worldwide
Gender-based violence (GBV) affects millions globally, cutting across all ages, races, and socioeconomic groups. It includes physical, sexual, emotional, and psychological abuse rooted in gender inequality.
According to the World Health Organization, about 1 in 3 women worldwide has experienced physical or sexual intimate partner violence. The United Nations reports that nearly 15 million adolescent girls aged 15-19 have experienced forced sex or other forms of sexual violence. GBV remains a critical public health and human rights challenge requiring urgent global attention.
Common Myths and Facts About GBV
Gender-Based Violence (GBV) affects millions worldwide and is rooted in power imbalances and social inequalities. Misconceptions about GBV often hinder effective prevention and support for survivors.
Myth: GBV only happens in certain communities. Fact: GBV occurs across all cultures, ages, and socioeconomic groups globally.
Myth: Victims provoke GBV by their behavior or clothing. Fact: Responsibility for GBV lies solely with the perpetrator, not the survivor.
Myth: GBV is only physical violence. Fact: GBV includes physical, emotional, sexual, and economic abuse.
Myth: GBV only affects women. Fact: While women are disproportionately affected, GBV can impact anyone regardless of gender.
Myth: Reporting GBV always leads to justice. Fact: Many survivors face barriers to justice, underscoring the need for systemic change.
Impact of GBV on Individuals and Communities
| Impact on Individuals | Impact on Communities |
|---|---|
| Physical injuries and chronic health conditions | Increased healthcare costs and strained medical resources |
| Mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and PTSD | Reduced workforce productivity and economic growth |
| Loss of self-esteem and social isolation | Breakdown of social cohesion and trust within the community |
| Disruption in education and employment opportunities | Higher rates of poverty and social inequality |
| Increased risk of substance abuse and suicidal behavior | Intergenerational cycles of violence and trauma |
Barriers to Reporting GBV
What prevents survivors from reporting Gender-Based Violence (GBV)? Fear of stigma and discrimination often stops survivors from seeking help. Many worry about not being believed or facing social isolation.
How does lack of trust in authorities affect GBV reporting? Survivors frequently mistrust law enforcement and judicial systems due to past negligence or bias. This mistrust discourages them from coming forward with their experiences.
Why is limited access to support services a barrier to reporting GBV? Inadequate availability of counseling and medical assistance leaves survivors feeling unsupported. Geographic and economic constraints hinder access to essential resources.
What role do cultural norms play in impeding GBV reporting? Deep-rooted patriarchal beliefs may blame survivors or normalize violence against certain groups. These norms create an environment where speaking out is discouraged or punished.
How does fear of retaliation impact survivors' willingness to report GBV? Threats from perpetrators or their associates intimidate survivors into silence. Lack of protective measures increases the risk of further harm after disclosure.
How to Support GBV Survivors
Supporting Gender-Based Violence (GBV) survivors requires compassion, active listening, and confidentiality. Encourage survivors to seek professional help such as counseling and legal assistance. Providing accessible resources and a non-judgmental environment fosters healing and empowerment.
Preventing Gender-Based Violence
Gender-Based Violence (GBV) affects millions worldwide, impacting physical and mental health. Preventing GBV requires community awareness and proactive intervention strategies.
Education on respect and equality forms the foundation for change. Empowering survivors and promoting safe environments reduces the prevalence of violence.
