Human development encompasses the physical, cognitive, and emotional growth individuals experience throughout their lifespan. This infographic visually breaks down the key stages and milestones, highlighting critical factors that influence progress from infancy to adulthood. It provides insights into the complex interaction between genetics, environment, and social influences that shape human potential.
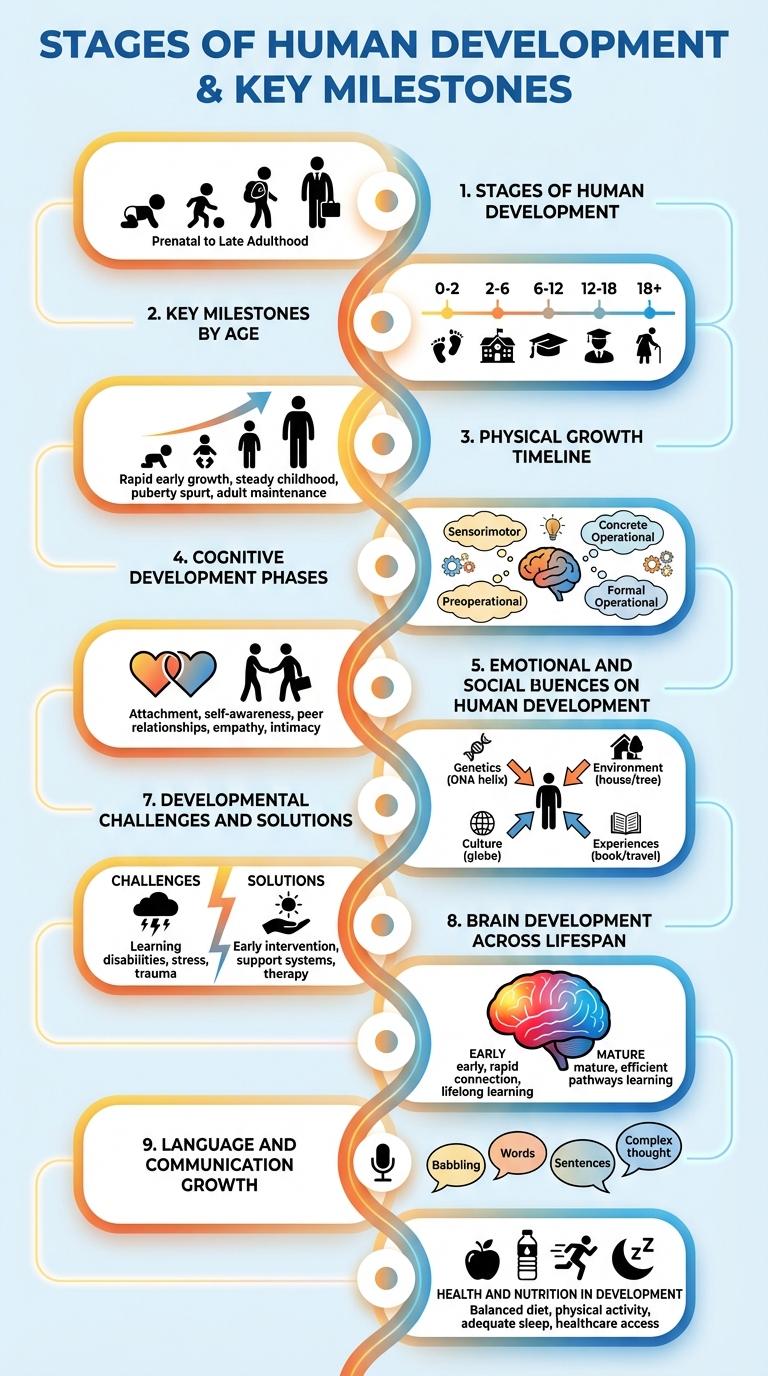
Stages of Human Development
Human development progresses through distinct stages that reflect physical, cognitive, and emotional growth. These stages are crucial for understanding the evolving needs and abilities of individuals over time.
The primary stages include infancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood, and old age. Each stage presents unique challenges and opportunities for development in various dimensions of life.
Key Milestones by Age
Human development follows a series of key milestones that indicate growth in physical, cognitive, and social skills. Tracking these milestones helps understand typical progress and identify when intervention may be needed.
- Infancy (0-2 years) - Rapid brain growth supports motor skills such as crawling and walking, along with early language acquisition.
- Early Childhood (3-5 years) - Improvement in fine motor skills and the ability to form simple sentences enhance communication and self-care.
- Middle Childhood (6-12 years) - Cognitive abilities expand with learning, problem-solving, and social interaction becoming more complex.
Physical Growth Timeline
Human development encompasses various physical changes from infancy through adulthood. Tracking these changes provides insight into growth patterns and health milestones.
- Infancy (0-2 years) - Rapid growth occurs, including increased height, weight, and motor skills development.
- Childhood (3-12 years) - Steady physical growth continues with improved coordination and muscle strength.
- Adolescence (13-18 years) - Puberty triggers significant growth spurts and hormonal changes affecting body composition.
Understanding physical growth timelines is essential for monitoring healthy development stages.
Cognitive Development Phases
What are the key phases of cognitive development in humans? Cognitive development progresses through distinct stages that shape thinking, problem-solving, and understanding. Each phase builds on the previous one, enhancing mental capabilities from infancy to adulthood.
How does the sensorimotor stage influence early learning? During the sensorimotor phase (0-2 years), infants explore the world through their senses and actions. This stage is crucial for developing object permanence and basic motor skills.
What occurs in the preoperational stage of cognitive growth? Between ages 2 and 7, children begin to use language and symbols to represent objects. Thinking is still egocentric, and imagination flourishes despite difficulty with logical reasoning.
Why is the concrete operational stage important for understanding logic? From 7 to 11 years, children develop the ability to think logically about concrete events. They grasp concepts like conservation and cause-and-effect, improving problem-solving skills.
What characterizes the formal operational stage in cognitive development? Starting around 12 years and continuing through adulthood, individuals gain the capacity for abstract and hypothetical thinking. This phase supports advanced reasoning and complex decision-making.
Emotional and Social Progression
Emotional and social progression plays a critical role in overall human development, influencing personal well-being and interpersonal relationships. Mastery of emotional regulation and social skills contributes significantly to success in various life domains.
- Emotional Awareness - Recognizing and understanding one's own emotions enhances self-control and resilience.
- Empathy Development - The ability to perceive and relate to others' feelings fosters stronger social connections.
- Social Communication - Effective expression and interpretation of social cues facilitates cooperation and conflict resolution.
Influences on Human Development
Human development is shaped by a combination of genetic, environmental, and social factors. Family relationships, cultural context, and educational opportunities significantly influence cognitive and emotional growth. Nutrition, healthcare access, and early childhood experiences play critical roles in physical and psychological development.
Developmental Challenges and Solutions
Human development faces significant challenges such as poverty, inadequate education, and limited healthcare access. These obstacles hinder individuals' ability to reach their full potential and affect overall societal progress.
Effective solutions include improving educational opportunities, expanding healthcare services, and promoting economic empowerment programs. Implementing these strategies fosters sustainable development and enhances quality of life globally.
Brain Development Across Lifespan
Brain development is a continuous process that begins in the womb and extends into early adulthood. Neural connections form rapidly during infancy, supporting cognitive and sensory functions.
The first few years of life are critical for synaptic growth and brain plasticity, enabling learning and adaptation. During adolescence, the prefrontal cortex matures, improving decision-making and impulse control. Brain development slows but continues into the mid-20s, solidifying complex reasoning and emotional regulation skills.
Language and Communication Growth
| Stage | Language and Communication Development |
|---|---|
| 0-6 Months | Babies begin cooing and making vowel sounds. Recognize familiar voices and respond to tone variations. |
| 6-12 Months | Start babbling with consonant sounds; understand simple words like "no" and "bye-bye". Respond to their names. |
| 1-2 Years | Use first words; combine two-word phrases. Vocabulary grows to 50-100 words. Begin pointing to objects when named. |
| 2-3 Years | Expand vocabulary to 200-1,000 words. Form simple sentences. Start answering simple questions and engaging in basic conversations. |
| 3-5 Years | Use complex sentences with proper grammar. Understand and tell stories. Engage in detailed conversations and follow multi-step directions. |
