Urbanization is rapidly transforming cities worldwide, shaping economic growth and social dynamics. Visualizing key statistics through infographics highlights migration patterns, infrastructure development, and environmental impacts. These insights provide a clear understanding of urban expansion challenges and opportunities.
Urbanization: The Global Shift
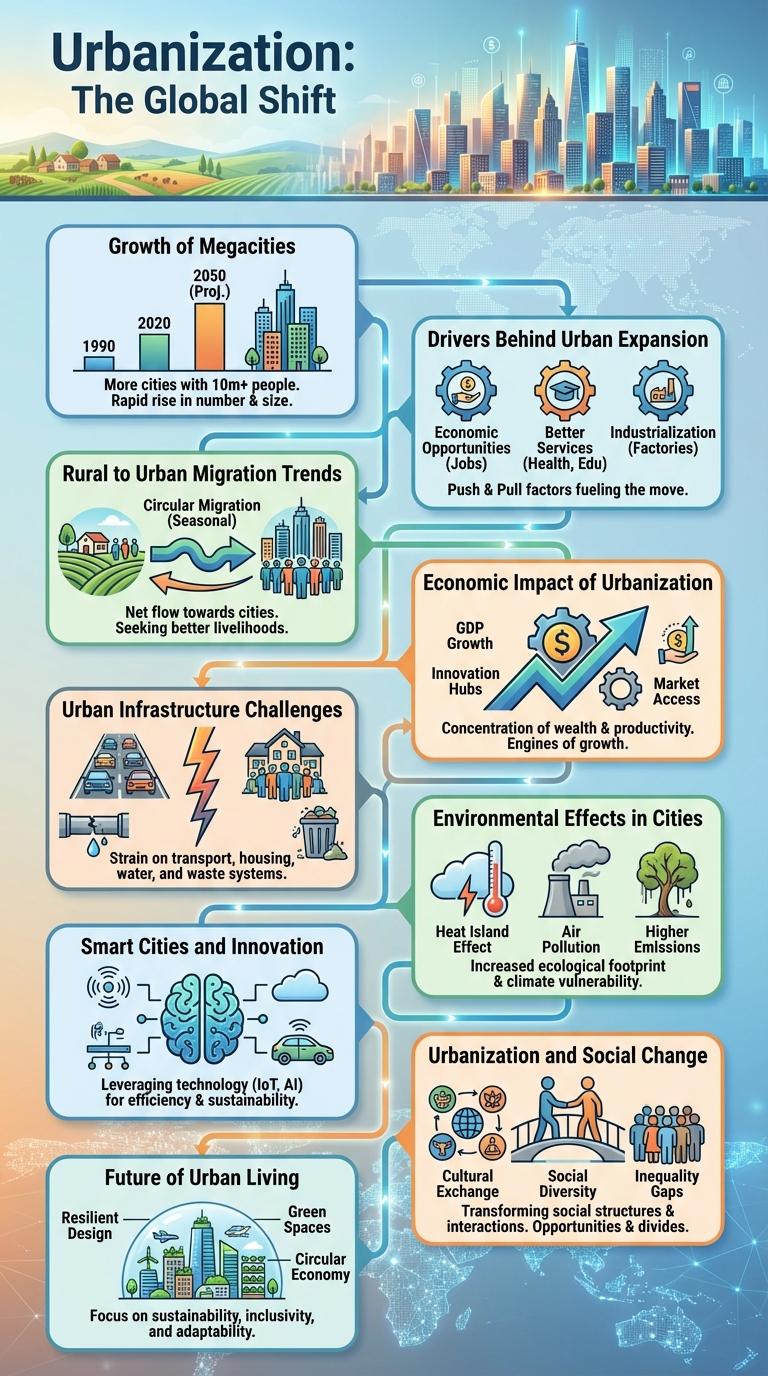
Urbanization marks a significant global demographic transformation where more people live in cities than rural areas. This trend shapes economic, social, and environmental dimensions worldwide.
- Rapid Urban Growth - Over 56% of the world's population now resides in urban areas, a figure projected to reach 68% by 2050.
- Megacities Expansion - Cities with populations exceeding 10 million are increasing, with over 33 megacities reported globally.
- Economic Impact - Urban centers contribute approximately 80% of global GDP, driving innovation and development.
Growth of Megacities
Urbanization has accelerated globally, leading to the rapid growth of megacities--urban areas with populations exceeding 10 million. These megacities are primarily concentrated in Asia, Africa, and Latin America, reshaping economic and social landscapes.
By 2030, it is projected that over 60% of the world's population will live in urban areas, with more than 40 megacities worldwide. Cities such as Tokyo, Delhi, and Shanghai continue to expand, facing challenges related to infrastructure, housing, and sustainability.
Drivers Behind Urban Expansion
| Driver | Impact on Urban Expansion |
|---|---|
| Population Growth | Increases demand for housing, services, and infrastructure in cities |
| Industrialization | Creates jobs, attracting rural populations to urban areas |
| Economic Opportunities | Encourages migration to cities for better employment and education |
| Transportation Development | Improves connectivity, leading to suburban growth and city sprawl |
| Government Policies | Urban planning and investment influence city expansion patterns |
Rural to Urban Migration Trends
Urbanization drives significant shifts in population from rural to urban areas. This migration reshapes economic landscapes and influences city planning worldwide.
Rural to urban migration trends highlight a steady increase in urban populations due to better employment, education, and healthcare opportunities. Developing countries experience rapid urban growth, often surpassing infrastructure capacity. Understanding these patterns aids policymakers in creating sustainable urban development strategies.
Economic Impact of Urbanization
Urbanization drives significant economic growth by concentrating resources, industries, and labor in cities. This concentration fosters innovation, increases productivity, and boosts GDP at both regional and national levels.
However, rapid urbanization can strain infrastructure and public services, leading to increased costs and potential economic disparities. Effective urban planning and investment are essential to maximize economic benefits and ensure sustainable development.
Urban Infrastructure Challenges
Urbanization accelerates the demand for sustainable infrastructure in rapidly growing cities. Addressing urban infrastructure challenges is critical to improving living conditions and economic development.
- Overburdened Transportation Systems - Increased population density strains public transit and road networks, causing congestion and delays.
- Insufficient Water and Sanitation - Rapid urban growth often outpaces the capacity of water supply and sanitation facilities, leading to health risks.
- Energy Supply Deficiencies - Growing urban centers face challenges in meeting the rising demand for reliable and clean energy sources.
Environmental Effects in Cities
Urbanization significantly increases pollution levels in cities, contributing to poor air and water quality. Expanding urban areas cause habitat loss and reduce biodiversity, disrupting local ecosystems. The rise in impervious surfaces like concrete leads to increased runoff and flooding, impacting city infrastructure and natural water cycles.
Smart Cities and Innovation
What defines a smart city in the era of rapid urbanization? Smart cities use advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and big data to enhance urban living. These innovations improve infrastructure, optimize resource management, and boost sustainability.
How does innovation drive urban development in smart cities? Innovative solutions target traffic congestion, energy efficiency, and public safety through real-time data and automated systems. This transforms traditional urban spaces into smarter, more responsive environments.
| Urban Challenge | Smart City Innovation |
|---|---|
| Traffic Management | AI-powered traffic signals reduce congestion |
| Energy Use | Smart grids optimize electricity distribution |
| Public Safety | Surveillance systems with AI detect threats |
| Waste Management | Sensor-based bins improve collection efficiency |
| Water Supply | IoT devices monitor and prevent leaks |
Urbanization and Social Change
Urbanization drives significant social change by reshaping community structures and lifestyles. It fosters economic opportunities while also creating challenges such as overcrowding and inadequate infrastructure. Social dynamics evolve as diverse populations converge in urban centers, influencing culture, education, and social mobility.
