Understanding unemployment through a clear and concise infographic highlights key statistics and trends that impact the economy and society. Visual representations of data reveal patterns in joblessness across different demographics and time periods. This approach simplifies complex information, making it easier to grasp the causes and effects of unemployment.
Understanding Unemployment: Key Facts
Unemployment is a critical economic indicator reflecting the percentage of the labor force without jobs but actively seeking work. It impacts economic growth, social stability, and individual well-being.
The global unemployment rate varies by region, influenced by factors such as education levels, economic policies, and technological changes. Monitoring unemployment trends helps governments develop effective employment strategies and social support programs.
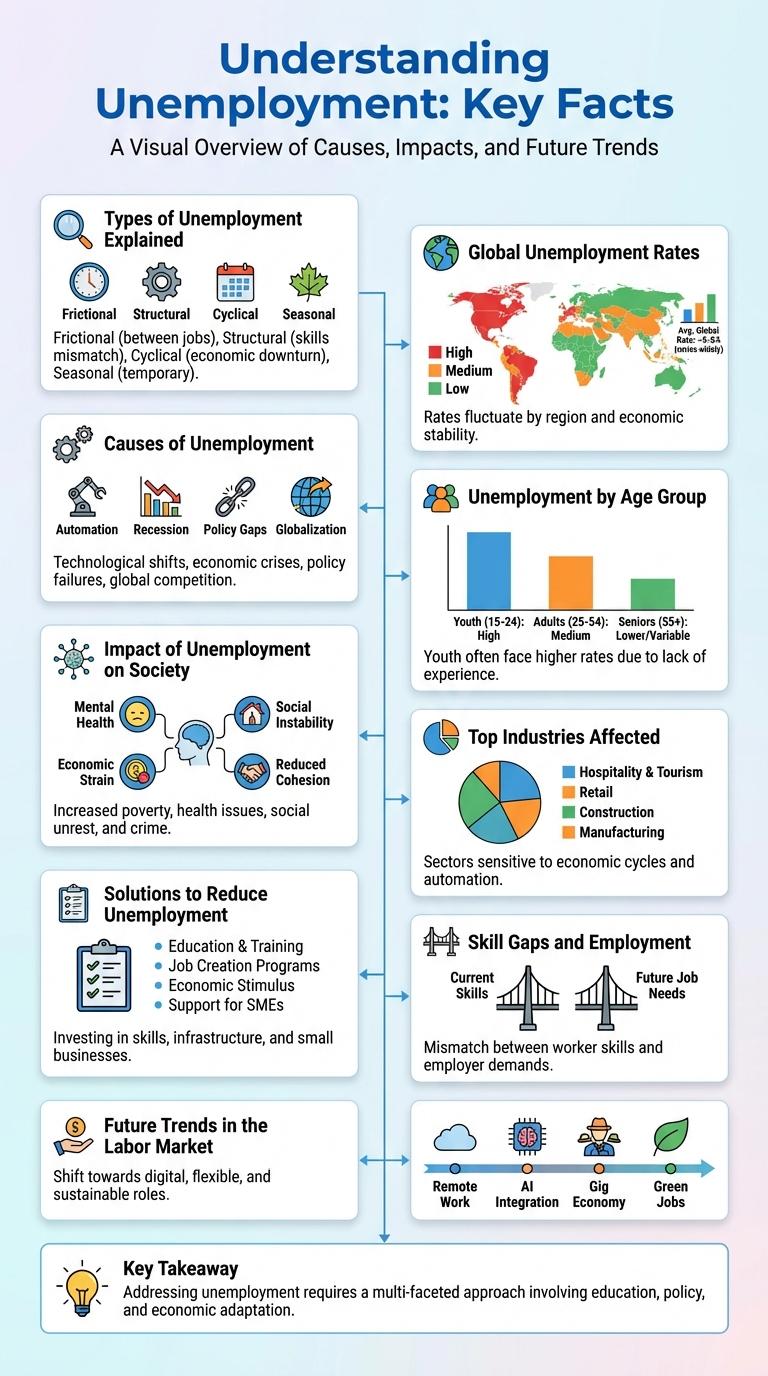
Types of Unemployment Explained
Unemployment is a critical economic issue with various underlying causes affecting the workforce. Understanding the types of unemployment helps in formulating targeted policies and solutions.
- Frictional Unemployment - Occurs when workers are temporarily between jobs or searching for new positions.
- Structural Unemployment - Results from mismatches between workers' skills and job requirements due to technological changes or industry shifts.
- Cyclical Unemployment - Linked to economic downturns where demand for goods and services decreases, reducing job availability.
- Seasonal Unemployment - Happens when industries slow down or shut down for a season, like tourism or agriculture.
- Classical Unemployment - Caused by wage rates being set above the market equilibrium, leading to excess labor supply.
Recognizing these unemployment types enables better economic forecasting and workforce management strategies.
Global Unemployment Rates
Global unemployment rates vary significantly by region, with developing countries experiencing higher levels of joblessness compared to advanced economies. The International Labour Organization reports that the global unemployment rate was approximately 5.7% in 2023, reflecting both economic recovery and ongoing labor market challenges. Youth unemployment remains a critical issue, often exceeding double the overall rate, impacting economic growth and social stability worldwide.
Causes of Unemployment
Unemployment arises from multiple economic and social factors that disrupt the job market. Understanding the causes helps policymakers design effective interventions.
Major causes include cyclical downturns, structural shifts, and frictional mismatches between job seekers and vacancies. Each type impacts unemployment differently, requiring targeted solutions.
Unemployment by Age Group
What is the rate of unemployment among different age groups? Unemployment varies significantly across age categories, reflecting diverse challenges faced by each group. Younger adults often experience higher unemployment rates due to limited work experience, while older adults face job market barriers related to skill mismatches and age discrimination.
Which age group has the highest unemployment rate? Data shows that individuals aged 16-24 consistently have the highest unemployment rates, often exceeding double the national average. This trend highlights the need for targeted education, training, and employment programs to support youth workforce entry.
| Age Group | Unemployment Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| 16-24 years | 12.5% |
| 25-34 years | 7.8% |
| 35-44 years | 5.2% |
| 45-54 years | 4.9% |
| 55 years and older | 6.1% |
Impact of Unemployment on Society
Unemployment significantly affects social and economic stability within communities. The lack of jobs creates a ripple effect that influences mental health, crime rates, and overall quality of life.
- Increased Poverty - Unemployment reduces household income, leading to higher poverty levels and social inequality.
- Mental Health Challenges - Joblessness is linked to increased stress, anxiety, and depression among affected individuals.
- Rising Crime Rates - Areas with high unemployment often experience an uptick in criminal activity due to financial desperation.
Top Industries Affected
| Industry | Unemployment Rate Impact (%) |
|---|---|
| Hospitality and Leisure | 18.5 |
| Retail Trade | 12.7 |
| Manufacturing | 9.4 |
| Transportation and Warehousing | 8.3 |
| Arts, Entertainment, and Recreation | 15.2 |
Solutions to Reduce Unemployment
Unemployment reduction requires targeted strategies such as skills training, job creation programs, and support for small businesses. Governments and organizations invest in education and vocational training to align workforce skills with market demands. Encouraging entrepreneurship and providing incentives for businesses can stimulate economic growth and generate employment opportunities.
Skill Gaps and Employment
Unemployment rates are significantly affected by the mismatch between available skills and job market demands. Closing skill gaps is essential to reduce unemployment and foster economic growth.
- Skill Mismatch - Many job seekers lack the technical abilities needed for current industry requirements, resulting in unfilled positions.
- Training Programs - Workforce development initiatives focused on upskilling can help bridge the gap between employee skills and employer needs.
- Technology Impact - Rapid technological advancements require continuous learning to keep pace with evolving employment criteria.
