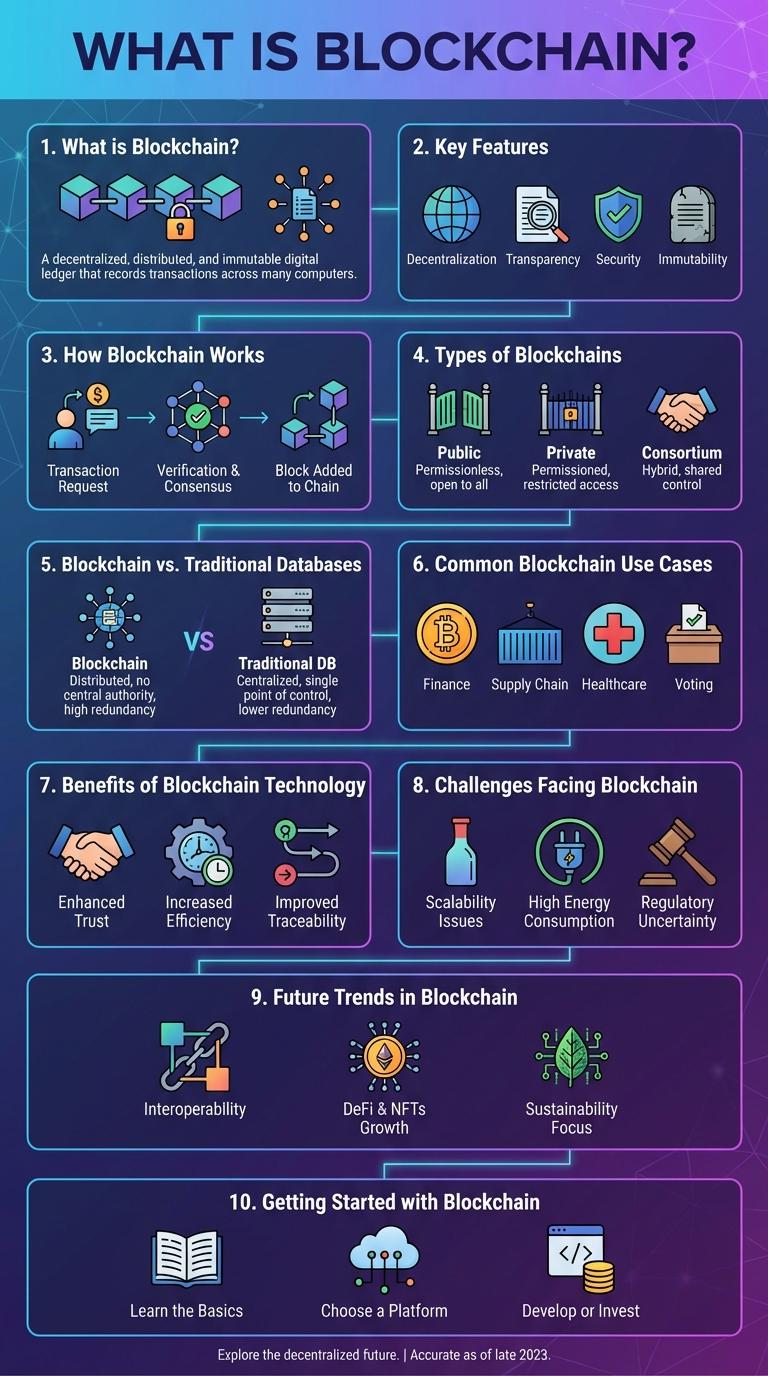
Blockchain technology revolutionizes data security by creating decentralized and immutable ledgers. It enables transparent transactions across multiple industries without the need for intermediaries. This infographic highlights key features, benefits, and real-world applications of blockchain technology.
What is Blockchain?
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers securely. It ensures transparency and immutability, making data tampering virtually impossible.
Key Features of Blockchain
Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that securely records transactions across multiple computers. Its key features include immutability, transparency, and security, which ensure data integrity and trust without intermediaries. The technology uses cryptographic hashing and consensus algorithms to validate and chronologically link blocks of data.
How Blockchain Works
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that securely records transactions across multiple computers. Each block contains a list of transactions, linked together to form a continuous chain.
- Transaction Initiation - A user requests a transaction, which is then broadcasted to a peer-to-peer network of computers called nodes.
- Block Creation - Transactions are validated and grouped into a block by consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work or Proof of Stake.
- Chain Linking - The validated block is added to the existing blockchain, creating a permanent and unalterable record of all transactions.
Types of Blockchains
Blockchain technology offers three main types of blockchains: public, private, and consortium. Each type serves different purposes, targeting various use cases and user access levels.
Public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum are decentralized and open to anyone, ensuring transparency and security. Private blockchains restrict access to specific participants, ideal for enterprises seeking control and privacy.
Blockchain vs. Traditional Databases
Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and secure approach to data management. It contrasts sharply with traditional databases, which rely on centralized control and trust.
- Decentralization - Blockchain operates on a distributed ledger, eliminating the need for a central authority.
- Immutability - Once recorded, blockchain data cannot be altered, ensuring permanent records.
- Data Structure - Traditional databases use tables, while blockchain organizes data in blocks linked sequentially.
Businesses seeking transparency and security increasingly prefer blockchain over traditional database systems.
Common Blockchain Use Cases
Blockchain technology revolutionizes data transparency and security across various industries. Its decentralized nature ensures trust and efficiency in digital transactions.
- Cryptocurrency - Enables secure, peer-to-peer transfers of digital currency without intermediaries.
- Supply Chain Management - Improves traceability and authenticity of products through transparent record-keeping.
- Smart Contracts - Automates contract execution based on predefined rules without third-party involvement.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology ensures secure and transparent transactions by maintaining a decentralized ledger accessible to all participants. It reduces fraud and enhances traceability in various industries, including finance, supply chain, and healthcare. The technology also enables faster and cost-effective processes by eliminating intermediaries and automating operations through smart contracts.
Challenges Facing Blockchain
Blockchain technology offers decentralized and secure data management but faces significant challenges that hinder widespread adoption. Understanding these obstacles is essential for developers and businesses aiming to leverage blockchain effectively.
Scalability remains a critical issue, as many blockchains struggle to process large volumes of transactions quickly. Regulatory uncertainty creates legal risks and slows down integration into existing financial and business systems. Security vulnerabilities, including potential 51% attacks and smart contract bugs, pose threats to blockchain reliability and trustworthiness.
Future Trends in Blockchain
| Future Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Expansion | Growth in blockchain applications for financial services without intermediaries, enhancing transparency and efficiency. |
| Integration with Internet of Things (IoT) | Blockchain ensures secure and automated data exchange between connected devices in IoT ecosystems. |
| Enhanced Scalability Solutions | Development of Layer 2 protocols and sharding techniques to increase transaction speed and reduce costs. |
| Enterprise Adoption | Businesses increasingly incorporate private and consortium blockchains for supply chain, identity verification, and data management. |
| Regulatory Framework Development | Governments worldwide establish clearer regulations to support innovation while managing risks associated with blockchain technologies. |
