Design thinking transforms problem-solving by emphasizing empathy, creativity, and iterative testing to develop user-centered solutions. This infographic breaks down the key stages of the design thinking process, highlighting how each phase fosters innovation and practical outcomes. Visualizing these steps provides a clear roadmap for teams aiming to tackle complex challenges effectively.
What is Design Thinking?
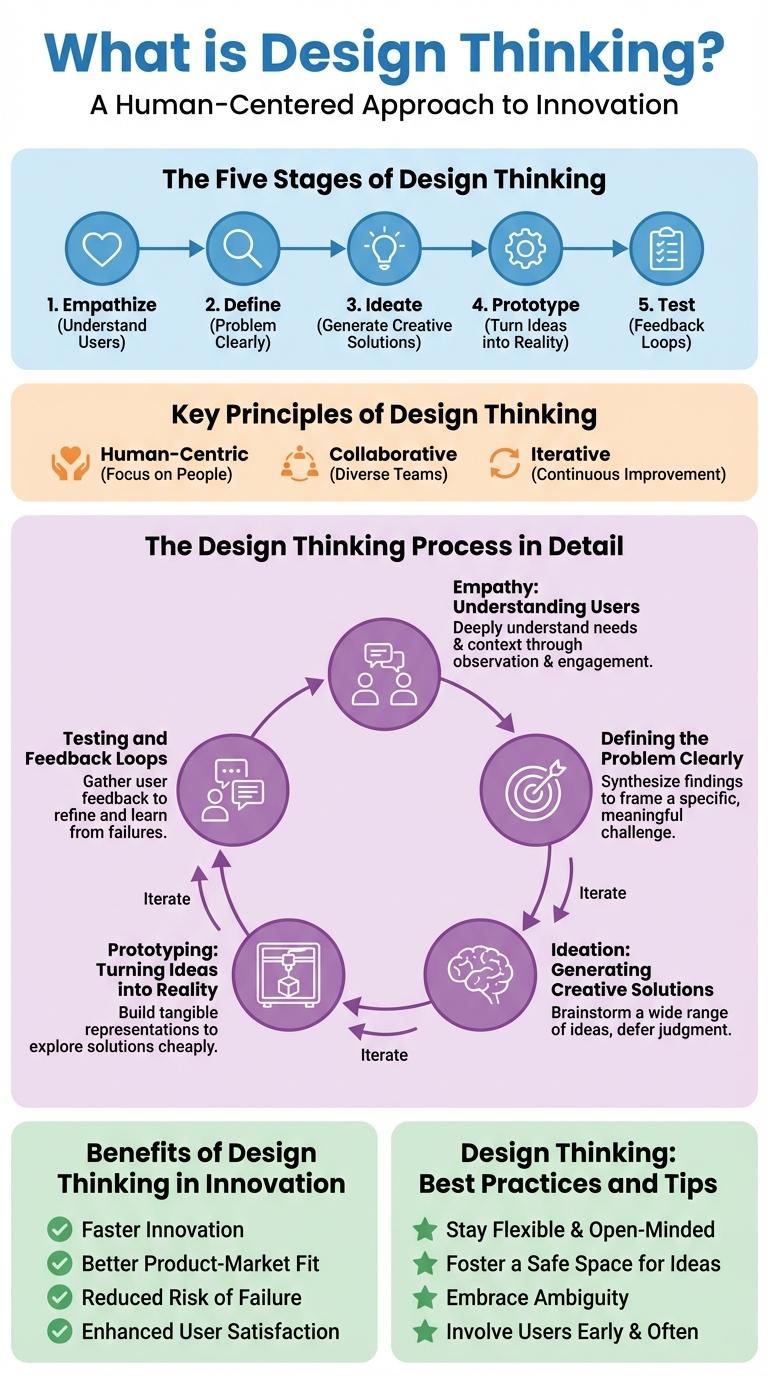
Design Thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation that integrates the needs of people, the possibilities of technology, and the requirements for business success. It emphasizes empathy, creativity, and iterative problem-solving.
This methodology involves understanding users' experiences, defining problems clearly, ideating solutions, prototyping, and testing. It is widely used across industries to foster innovative products and services.
The Five Stages of Design Thinking
Design thinking is a user-centered approach to problem-solving that fosters innovation through empathy and creativity. It involves five distinct stages: Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test, each crucial for developing effective solutions. These stages encourage continuous feedback and iteration to refine ideas and address real user needs.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Empathize | Understand user experiences and emotions through observation and research. |
| Define | Identify core problems and frame clear problem statements. |
| Ideate | Generate a wide range of creative ideas and potential solutions. |
| Prototype | Create tangible representations of ideas to explore solutions. |
| Test | Evaluate prototypes with users to gather feedback and improve. |
Key Principles of Design Thinking
Design thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation that emphasizes empathy, creativity, and iterative problem-solving. Key principles include understanding user needs deeply, fostering collaboration across diverse teams, and embracing experimentation through prototyping. This process drives innovation by continually refining solutions based on user feedback and real-world testing.
Empathy: Understanding Users
Empathy is the cornerstone of design thinking, emphasizing a deep understanding of users' needs and emotions. This approach drives innovation by placing the user at the center of the problem-solving process.
- User Interviews - Collect qualitative data by engaging directly with users to uncover their experiences and pain points.
- Observation - Study users in their natural environment to gain insights into their behaviors and interactions.
- Persona Development - Create detailed user profiles to represent different segments and guide design decisions.
Empathy enables designers to create meaningful solutions that truly resonate with users.
Defining the Problem Clearly
Design thinking begins with defining the problem clearly to ensure solutions address real user needs. A well-defined problem statement guides the entire creative process and aligns team efforts.
Effective problem definition involves deep user research and identifying pain points accurately. This step prevents wasted time on irrelevant solutions and sparks innovative ideas.
Ideation: Generating Creative Solutions
Ideation is a core phase in design thinking that drives the generation of creative solutions. It encourages diverse perspectives to unlock innovative ideas beyond conventional boundaries.
- Divergent Thinking - Encourages exploring multiple avenues and brainstorming freely without judgment.
- Collaborative Engagement - Harnesses group diversity to enhance creativity and solution scope.
- Prototyping Focus - Translates ideas into tangible concepts to test and refine quickly.
Prototyping: Turning Ideas into Reality
Prototyping is a critical step in design thinking that transforms abstract ideas into tangible forms. This process enables designers to explore, test, and refine concepts efficiently.
- Rapid Experimentation - Prototyping allows quick iteration to evaluate different design solutions and identify improvements early.
- User-Centered Feedback - Creating prototypes facilitates gathering actionable insights directly from users to enhance usability.
- Risk Reduction - Building prototypes helps detect potential flaws before full-scale implementation, minimizing costly errors.
Testing and Feedback Loops
| Testing | Testing involves evaluating prototypes or solutions with real users to identify issues and gather user experiences. It ensures the product meets user needs and uncovers usability problems early. |
|---|---|
| Feedback Loops | Feedback loops enable continuous improvement by collecting user input after each test phase. This iterative process refines design elements, enhancing functionality and user satisfaction. |
| Purpose | Validating assumptions, reducing risk, and ensuring solutions align with user expectations through repeated cycles of testing and feedback. |
| Methods | User interviews, usability testing, A/B testing, surveys, and analytics tools for collecting qualitative and quantitative feedback. |
| Outcome | Improved design decisions, higher product quality, and increased adoption rates supported by data-driven insights from continuous testing phases. |
Benefits of Design Thinking in Innovation
How does design thinking enhance innovation? Design thinking fosters creativity by encouraging diverse perspectives and iterative problem-solving. It drives user-centered solutions that align closely with market needs, accelerating successful innovation.
