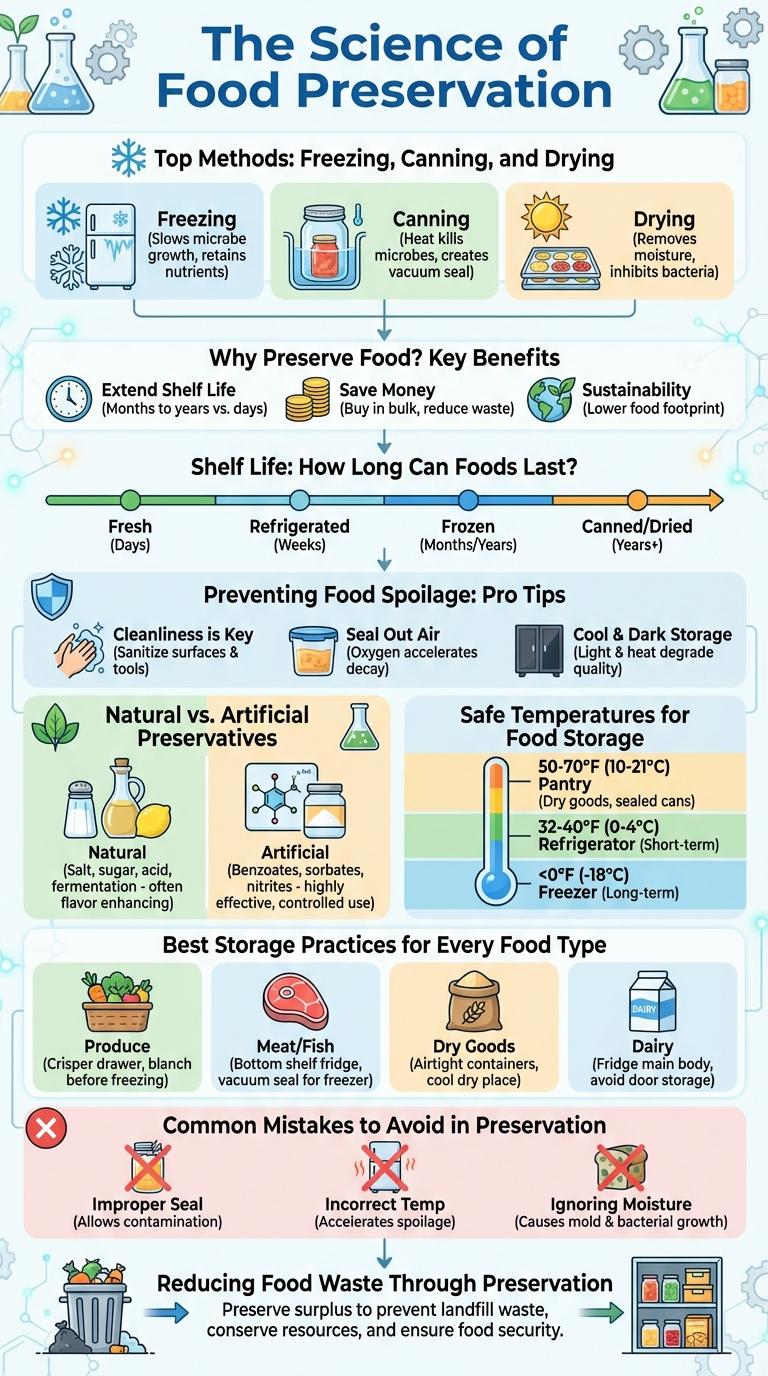
Food preservation techniques extend the shelf life of perishable items by slowing down spoilage and maintaining nutritional value. Methods such as freezing, drying, canning, and vacuum sealing retain flavor and texture while preventing bacterial growth. This infographic highlights key preservation strategies, benefits, and tips to reduce food waste and ensure safety.
The Science of Food Preservation
Food preservation slows down spoilage by inhibiting microbial growth and enzymatic reactions. Scientific methods extend shelf life and maintain nutritional quality.
- Freezing - Low temperatures halt microbial activity, preserving food texture and nutrients.
- Canning - Heat treatment destroys pathogens and seals food in airtight containers.
- Dehydration - Removing moisture prevents bacterial and mold growth, extending edibility.
Top Methods: Freezing, Canning, and Drying
What are the most effective methods for preserving food? Freezing, canning, and drying stand out as top techniques. Each method extends shelf life and helps maintain nutritional value.
| Method | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Freezing | Slows microbial growth and enzymatic activity, preserves texture and flavor |
| Canning | Seals food in airtight containers, prevents spoilage from bacteria and molds |
| Drying | Removes moisture to inhibit microbial growth, reduces weight for storage |
Why Preserve Food? Key Benefits
| Why Preserve Food? | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Extend Shelf Life | Prevents spoilage and reduces food waste by maintaining freshness longer. |
| Maintain Nutritional Value | Preservation methods like freezing and canning help retain essential vitamins and minerals. |
| Improve Food Safety | Slows the growth of bacteria, fungi, and other pathogens, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses. |
| Convenience and Availability | Allows storage of seasonal foods for year-round consumption and simplifies meal preparation. |
| Cost Savings | Buying in bulk and preserving surplus food lowers grocery expenses and minimizes waste. |
Shelf Life: How Long Can Foods Last?
Food preservation methods significantly impact the shelf life of various foods. Proper storage techniques help maintain freshness and prevent spoilage for longer periods.
Dry goods like rice and pasta can last up to 1-2 years when stored in airtight containers. Fresh fruits and vegetables generally last from a few days to a couple of weeks depending on the type and storage conditions.
Preventing Food Spoilage: Pro Tips
Effective food preservation techniques are essential to prevent spoilage and maintain nutritional value. Proper storage conditions such as refrigeration, freezing, and vacuum sealing slow down microbial growth and enzymatic reactions. Regularly monitoring expiration dates and using airtight containers extend the freshness of perishable items.
Natural vs. Artificial Preservatives
Food preservation extends the shelf life of products by preventing spoilage caused by microbes, oxidation, and other factors. Two main categories of preservatives used are natural and artificial, each with unique properties and effects on food quality.
Natural preservatives include substances like salt, sugar, vinegar, and certain essential oils, which inhibit microbial growth through natural processes. Artificial preservatives such as sodium benzoate, potassium sorbate, and BHA are chemically synthesized to provide consistent and long-lasting protection. Understanding the differences helps consumers make informed choices about food safety and health.
Best Storage Practices for Every Food Type
Proper food storage preserves freshness, prevents spoilage, and extends shelf life. Different food types require specific storage conditions to maintain quality and safety.
- Fruits - Store most fruits in the refrigerator to slow ripening, while some like bananas and avocados should be kept at room temperature until ripe.
- Vegetables - Keep vegetables in perforated plastic bags in the crisper drawer to maintain humidity and reduce moisture loss.
- Dairy - Store dairy products in the coldest part of the refrigerator, away from door shelves, to preserve freshness and prevent contamination.
- Meat and Poultry - Refrigerate raw meats at or below 40degF (4degC), ideally on the lowest shelf to prevent cross-contamination and use within recommended timeframes.
- Dry Goods - Keep grains, nuts, and flours in airtight containers at room temperature in a cool, dry place to avoid moisture and pest damage.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Preservation
Proper food preservation extends shelf life and prevents spoilage, ensuring food safety and quality. Avoiding common mistakes is crucial for effective preservation methods.
- Improper Temperature Control - Storing food at incorrect temperatures can promote bacterial growth and spoilage.
- Inadequate Sealing - Poorly sealed containers allow air and moisture to enter, leading to freezer burn or mold development.
- Using Damaged Containers - Cracked or warped containers compromise protection and reduce preservation effectiveness.
Mastering correct preservation practices reduces waste and maintains nutritional value.
Safe Temperatures for Food Storage
Maintaining safe temperatures is crucial for effective food preservation to prevent bacterial growth. Refrigerators should be set at or below 40degF (4degC), while freezers must be kept at 0degF (-18degC) or lower. Hot foods must be stored at a minimum of 140degF (60degC) to ensure safety and prevent spoilage.
