An infographic about operating systems visually presents key components, types, and functions of OS software in an easy-to-understand format. It highlights how operating systems manage hardware resources, provide user interfaces, and enable application execution. Essential concepts like multitasking, security, and file management are clearly illustrated to enhance comprehension.
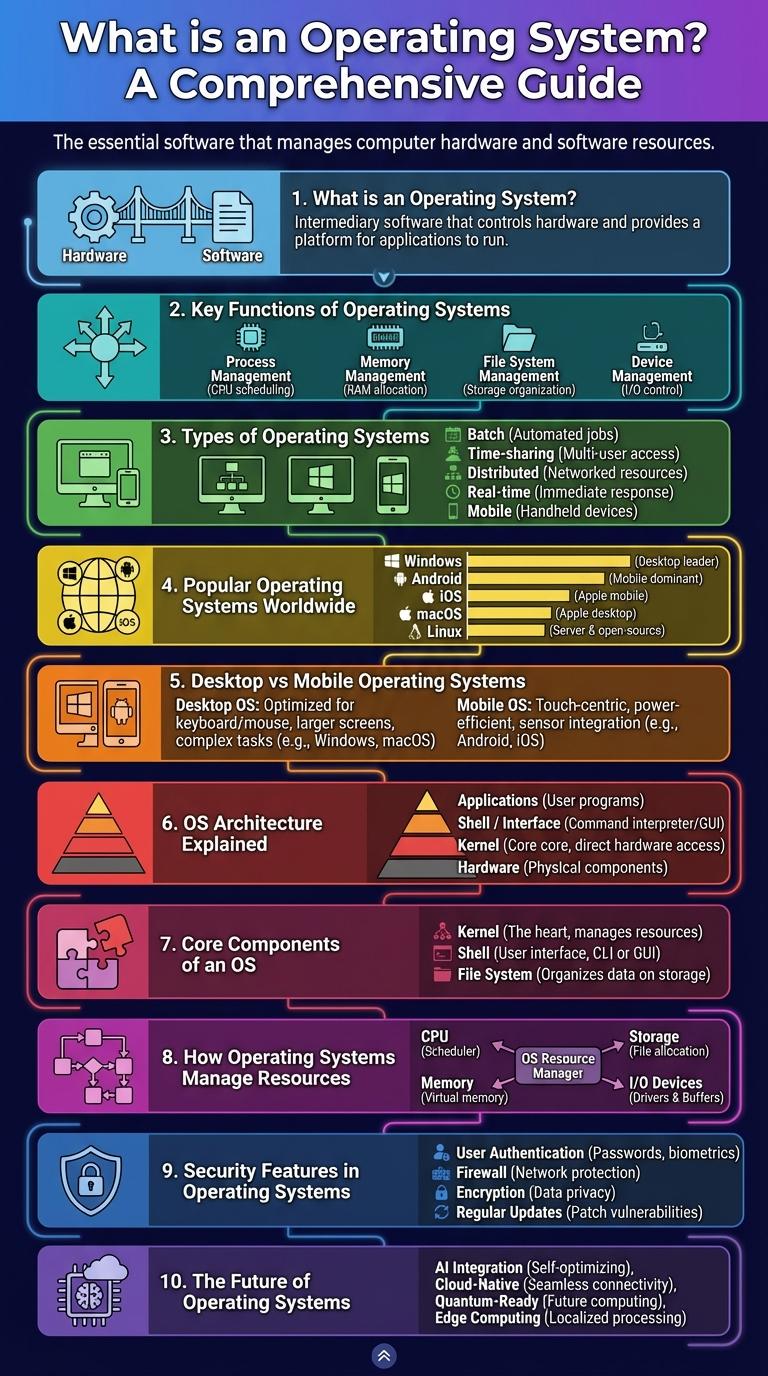
What is an Operating System?
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources. It provides a user interface and controls the execution of all programs.
- Resource Management - Allocates memory, processing power, and storage among various applications efficiently.
- User Interface - Offers graphical or command-line interfaces enabling users to interact with the computer.
- Process Control - Manages the execution of processes, ensuring multitasking and system stability.
Key Functions of Operating Systems
| Key Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Management | Handles creation, scheduling, and termination of processes to ensure efficient CPU usage. |
| Memory Management | Allocates and manages system memory, ensuring each application has enough resources. |
| File System Management | Organizes, stores, retrieves, and controls access to data on storage devices. |
| Device Management | Manages device communication via drivers, controlling input and output devices. |
| Security and Access Control | Protects system resources and user data through authentication and permission settings. |
Types of Operating Systems
An operating system (OS) manages computer hardware and software resources. There are several types of operating systems including batch, time-sharing, distributed, embedded, and real-time systems. Each type serves specific functions tailored to different computing environments.
| Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Batch OS | Processes batches of jobs without user interaction |
| Time-Sharing OS | Allows multiple users to use the system simultaneously |
| Distributed OS | Manages a group of distinct computers as a single system |
| Embedded OS | Designed for embedded systems like appliances and vehicles |
| Real-Time OS | Provides immediate processing for time-critical applications |
Popular Operating Systems Worldwide
Operating systems (OS) are essential software that manage computer hardware and software resources. They provide the interface and environment for applications to function effectively worldwide.
- Windows dominates desktop OS market - Microsoft Windows holds over 75% of the global desktop operating system share, making it the most widely used OS in personal computers.
- Android leads mobile OS usage - Google's Android powers around 70% of smartphones worldwide, making it the top mobile operating system by user base.
- macOS is preferred for creative industries - Apple's macOS has a strong presence in creative and professional sectors due to its optimized software and hardware integration.
Operating systems play a pivotal role in defining user experiences across various digital devices globally.
Desktop vs Mobile Operating Systems
What are the main differences between desktop and mobile operating systems? Desktop operating systems are designed for powerful hardware with extensive multitasking capabilities, while mobile operating systems prioritize battery efficiency and touch interface optimization. Each system caters to unique user experiences based on device functionality.
OS Architecture Explained
An operating system (OS) manages hardware and software resources, providing a user interface and efficient process control. It acts as an intermediary between users and the computer hardware, ensuring smooth operation.
The OS architecture typically consists of the kernel, system libraries, and user interface components. The kernel handles core functions such as memory management, process scheduling, and device communication.
Core Components of an OS
An operating system (OS) manages computer hardware and software resources, providing essential services for applications. Core components include the kernel, which controls hardware interactions and system resources. Other vital parts are the file system for data management, the user interface for input/output operations, and device drivers that enable hardware communication.
How Operating Systems Manage Resources
Operating systems efficiently manage computer hardware and software resources to ensure smooth performance. They coordinate tasks such as memory allocation, processor scheduling, and device communication.
- Memory Management - Allocates and tracks memory usage, ensuring programs have sufficient space without interfering with each other.
- Process Scheduling - Prioritizes and distributes CPU time among running processes to maximize efficiency and responsiveness.
- Device Management - Controls input/output devices through drivers, managing data transfer between hardware and software.
Security Features in Operating Systems
An operating system (OS) incorporates various security features to protect computing resources and user data. These features help prevent unauthorized access, malware attacks, and data breaches.
Common security mechanisms include user authentication, access control, encryption, and auditing. Together, these tools enhance system integrity, confidentiality, and availability, ensuring a secure computing environment.
