Digital literacy encompasses the skills needed to effectively navigate, evaluate, and create information using digital technologies. Mastering digital literacy enhances communication, critical thinking, and problem-solving abilities in an increasingly connected world. Infographics visually simplify complex data, making digital literacy concepts more accessible and engaging for diverse audiences.
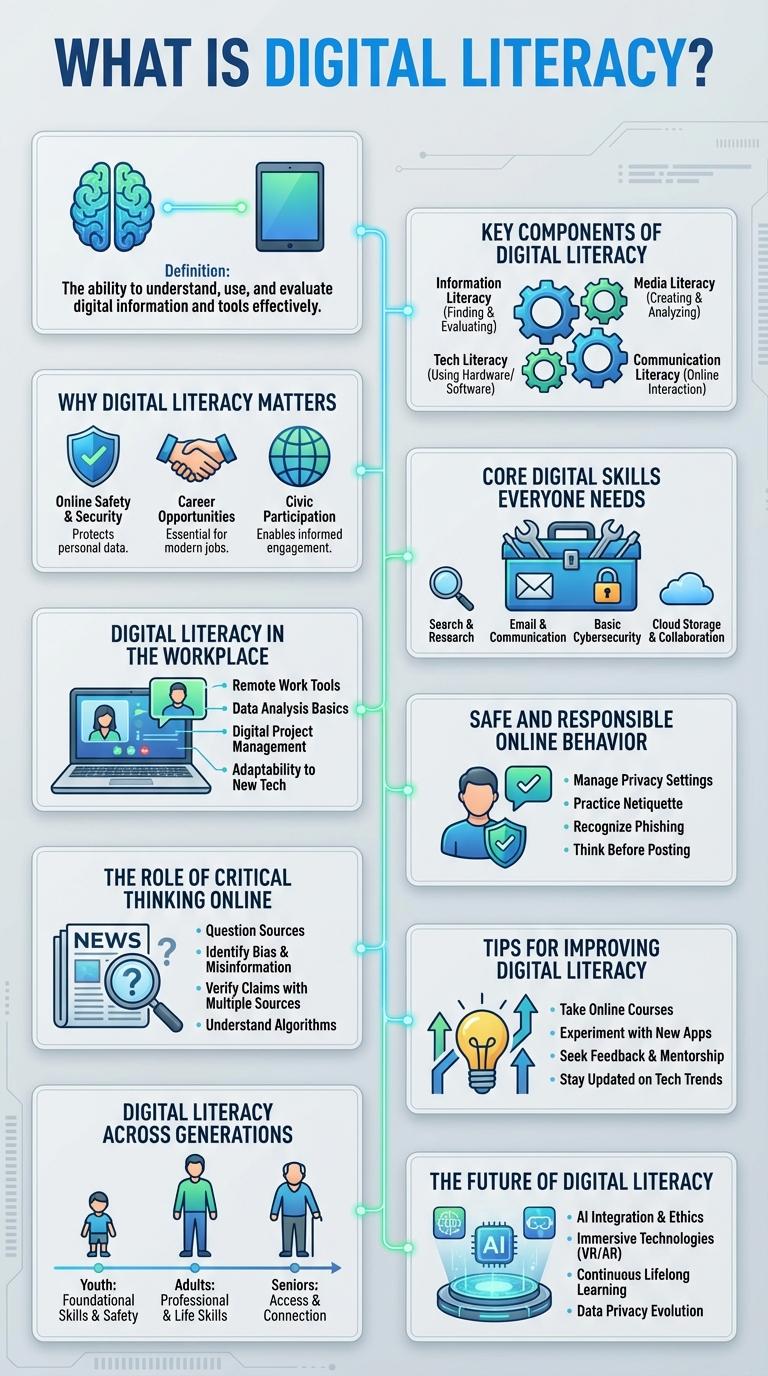
What is Digital Literacy?
Digital literacy refers to the ability to effectively use digital tools and technologies to find, evaluate, create, and communicate information. It encompasses a range of skills essential for navigating the digital world safely and efficiently.
- Information Evaluation - The skill to critically assess the accuracy and credibility of digital content.
- Technical Proficiency - Competence in using digital devices, software, and online platforms.
- Online Communication - The capability to interact, collaborate, and share information through digital channels responsibly.
Mastering digital literacy empowers individuals to participate fully in today's technology-driven society.
Key Components of Digital Literacy
What are the key components of digital literacy? Digital literacy involves understanding how to effectively use digital tools and platforms. It includes skills such as online communication, information evaluation, and digital content creation.
How does online communication contribute to digital literacy? Online communication skills enable users to interact responsibly and clearly across digital channels. This includes mastering email etiquette, social media usage, and virtual collaboration tools.
Why is information evaluation important in digital literacy? Being able to critically assess online information helps users identify credible sources and avoid misinformation. It involves checking facts, recognizing bias, and understanding digital footprints.
What role does digital content creation play in digital literacy? Creating digital content allows users to express ideas and share knowledge effectively. This encompasses skills in media production, graphic design, and web publishing.
How do privacy and security awareness fit into digital literacy? Awareness of privacy and security measures protects users from data breaches and cyber threats. It includes understanding passwords, safe browsing, and data protection laws.
Why Digital Literacy Matters
Digital literacy is essential for navigating today's technology-driven world effectively. It empowers individuals to access, evaluate, and create information using digital platforms.
- Enhances Employment Opportunities - Digital skills increase job prospects across nearly all industries requiring tech proficiency.
- Promotes Critical Thinking - Users can critically assess online information and avoid misinformation.
- Facilitates Lifelong Learning - Digital literacy supports continuous skill development and access to educational resources.
Core Digital Skills Everyone Needs
Digital literacy encompasses the ability to effectively use digital tools and platforms. Mastering core digital skills is essential for navigating today's technology-driven world.
Key digital skills include information evaluation, online communication, and basic troubleshooting. Developing these competencies empowers individuals to work, learn, and connect efficiently in digital environments.
Digital Literacy in the Workplace
Digital literacy in the workplace is essential for effective communication, collaboration, and productivity. Employees must possess skills to navigate software, manage data securely, and utilize digital tools efficiently.
Organizations benefit from a digitally literate workforce through enhanced innovation and streamlined processes. Training programs focusing on cybersecurity, data management, and online collaboration improve overall business performance.
Safe and Responsible Online Behavior
Digital literacy encompasses the ability to navigate the internet safely and responsibly, protecting personal information from online threats. Understanding privacy settings, recognizing phishing attempts, and practicing respectful communication are key components of safe online behavior. Developing these skills promotes a secure digital environment and fosters positive interactions across various online platforms.
The Role of Critical Thinking Online
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Critical thinking online involves analyzing digital content for accuracy, bias, and reliability before accepting or sharing information. |
| Key Skills | Evaluating sources, recognizing misinformation, questioning assumptions, and identifying logical fallacies on digital platforms. |
| Importance | Helps users avoid fake news, reduces spread of misinformation, and promotes informed decision-making in digital environments. |
| Application | Using fact-checking websites, cross-referencing multiple sources, and critically assessing social media content before engagement. |
| Benefits | Encourages digital responsibility, enhances online communication quality, and supports a more informed, discerning digital community. |
Tips for Improving Digital Literacy
Enhancing digital literacy involves understanding how to safely navigate the internet, critically evaluate online sources, and effectively use digital tools. Developing skills such as password management, recognizing phishing scams, and using productivity software boosts confidence in digital environments. Regular practice and staying updated with emerging technologies ensure continued competence in a rapidly evolving digital world.
Digital Literacy Across Generations
Digital literacy varies significantly across different generations, influenced by their exposure to technology during formative years. Understanding these differences helps tailor educational programs to improve digital skills for all age groups.
The infographic highlights digital literacy levels and challenges faced by Baby Boomers, Generation X, Millennials, and Generation Z.
- Baby Boomers - Tend to have basic digital skills, often requiring support for advanced technology use.
- Generation X - Moderate proficiency, balancing traditional and digital work environments.
- Millennials - High digital literacy, comfortable with multitasking across multiple devices and platforms.
- Generation Z - Digital natives with intuitive understanding of emerging technologies and social media.
- Educational Impact - Customized digital literacy training boosts confidence and competence across all age groups.
