Automation transforms industries by streamlining repetitive tasks and increasing efficiency. Infographics visually represent complex data, making it easier to understand automation trends and benefits. This visual tool highlights key statistics and insights to demonstrate the impact of automation on productivity and innovation.
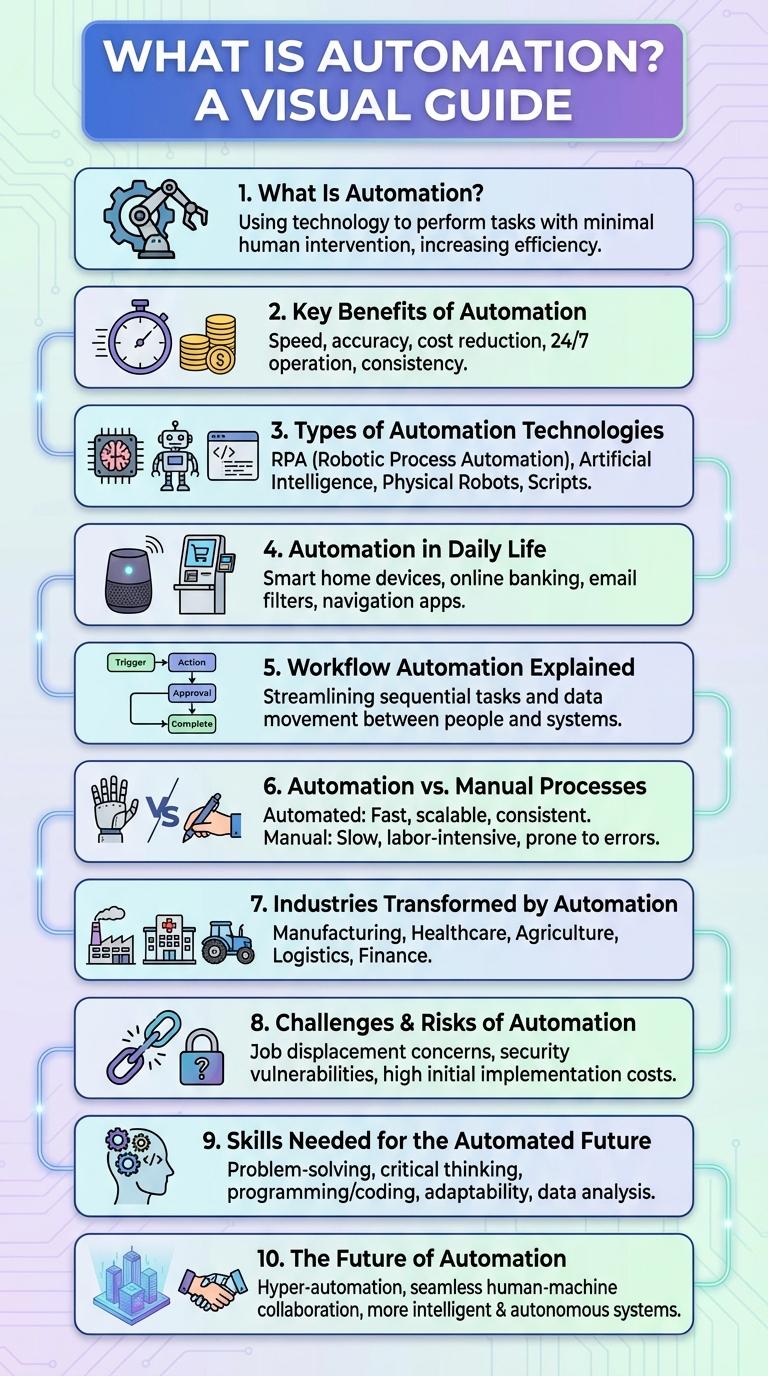
What Is Automation?
| What Is Automation? | Key Insights |
|---|---|
| Definition | Automation uses technology to perform tasks with minimal human intervention. |
| Purpose | Increase efficiency, reduce errors, and save time in repetitive processes. |
| Applications | Manufacturing, software development, data entry, customer service. |
| Core Technologies | Robotics, artificial intelligence, machine learning, control systems. |
| Benefits | Cost reduction, improved accuracy, consistent output, scalability. |
Key Benefits of Automation
Automation transforms business operations by streamlining repetitive tasks, increasing efficiency, and reducing operational costs. It enables companies to focus on strategic activities that drive growth and innovation.
Key benefits of automation include improved accuracy, faster processing times, and enhanced consistency across workflows. Organizations also experience greater scalability and better resource management through automated systems.
Types of Automation Technologies
Automation technologies streamline processes by using machines and software to perform tasks without human intervention. Common types include robotic process automation (RPA), industrial automation, and cognitive automation, each designed for specific applications. These technologies improve efficiency, reduce errors, and lower operational costs across various industries.
Automation in Daily Life
Automation seamlessly integrates into daily life, enhancing efficiency across various tasks. From smart home devices to automated scheduling, technology simplifies routine activities.
Household appliances like robotic vacuum cleaners and smart thermostats optimize energy use and save time. Automation in personal devices improves convenience and supports better task management.
Workflow Automation Explained
Workflow automation streamlines repetitive tasks by using technology to execute processes without human intervention. It enhances efficiency and accuracy across various business operations.
- Definition - Workflow automation involves designing, creating, and automating business processes to improve productivity.
- Key Benefits - It reduces manual errors, accelerates task completion, and frees up employee time for strategic activities.
- Common Tools - Popular platforms include Zapier, Microsoft Power Automate, and UiPath for automating diverse workflows.
Implementing workflow automation drives operational excellence and supports scalable business growth.
Automation vs. Manual Processes
Automation significantly enhances efficiency by replacing manual processes with technology-driven solutions. It reduces human error and accelerates task completion, offering consistent and scalable outputs.
- Speed - Automation completes repetitive tasks faster than manual methods, boosting overall productivity.
- Accuracy - Automated systems minimize errors common in manual data entry and process handling.
- Cost Efficiency - Long-term operational costs decrease as automation reduces labor expenses and resource usage.
Industries Transformed by Automation
Which industries have been most transformed by automation?
Automation has revolutionized multiple sectors by enhancing efficiency and reducing operational costs. Key industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, retail, and agriculture have experienced significant changes driven by advanced automation technologies.
| Industry | Impact of Automation |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automation streamlines production lines, increasing output and improving quality control. |
| Healthcare | Robotic surgery and automated diagnostics improve patient outcomes and operational efficiency. |
| Logistics | Automated warehousing and transportation optimize supply chain management. |
| Retail | Automation enables inventory management, self-checkout systems, and personalized marketing. |
| Agriculture | Precision farming technologies increase crop yields and reduce resource usage. |
Challenges & Risks of Automation
Automation introduces significant challenges, including job displacement affecting millions worldwide and the need for workforce reskilling. Cybersecurity risks escalate as automated systems become prime targets for hacking and data breaches. Dependence on automation may lead to reduced human oversight, increasing the potential for critical system failures.
Skills Needed for the Automated Future
Automation is transforming the job market by increasing demand for technical and analytical skills. Workers must adapt by developing competencies that complement automated technologies.
- Technical Proficiency - Mastery of programming, robotics, and software tools is essential to design and maintain automated systems.
- Critical Thinking - Ability to analyze problems and optimize workflows that involve human and machine collaboration.
- Digital Literacy - Understanding data management, cybersecurity, and cloud computing ensures effective interaction with automated platforms.
