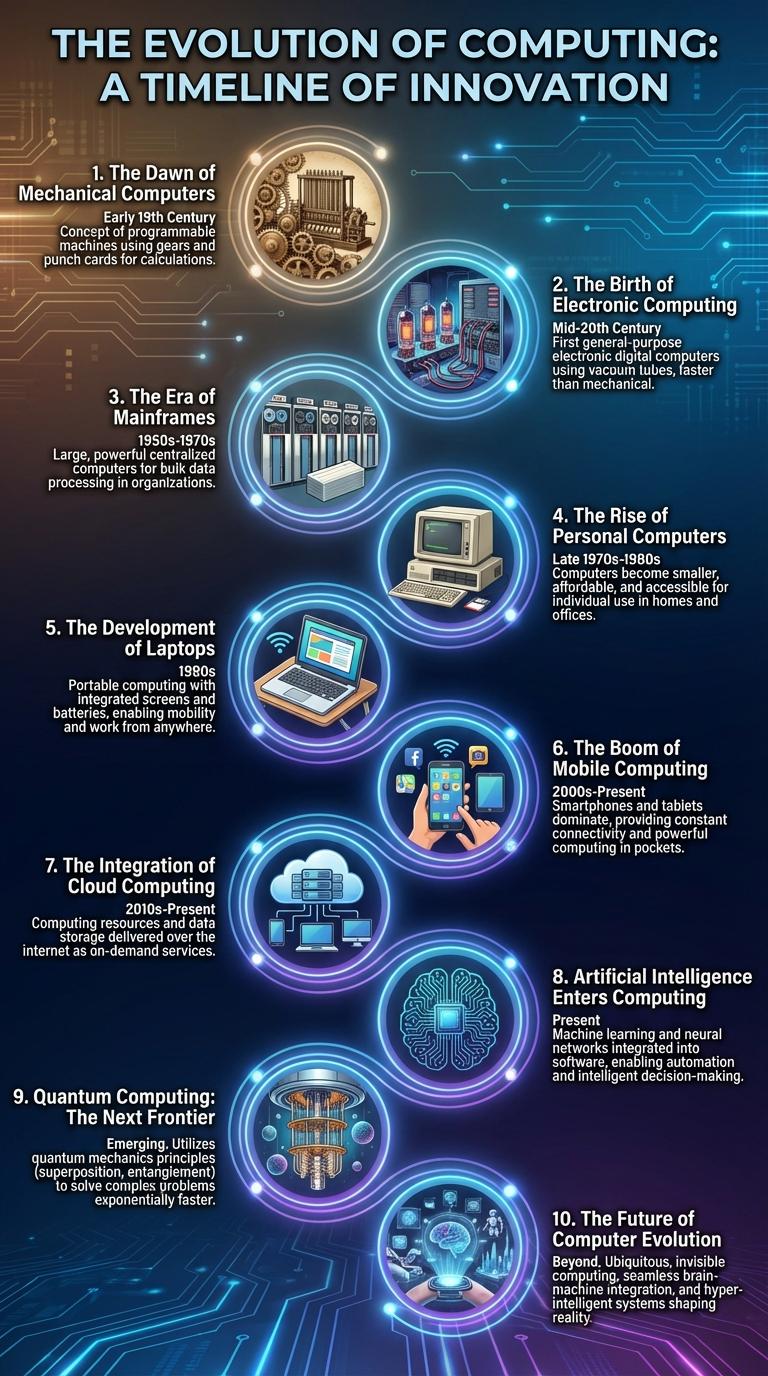
The evolution of computers highlights significant advancements from early mechanical devices to today's powerful digital machines. Key milestones include the transition from vacuum tubes to transistors and the rise of integrated circuits, leading to exponential increases in processing speed and storage capacity. This infographic visually traces these technological breakthroughs, showcasing how computers have transformed industries and everyday life.
The Dawn of Mechanical Computers
The dawn of mechanical computers marks the beginning of automated calculation devices in the 19th century. Charles Babbage conceptualized the Analytical Engine, regarded as the first mechanical general-purpose computer.
Mechanical computers used gears, levers, and cams to perform calculations with high precision. This era laid the foundational principles for modern computing technology still in use today.
The Birth of Electronic Computing
The birth of electronic computing marks a revolutionary shift from mechanical calculation devices to digital machines. This era introduced programmable, high-speed computers capable of complex computations.
- ENIAC (1945) - The first general-purpose electronic digital computer, ENIAC, performed large-scale calculations for artillery ballistic trajectories.
- Stored-Program Concept - Proposed by John von Neumann, this design allowed computers to store instructions in memory, enabling more flexible computing.
- Vacuum Tubes - These electronic components replaced mechanical switches, drastically increasing computation speed and reliability.
The Era of Mainframes
The Era of Mainframes began in the 1950s, marking the introduction of large, powerful computers used primarily by governments and large corporations. These machines, like the IBM 700 series, dominated computing due to their ability to process vast amounts of data for complex calculations. Mainframes laid the foundation for modern computing by enabling batch processing and supporting multiple users simultaneously.
The Rise of Personal Computers
The rise of personal computers began in the 1970s with the introduction of affordable and user-friendly models like the Apple II and IBM PC. These devices transformed computing from a business and academic tool into a household necessity. Rapid advancements in hardware and software fueled widespread adoption, making personal computers central to everyday life and work.
The Development of Laptops
The evolution of laptops revolutionized computing by making portable performance accessible. Early models prioritized mobility, gradually integrating advanced technology for enhanced functionality.
The first laptops appeared in the early 1980s, featuring bulky designs and limited processing power. Over time, improvements in battery technology, weight reduction, and screen resolution transformed laptops into powerful yet lightweight devices. Modern laptops offer high-speed processors, extensive storage, and versatile connectivity options, supporting a wide range of professional and personal applications.
The Boom of Mobile Computing
How did mobile computing transform the evolution of computers?
Mobile computing sparked a revolutionary shift from stationary desktop systems to portable devices, making computing accessible anywhere. Advances in wireless technology and compact hardware fueled the rapid adoption of smartphones and tablets in the late 2000s.
The Integration of Cloud Computing
| Era | Key Developments in Cloud Computing Integration |
|---|---|
| 1960s - Mainframe Era | Introduction of time-sharing systems, early concept of resource pooling resembling cloud principles. |
| 1990s - Internet Expansion | Emergence of web-based applications; beginnings of remote data access and storage. |
| 2000s - Cloud Computing Birth | Launch of Amazon Web Services (AWS) in 2006; scalable infrastructure as a service (IaaS) gains traction. |
| 2010s - Mainstream Adoption | Integration of cloud platforms into enterprise IT; rise of software as a service (SaaS) models transforming software delivery. |
| 2020s - Hybrid & Edge Cloud | Growth of hybrid cloud and edge computing; enhanced data security and real-time processing capabilities. |
Artificial Intelligence Enters Computing
The evolution of computers marked a significant milestone with the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI). AI transformed computing by enabling machines to perform tasks that require human-like intelligence.
- Machine Learning Emerges - Algorithms began enabling computers to learn from data without explicit programming.
- Natural Language Processing Advances - Computers started understanding and generating human language more effectively.
- AI-Powered Automation - Intelligent automation improved efficiency across industries by handling complex tasks.
Artificial Intelligence continues to drive innovation, shaping the future of computing with smarter, adaptive technologies.
Quantum Computing: The Next Frontier
Quantum computing represents a revolutionary leap in computational power, utilizing quantum bits or qubits to perform complex calculations exponentially faster than classical computers. Unlike traditional binary systems, qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously through superposition.
This technology promises breakthroughs in cryptography, drug discovery, and optimization problems beyond the reach of current computers. Leading companies and research institutions are investing heavily to overcome challenges such as qubit stability and error correction.
