Artificial intelligence (AI) transforms industries by enabling machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. This infographic visually breaks down key AI concepts, applications, and advancements to provide a clear understanding of its growing impact. Explore how AI innovations are shaping the future across various sectors.
The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has evolved dramatically since its inception in the mid-20th century. Early AI focused on rule-based systems capable of basic problem-solving and logical inference.
Advancements in machine learning and neural networks have propelled AI from simple algorithms to complex models that mimic human cognition. Today, AI powers applications across industries including healthcare, finance, and autonomous systems.
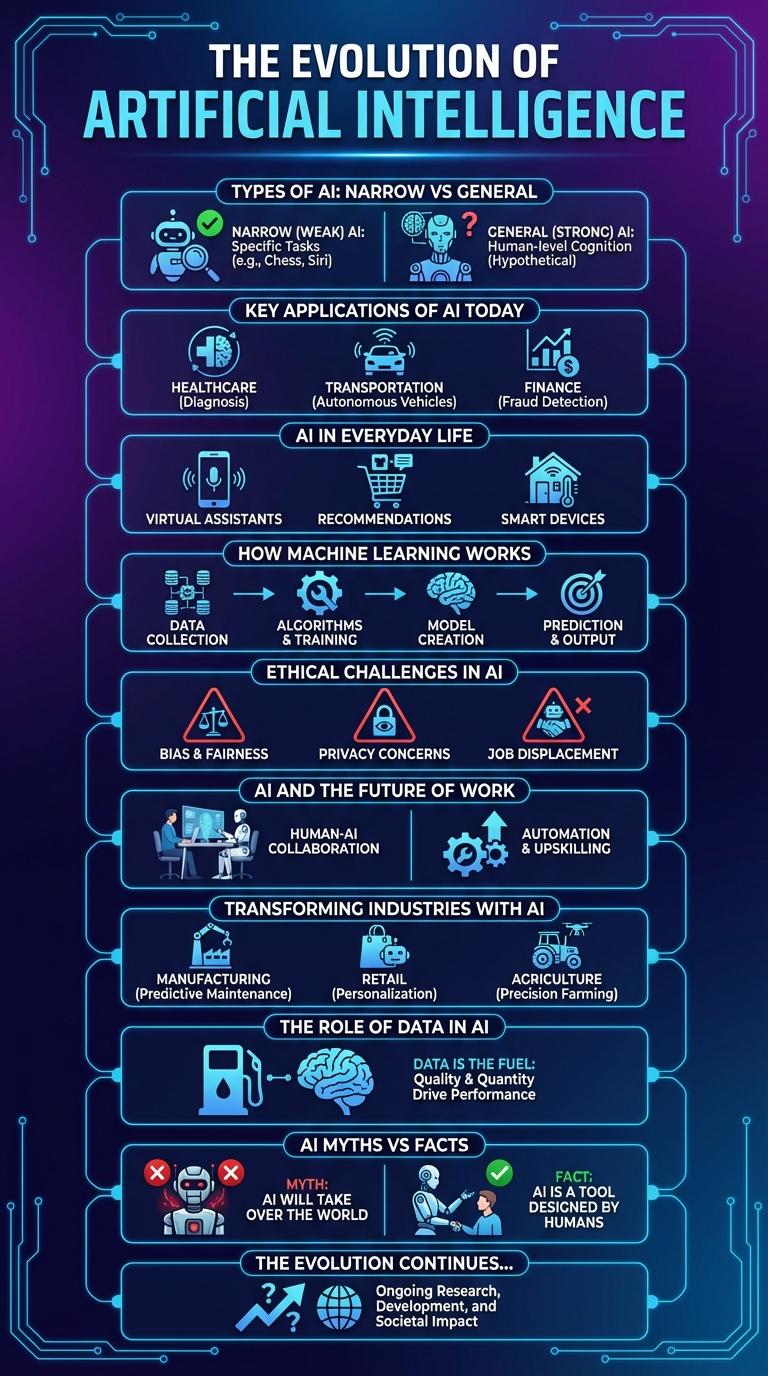
Types of AI: Narrow vs General
| Type of AI | Description |
|---|---|
| Narrow AI (Weak AI) | Designed to perform a specific task or a set of related tasks. Examples include voice assistants, facial recognition, and recommendation systems. Operates within a limited domain and cannot generalize beyond its programming. |
| General AI (Strong AI) | Exhibits human-like intelligence across a wide range of tasks. Capable of reasoning, learning, and understanding complex concepts. Not yet achieved in practice but represents the goal of creating machines with versatile cognitive abilities. |
Key Applications of AI Today
Artificial Intelligence (AI) transforms multiple industries by enhancing efficiency and decision-making. Its applications range from everyday tools to advanced technological systems.
AI drives innovation through smart automation, data analysis, and personalized experiences.
- Healthcare - AI supports disease diagnosis, patient monitoring, and drug discovery to improve medical outcomes.
- Finance - AI enables fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and risk management in banking and investment sectors.
- Retail - AI personalizes customer experiences, optimizes inventory, and streamlines supply chains.
AI in Everyday Life
Artificial Intelligence (AI) seamlessly integrates into daily routines, enhancing convenience and efficiency. From smart assistants to personalized recommendations, AI technologies transform how people interact with devices and services.
In everyday life, AI powers virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, enabling hands-free control and instant information access. AI-driven algorithms curate content on streaming platforms and social media, tailoring suggestions to individual preferences. Smart home devices utilize AI to optimize energy usage and improve security, making homes smarter and more responsive.
How Machine Learning Works
Machine Learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that enables systems to learn from data and improve over time without explicit programming. It uses algorithms to identify patterns and make decisions based on input information.
- Data Collection - Raw data is gathered from various sources to train the machine learning model.
- Training - Algorithms analyze the data to recognize patterns and build predictive models.
- Validation - Models are tested with new data to ensure accuracy and reliability.
- Deployment - The trained model is implemented into real-world applications for decision-making.
- Continuous Learning - Models update and refine themselves as they receive more data over time.
Machine learning transforms raw data into actionable insights by enabling adaptive, data-driven technologies.
Ethical Challenges in AI
Ethical challenges in AI include issues such as bias, privacy, and accountability. AI systems can unintentionally perpetuate existing biases, leading to unfair treatment in areas like hiring and law enforcement. Ensuring transparent decision-making and protecting user data are critical steps toward responsible AI deployment.
AI and the Future of Work
Artificial Intelligence is transforming the future of work by automating repetitive tasks and enhancing decision-making processes. Companies are increasingly adopting AI tools to improve efficiency and productivity across various industries.
AI enables new job roles centered around technology management, data analysis, and creative problem-solving. The workforce of tomorrow will require a blend of technical skills and human creativity to thrive alongside intelligent machines.
Transforming Industries with AI
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing industries by automating complex processes and enhancing decision-making. Its adaptive technologies drive efficiency, innovation, and growth across sectors worldwide.
- Healthcare Advancements - AI algorithms enable predictive diagnostics and personalized treatment plans, improving patient outcomes.
- Manufacturing Optimization - Intelligent automation streamlines production lines, reducing downtime and increasing productivity.
- Financial Services Innovation - AI-powered analytics detect fraud and optimize investment strategies, safeguarding assets and maximizing returns.
The Role of Data in AI
What is the role of data in artificial intelligence? Data serves as the foundational input that enables AI systems to learn, adapt, and make decisions. High-quality, diverse datasets improve the accuracy and efficiency of AI models.
How does data influence AI performance? The volume and variety of data directly impact the machine learning process, allowing algorithms to detect patterns and make predictions. Without sufficient data, AI systems cannot generalize well or perform reliably.
Why is data preprocessing important in AI development? Data preprocessing cleans and organizes raw information, removing errors and inconsistencies. This step ensures that the AI model trains on accurate and relevant data, enhancing overall performance.
What types of data are essential for AI? Structured data, such as databases and spreadsheets, and unstructured data, including images, text, and audio, are critical for diverse AI applications. Different AI models require specific data types to function effectively.
How does data security impact AI systems? Protecting data privacy and ensuring security prevents unauthorized access and biases in AI outcomes. Ethical handling of data contributes to trustworthy and responsible AI implementations.
