JavaScript Promises enable efficient handling of asynchronous operations by representing the eventual completion or failure of an action. They simplify complex callback chains, improving code readability and maintainability. This infographic visually breaks down Promise states, methods, and practical use cases for streamlined JavaScript development.
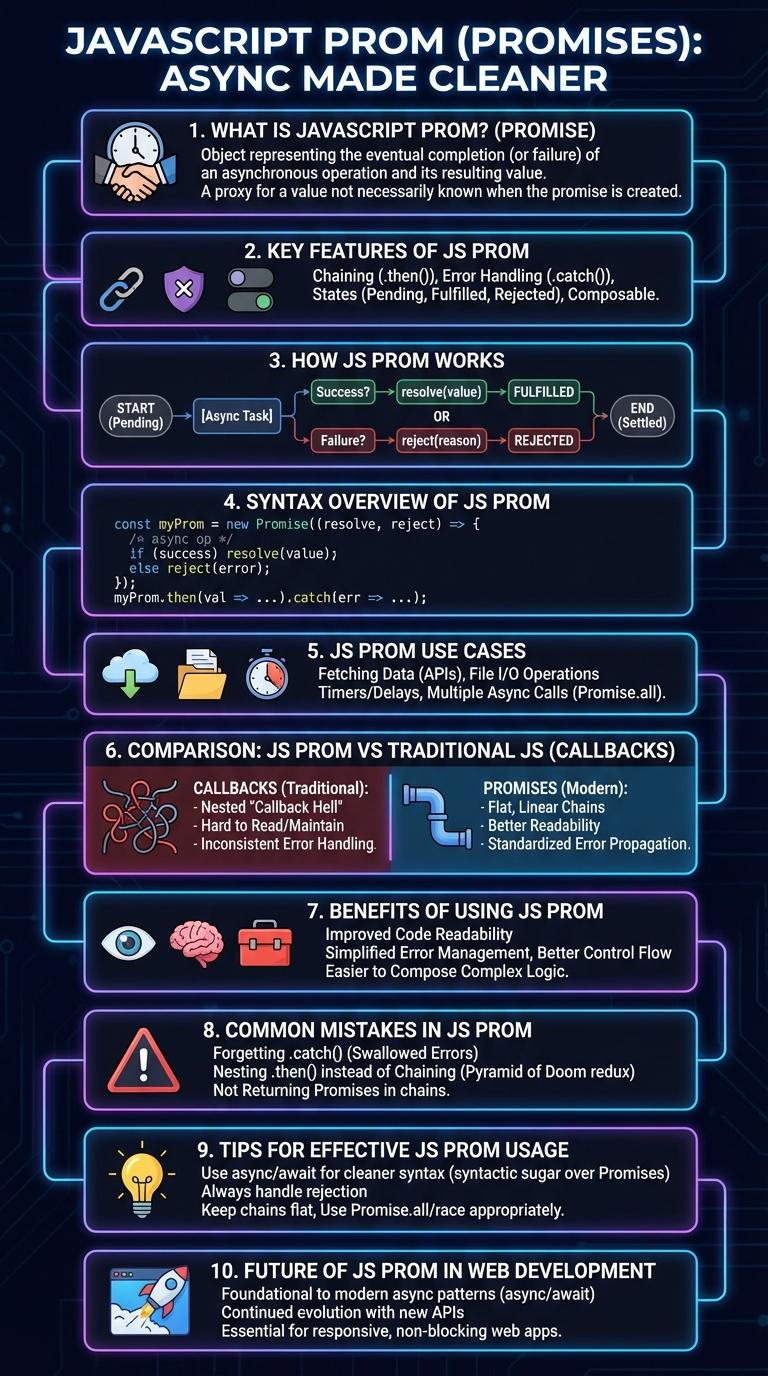
What is JavaScript Prom?
JavaScript Prom is a powerful feature used to handle asynchronous operations. It allows developers to write cleaner and more manageable code when working with tasks that take time to complete.
Promises represent the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation and its resulting value. They have three states: pending, fulfilled, and rejected. Using Promises helps avoid callback hell and improves code readability.
Key Features of JS Prom
JavaScript Promises represent asynchronous operations that will complete in the future, allowing better management of asynchronous code. They provide a cleaner alternative to callbacks by enabling chaining and error handling.
- Pending, Fulfilled, Rejected - Promises have three states to track the progress of the asynchronous task.
- Chaining - Promises enable sequential asynchronous operations through .then() methods.
- Error Handling - Promises simplify catching and propagating errors with .catch() methods.
JavaScript Promises enhance code readability and maintainability by streamlining asynchronous workflows.
How JS Prom Works
JavaScript Promises represent the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation and its resulting value. A Promise has three states: pending, fulfilled, and rejected, allowing developers to handle asynchronous code more efficiently. The `.then()` method processes fulfilled promises, while `.catch()` handles rejections, ensuring robust error management in asynchronous workflows.
Syntax Overview of JS Prom
JavaScript Promises represent the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation. They provide a cleaner alternative to callbacks.
- Promise Constructor - Creates a new Promise object using an executor function with resolve and reject parameters.
- Then Method - Attaches callbacks for the resolved state of the Promise to handle success responses.
- Catch Method - Handles rejected Promise results by catching errors or failures during asynchronous operations.
JS Prom Use Cases
JavaScript Promises simplify handling asynchronous operations by providing a clean way to manage success and failure states. They are widely used in scenarios like API calls, file reading, and timers.
Common use cases include fetching data from servers with XMLHttpRequest or Fetch API, managing multiple asynchronous tasks with Promise.all, and handling user interactions that depend on delayed responses. Promises improve code readability and error management in complex asynchronous workflows.
Comparison: JS Prom vs Traditional JS
| Aspect | JS Promise | Traditional JS (Callbacks) |
|---|---|---|
| Syntax | Chained `.then()` and `.catch()` methods | Nested callback functions |
| Error Handling | Centralized `.catch()` for handling errors | Error management inside each callback |
| Readability | Linear, more readable async flow | Callback hell with deep nesting |
| Asynchronous Control | Supports chaining and promise combinators (`Promise.all`, `Promise.race`) | Difficult to manage multiple async operations |
| State Management | Immutable states: pending, fulfilled, rejected | No built-in state handling |
Benefits of Using JS Prom
JavaScript Promises simplify asynchronous coding by providing a clear and structured way to handle operations that complete in the future. They enhance code readability and maintainability by avoiding deeply nested callbacks, known as "callback hell." Promises also improve error handling, allowing developers to catch and manage errors effectively through chaining methods like .then() and .catch().
Common Mistakes in JS Prom
What are common mistakes when using JavaScript Promises? Many developers misuse `.then()` chaining and ignore error handling, leading to unexpected results. Understanding proper Promise chaining and consistent `.catch()` usage prevents such issues.
How does forgetting to return a Promise inside `.then()` cause problems? Omitting the return statement breaks the chain, resulting in unresolved Promises and unpredictable behavior. Always return a Promise or value inside `.then()` for correct sequencing.
Why is neglecting `.catch()` dangerous in Promise code? Skipping `.catch()` handlers causes unhandled promise rejections that can crash applications or hide bugs. Attaching `.catch()` ensures errors are captured and managed.
What happens if multiple Promises aren't synchronized properly? Without `Promise.all` or similar methods, dependent Promises can resolve out of order, leading to data inconsistencies. Use synchronization utilities to handle concurrency.
How does nesting Promises instead of chaining affect code maintainability? Nesting causes callback hell similar to old async patterns, making code harder to read and debug. Chaining Promises flattens the structure and improves clarity.
Tips for Effective JS Prom Usage
JavaScript Promises simplify handling asynchronous operations by providing a clean, readable structure for success and error handling. They ensure code executes sequentially without blocking the main thread.
Always chain `.then()` and `.catch()` methods to handle resolved and rejected promises effectively. Use `Promise.all()` for running multiple promises concurrently and handling their combined results.
