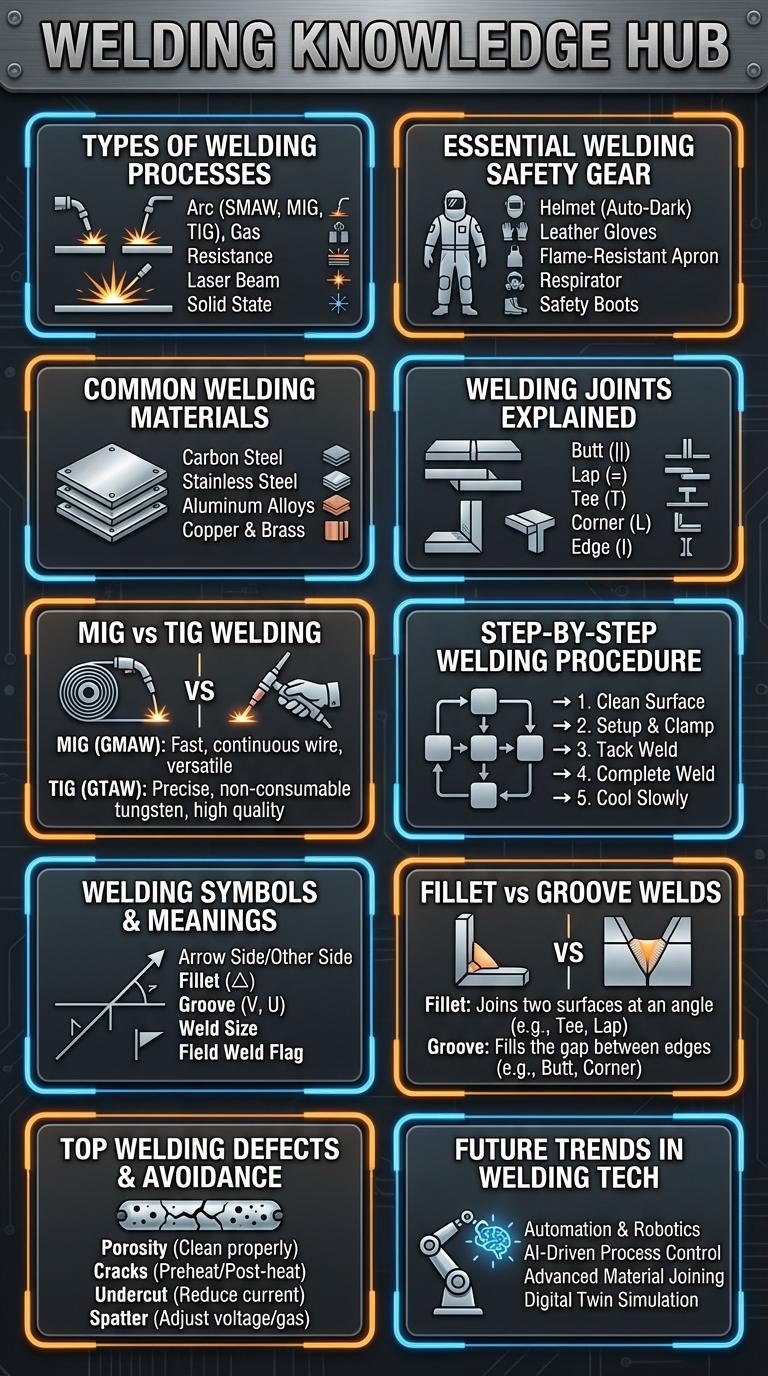
Welding combines metals through intense heat and pressure to create strong, durable joints essential in construction and manufacturing. Understanding different welding types, techniques, and safety measures enhances efficiency and quality in metal fabrication. This infographic breaks down key welding concepts, tools, and best practices for professionals and enthusiasts alike.
Types of Welding Processes
What are the main types of welding processes used in industry today? Welding involves various methods to join metals, each suited for specific applications and materials.
| Welding Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) | Uses a consumable electrode coated in flux to lay the weld. Suitable for general fabrication and maintenance work. |
| Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW/MIG) | Employs a continuous wire electrode and shielding gas. Ideal for thin to medium thickness metals with fast welding speeds. |
| Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW/TIG) | Uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode with inert gas shielding. Provides precise, high-quality welds for stainless steel and aluminum. |
| Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) | Similar to GMAW but uses a tubular wire filled with flux. Effective in outdoor or windy conditions with deep penetration. |
| Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) | Involves a continuously fed consumable electrode beneath a blanket of granular flux. Common in heavy industrial applications for thick materials. |
Essential Welding Safety Gear
Welding involves intense heat, light, and fumes that pose significant hazards. Proper safety gear is crucial to protect welders from injuries and long-term health risks.
- Welding Helmet - Shields the face and eyes from sparks, UV radiation, and heat during welding operations.
- Protective Gloves - Provides heat resistance and protects hands from burns and electric shock.
- Flame-Resistant Clothing - Reduces the risk of burns by preventing sparks and molten metal from reaching the skin.
Using essential welding safety gear ensures a safer work environment and reduces the likelihood of accidents.
Common Welding Materials
| Material | Common Uses |
|---|---|
| Steel | Construction, automotive, manufacturing |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, transportation, packaging |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, chemical industry, medical devices |
| Copper | Electrical wiring, plumbing, heat exchangers |
| Nickel Alloys | High-temperature environments, aerospace, power generation |
Welding Joints Explained
Welding joints are critical connections where two or more metal pieces are fused together to form a strong, durable bond. Understanding different types of welding joints enhances the effectiveness and quality of metal fabrication projects.
The main categories of welding joints include butt, corner, edge, lap, and T-joints. Each joint type offers unique advantages and is selected based on the requirements of strength, accessibility, and weld placement.
MIG vs TIG Welding
MIG and TIG welding are two popular welding techniques used across various industries. Both methods use electric arcs to join metals but differ in their processes and applications.
MIG welding, or Metal Inert Gas welding, uses a continuous wire feed as an electrode and is known for its speed and ease of use, making it ideal for thicker metals. TIG welding, or Tungsten Inert Gas welding, employs a non-consumable tungsten electrode and provides superior precision and control, especially useful for thinner materials and detailed work. MIG welding is generally preferred for construction and automotive industries, while TIG welding excels in aerospace and art metalwork due to its high-quality welds.
Step-by-Step Welding Procedure
Welding is a fabrication process that joins materials, typically metals or thermoplastics, by causing coalescence. A step-by-step welding procedure ensures strong and durable joints by following precise guidelines.
The first step in welding involves preparing the materials by cleaning and positioning them correctly. Proper safety equipment must always be worn, including gloves, helmets, and protective clothing, to prevent injuries during the process.
Welding Symbols and Their Meanings
Welding symbols are standardized icons used in blueprints to communicate essential information about weld types, sizes, and finishes. Each symbol consists of a reference line, an arrow, and specific indicators that describe the weld's characteristics. Understanding these symbols ensures accurate interpretation and execution of welding tasks in manufacturing and construction.
Fillet vs Groove Welds
Fillet welds are triangular and commonly used to join two surfaces at a right angle, providing moderate strength and ease of application. Groove welds involve welding within a groove between two pieces, offering deeper penetration and higher strength for critical structural connections. Understanding the differences in shape, strength, and application helps choose the appropriate weld type for specific engineering tasks.
Top Welding Defects & How to Avoid Them
Welding defects can compromise the strength and durability of metal joints, leading to costly repairs and safety hazards. Identifying and preventing common welding flaws ensures higher quality and longer-lasting welds.
Top Welding Defects & How to Avoid Them:
- Porosity - Gas pockets trapped in the weld metal weaken the joint and can be avoided by controlling humidity and using clean materials.
- Cracks - Fractures caused by rapid cooling or excessive stress require proper preheating and controlled cooling rates to prevent.
- Incomplete Fusion - Occurs when weld metal fails to blend properly with the base metal; correct welding technique and adequate heat input are essential to avoid this.
