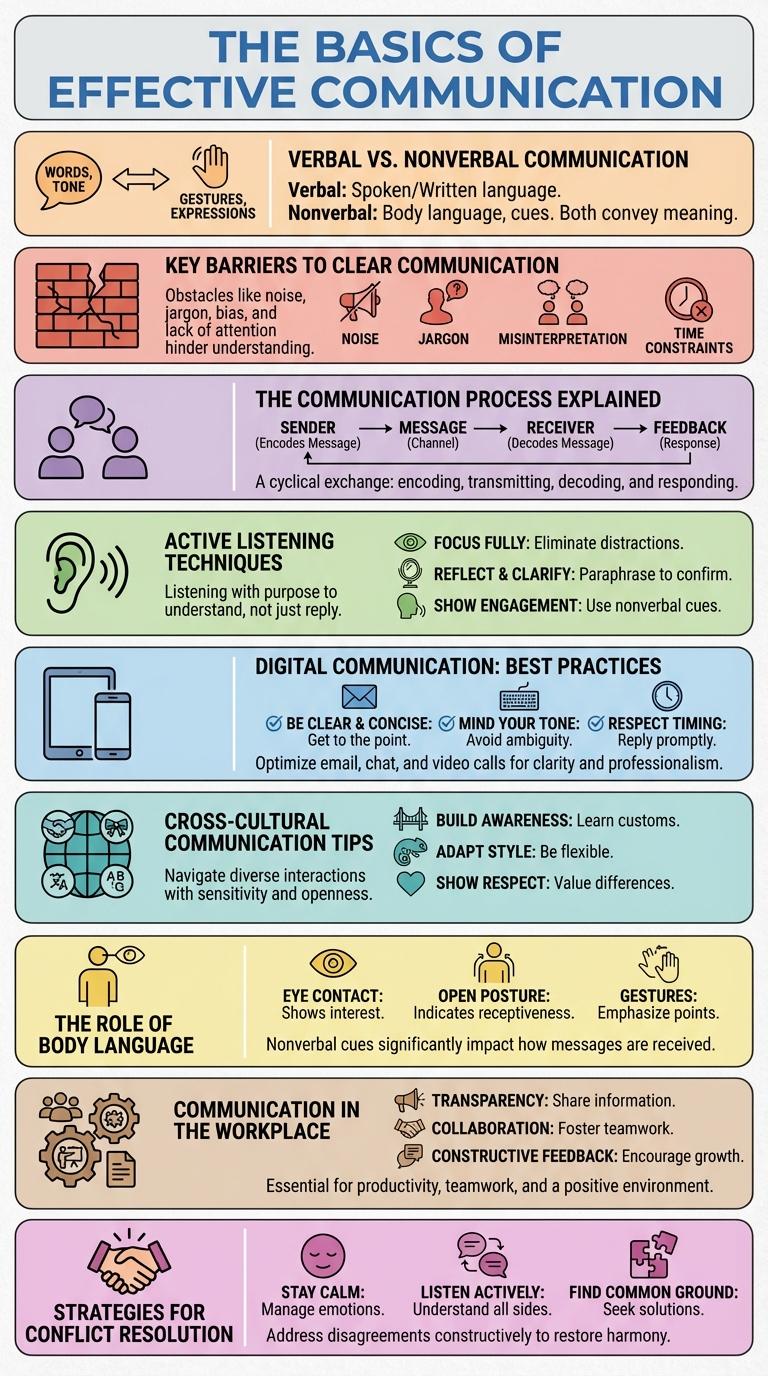
Visualizing key concepts, this infographic highlights essential elements of effective communication, including verbal and nonverbal cues, active listening, and feedback mechanisms. It breaks down complex ideas into clear, engaging graphics that enhance understanding and retention. The design supports improved interpersonal skills and fosters stronger connections in personal and professional interactions.
The Basics of Effective Communication
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Clarity | Express ideas in a clear, concise manner to avoid misunderstandings. |
| Active Listening | Fully concentrate on the speaker, understand the message, and respond thoughtfully. |
| Nonverbal Signals | Use body language, eye contact, and facial expressions to reinforce the message. |
| Feedback | Provide constructive feedback to ensure the message has been understood correctly. |
| Empathy | Understand and respect the emotions and perspectives of others during communication. |
Verbal vs. Nonverbal Communication
Communication involves both verbal and nonverbal methods, each playing a crucial role in conveying messages effectively. Verbal communication relies on spoken or written words, enabling clear and direct information exchange. Nonverbal communication includes body language, facial expressions, and gestures, often revealing emotions and attitudes beyond words.
Key Barriers to Clear Communication
Effective communication is essential for collaboration and understanding in any environment. However, several key barriers can obstruct the clarity of messages exchanged between individuals.
Common barriers include language differences, cultural misunderstandings, and lack of attention or distractions. Emotional factors and assumptions also play a significant role in distorting intended messages.
The Communication Process Explained
Effective communication is essential for sharing ideas and information clearly. Understanding the communication process helps improve interactions in personal and professional settings.
- Sender - The person or entity who initiates the message by encoding their thoughts into a communicable form.
- Message - The information or content that the sender wants to convey to the receiver.
- Channel - The medium through which the message is transmitted, such as spoken words, written text, or digital media.
- Receiver - The person or group who receives and decodes the sender's message to interpret its meaning.
- Feedback - The response from the receiver that indicates whether the message was understood correctly or requires clarification.
This process is dynamic and can be influenced by noise, context, and the relationship between communicators.
Active Listening Techniques
Effective communication relies heavily on active listening to ensure clarity and understanding. Mastering active listening techniques enhances engagement and fosters better relationships.
- Maintain Eye Contact - Focused eye contact shows attentiveness and respect during conversations.
- Provide Feedback - Nodding or verbal affirmations signal that the message is being received.
- Avoid Interruptions - Allow the speaker to finish without interjecting to fully comprehend their message.
Digital Communication: Best Practices
Effective digital communication is essential for productive collaboration and clear information sharing in modern environments. Adopting best practices enhances understanding, engagement, and efficiency across digital platforms.
- Clarity and Brevity - Use concise language and clear messages to minimize misunderstandings and increase readability.
- Active Listening - Pay close attention to feedback and responses to ensure accurate comprehension and appropriate reactions.
- Appropriate Channel Selection - Choose the right digital tool (email, chat, video) based on message urgency and complexity.
Cross-Cultural Communication Tips
Effective cross-cultural communication bridges gaps between diverse backgrounds and fosters mutual understanding. Awareness of cultural differences enhances clarity and reduces misunderstandings in global interactions.
Use simple language and avoid idioms that may confuse non-native speakers. Respect cultural norms, practice active listening, and remain open-minded to build trust and rapport across cultures.
The Role of Body Language
How important is body language in effective communication? Body language conveys over 55% of the message in face-to-face interactions. Understanding gestures, facial expressions, and posture helps decode unspoken emotions and intentions.
Communication in the Workplace
Effective communication in the workplace enhances collaboration, boosts productivity, and reduces misunderstandings among team members. Key methods include clear verbal exchanges, active listening, and the use of digital tools such as emails and instant messaging. Organizations that prioritize communication see improved employee engagement and stronger project outcomes.
