Infographics about language visually present key data and insights that highlight linguistic diversity, usage patterns, and language evolution. They simplify complex information through engaging graphics, making it easier to grasp language statistics and trends. These visual summaries aid in understanding how languages influence culture and communication worldwide.
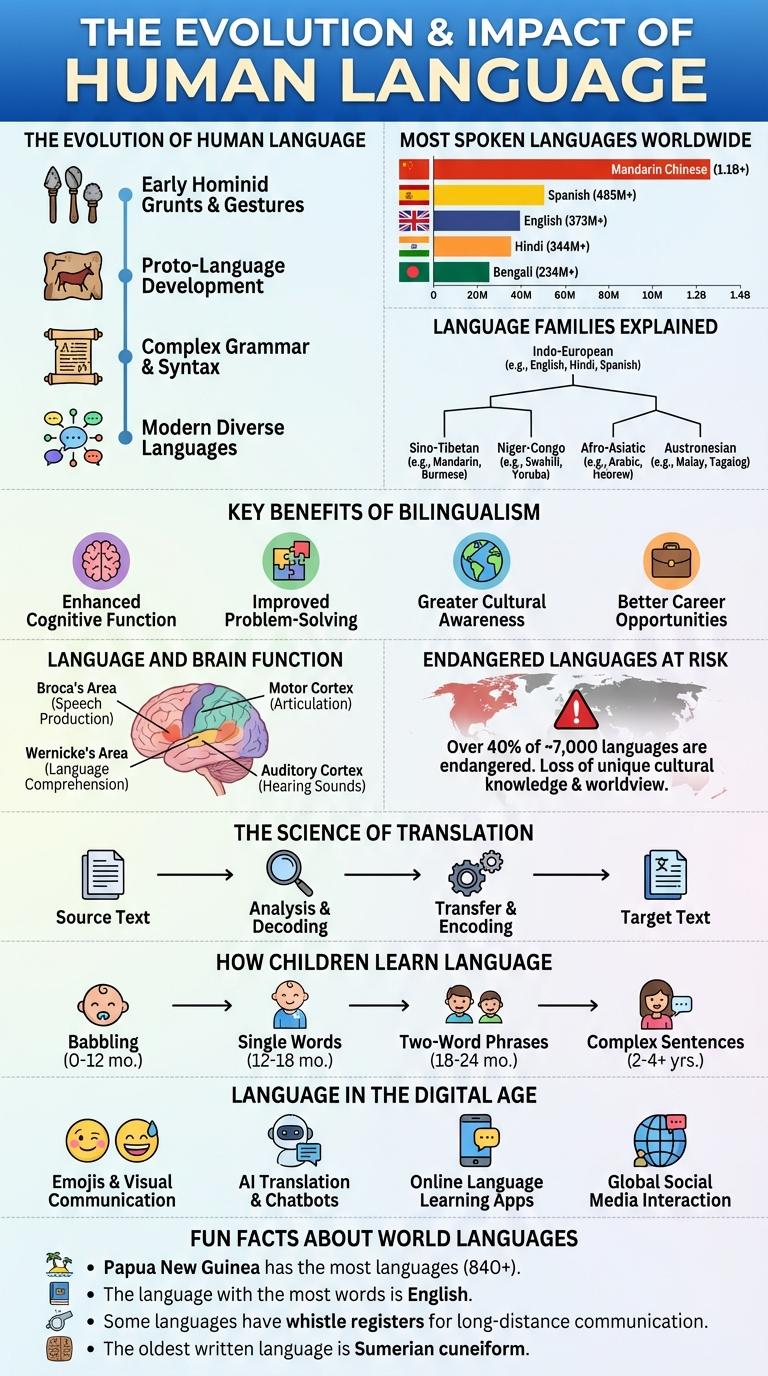
The Evolution of Human Language
Human language has evolved over thousands of years, reflecting changes in society, culture, and technology. The development of language allowed complex communication and the preservation of knowledge across generations.
- Origins in Prehistoric Times - Early human communication involved gestures and vocalizations before developing structured languages.
- Creation of Written Scripts - Writing systems emerged around 5,000 years ago, enabling record-keeping and literature.
- Language Diversification - Over 7,000 languages exist today, shaped by geographic, social, and cultural influences.
- Technological Influence - Digital communication and AI have transformed how language is used and transmitted.
- Ongoing Evolution - Languages continuously adapt, absorbing new words and expressions from global interaction.
Most Spoken Languages Worldwide
The most spoken languages worldwide encompass a vast array of cultures and regions. Mandarin Chinese leads with over 1 billion native speakers, followed by Spanish and English, each with hundreds of millions. These languages dominate global communication, business, and media, reflecting diverse linguistic heritages.
| Language | Native Speakers (Millions) |
|---|---|
| Mandarin Chinese | 1,100 |
| Spanish | 480 |
| English | 370 |
| Hindi | 340 |
| Arabic | 310 |
Language Families Explained
Language families are groups of languages that share a common ancestral origin. Major language families include Indo-European, Sino-Tibetan, Afro-Asiatic, and Niger-Congo. Understanding language families helps trace cultural history and linguistic evolution worldwide.
Key Benefits of Bilingualism
What are the key benefits of bilingualism? Bilingual individuals experience enhanced cognitive abilities, such as improved memory and problem-solving skills. They also show greater cultural awareness and better communication in diverse environments.
Language and Brain Function
Language processing engages multiple regions of the brain, including Broca's area and Wernicke's area. These areas are crucial for speech production and comprehension, respectively.
Neuroimaging studies reveal that both hemispheres contribute to language, with the left hemisphere typically dominating. Understanding language-brain connections aids in diagnosing and treating speech disorders.
Endangered Languages at Risk
Thousands of languages worldwide face the threat of extinction, with many losing speakers each year. Endangered languages carry unique cultural heritage and knowledge vital to human diversity.
Nearly 40% of the world's approximately 7,000 languages are endangered. Factors such as globalization, urbanization, and dominant language spread accelerate language loss. Efforts to document and revive endangered languages are essential for preserving cultural identity and linguistic diversity.
The Science of Translation
Translation bridges languages by converting text or speech while preserving meaning and context. It involves complex cognitive processes and linguistic expertise.
Neuroscience reveals that professional translators activate specific brain regions related to language, memory, and problem-solving. Technology, such as AI and machine learning, enhances translation accuracy and efficiency.
How Children Learn Language
Language acquisition in children is a complex and natural process influenced by cognitive development and social interaction. Understanding how children learn language helps improve educational methods and communication strategies.
Early language exposure plays a crucial role in shaping a child's vocabulary and grammar skills.
- Imitation - Children replicate sounds and words from those around them to learn language structures.
- Social Interaction - Engaging with caregivers and peers enhances language comprehension and use.
- Reinforcement - Positive feedback strengthens language skills and encourages continued learning.
Language in the Digital Age
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Global Language Usage | Over 4.5 billion people use the internet, with English being the most common language online, followed by Chinese and Spanish. |
| Digital Communication | Text messaging, social media, and instant messaging influence language evolution, introducing new slang, acronyms, and emojis. |
| Language Learning Platforms | Apps like Duolingo and Babbel have over 500 million users worldwide, revolutionizing access to language education. |
| Machine Translation | AI-powered tools like Google Translate support over 100 languages, enabling instant communication across linguistic barriers. |
| Content Creation | Blogs, podcasts, and videos in diverse languages increase cultural exchange and multilingual content accessibility online. |
