Understanding media literacy is essential in navigating today's complex information landscape. It equips individuals with critical thinking skills to analyze, evaluate, and create media content effectively. This infographic breaks down key concepts and practical tips to enhance your media literacy in a digital world.
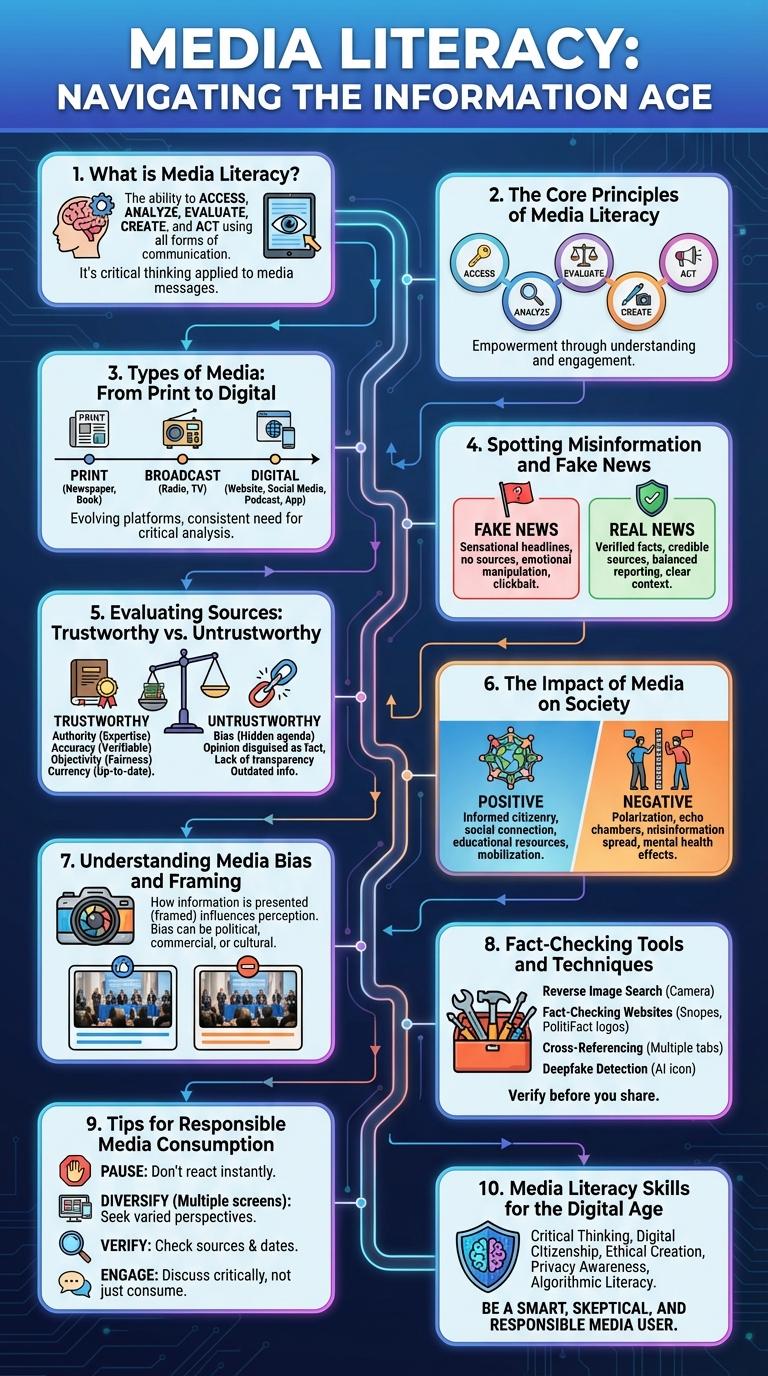
What is Media Literacy?
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Media literacy is the ability to access, analyze, evaluate, and create media in various forms. It empowers individuals to critically engage with content across platforms. |
| Purpose | To equip people with skills to interpret media messages, understand underlying motives, and recognize biases or misinformation. |
| Key Skills | Critical thinking, source evaluation, understanding media techniques, recognizing persuasive intent, and ethical creation of content. |
| Importance | Enhances informed decision-making, promotes responsible consumption of information, and supports democratic participation in society. |
| Applications | Used in education, journalism, advertising awareness, and combating fake news or propaganda. |
The Core Principles of Media Literacy
Media literacy empowers individuals to critically analyze content across various platforms. Understanding the core principles aids in distinguishing reliable information from misinformation.
The core principles include recognizing different types of media, understanding the purpose behind content, and evaluating the source's credibility. These fundamentals enhance informed decision-making in a media-saturated world.
Types of Media: From Print to Digital
Media literacy involves understanding various types of media and their impact on information consumption. It spans from traditional print sources to modern digital platforms.
Print media includes newspapers, magazines, and books that deliver information in a physical format. Broadcast media covers television and radio, providing audio-visual content to wide audiences. Digital media encompasses websites, social media, and streaming services, offering interactive and real-time information.
Spotting Misinformation and Fake News
Understanding media literacy is crucial for identifying misinformation and fake news in today's digital landscape. Developing critical thinking skills helps individuals discern credible sources from false information.
- Check the Source - Verify the credibility of the website or author before trusting information.
- Examine the Evidence - Look for supporting data, legitimate references, and confirm facts through reliable outlets.
- Spot Emotional Language - Recognize sensational or biased language designed to evoke strong emotions rather than present facts.
Effective spotting of misinformation protects users from manipulation and supports informed decision-making.
Evaluating Sources: Trustworthy vs. Untrustworthy
Media literacy requires the ability to evaluate sources to distinguish between trustworthy and untrustworthy information. Recognizing credible sources helps prevent misinformation and supports informed decision-making.
- Credibility - Trustworthy sources have verified authorship and reputation, while untrustworthy sources often lack transparency.
- Evidence - Reliable sources provide clear citations and data, whereas unreliable ones rely on opinion or unverified claims.
- Bias - Trustworthy sources present balanced perspectives, in contrast to untrustworthy sources that may manipulate facts to fit agendas.
The Impact of Media on Society
Media shapes public perception, influencing opinions and behaviors across diverse audiences. The rapid spread of information via digital platforms amplifies both positive awareness and misinformation. Understanding media's impact fosters critical thinking and strengthens societal resilience against manipulative content.
Understanding Media Bias and Framing
Media literacy is essential for identifying bias and framing in news coverage. Understanding these concepts helps audiences critically evaluate the information they consume.
Media bias occurs when news outlets present information in a way that favors a particular perspective or agenda. Framing shapes how stories are told, influencing public perception through selective emphasis.
Fact-Checking Tools and Techniques
What are essential fact-checking tools and techniques in media literacy?
Fact-checking tools help verify the accuracy of information online. Techniques include cross-referencing sources, using reverse image search, and consulting trusted fact-checking websites.
Tips for Responsible Media Consumption
Media literacy empowers individuals to critically evaluate the information they consume. Responsible media consumption prevents misinformation and promotes informed decision-making.
- Verify Sources - Check the credibility of the source before trusting the information.
- Cross-Check Facts - Compare data across multiple reliable outlets to ensure accuracy.
- Be Aware of Bias - Recognize personal and media biases that affect content interpretation.
- Limit Screen Time - Reduce exposure to prevent information overload and fatigue.
- Engage Critically - Question motives behind media messages and seek diverse perspectives.
