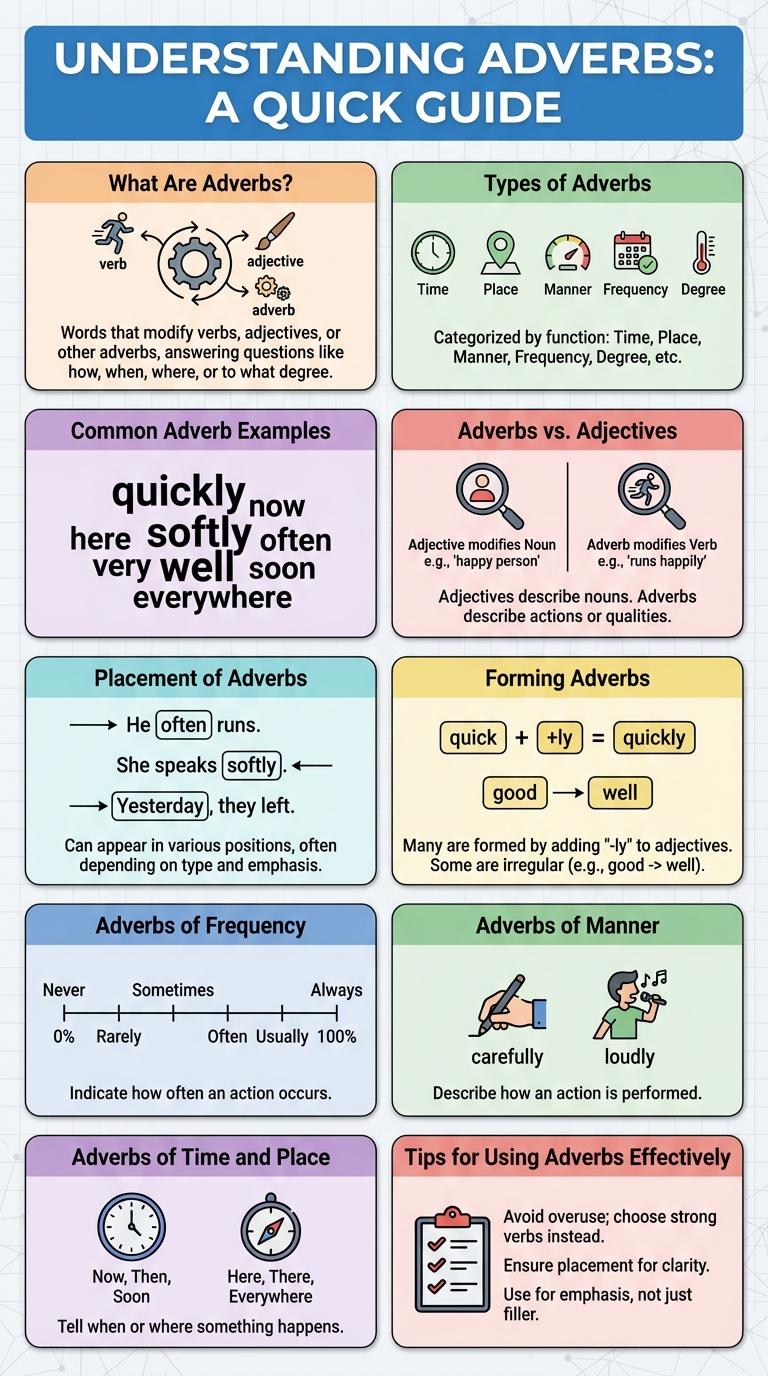
Adverbs enhance sentences by modifying verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, providing clarity and detail about how, when, where, or to what extent an action occurs. Understanding their various types and functions helps improve both writing and communication skills. This infographic visually breaks down the key categories and examples of adverbs for quick and easy learning.
What Are Adverbs?
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, providing additional information about how, when, where, or to what extent an action occurs. They enhance the meaning of sentences by specifying details like manner, time, place, frequency, or degree.
Adverbs often end in "-ly," but many do not, such as "very," "well," or "soon." They answer questions like "How?", "When?", "Where?", and "To what extent?". Understanding adverbs helps improve clarity and expressiveness in writing and speech.
Types of Adverbs
What are the different types of adverbs? Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs by providing more information about manner, place, time, frequency, degree, or certainty. Common types include adverbs of manner, place, time, frequency, and degree.
| Type of Adverb | Example |
|---|---|
| Manner | quickly, softly |
| Place | here, everywhere |
| Time | now, yesterday |
| Frequency | often, rarely |
| Degree | very, almost |
Common Adverb Examples
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, providing more detail about how, when, where, or to what extent an action occurs. Common adverbs include quickly, silently, very, often, and here. These words enhance sentences by clarifying manner, frequency, place, or degree efficiently.
Adverbs vs. Adjectives
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, describing how, when, where, or to what extent an action occurs. Adjectives modify nouns or pronouns, providing more detail about a person, place, thing, or idea.
Adverbs often end in "-ly," such as quickly, softly, or carefully. Adjectives typically appear before the noun they modify, like a blue sky or a smart student.
Placement of Adverbs
| Placement | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Beginning of Sentence | Adverbs placed here often modify the entire sentence, indicating time, place, or manner (e.g., "Yesterday, she arrived early.") |
| Before Main Verb | Common with adverbs of frequency, they appear before the main verb to show how often an action occurs (e.g., "He always studies hard.") |
| After the Verb "To Be" | Adverbs follow forms of "to be" to describe the subject or express time, place, or degree (e.g., "She is often late.") |
| End of Sentence | Adverbs can appear at the end to highlight manner, place, or time of the action (e.g., "He drives carefully.") |
| Between Auxiliary and Main Verb | In compound tenses, adverbs are placed between auxiliary and main verb to modify the action precisely (e.g., "She has never seen that movie.") |
Forming Adverbs
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs to provide more detail about actions or qualities. Forming adverbs often involves specific patterns and rules based on the base word.
- Adding -ly - Most adverbs are formed by adding "-ly" to adjectives, such as "quick" becoming "quickly."
- Adverbs identical to adjectives - Some adverbs share the same form as their adjective counterparts, e.g., "fast" and "hard."
- Irregular adverbs - Certain adverbs do not follow typical patterns, like "well" from the adjective "good."
Understanding how to form adverbs enhances clarity and precision in communication.
Adverbs of Frequency
Adverbs of frequency describe how often an action occurs. They help clarify the timing of habits or repeated events.
Common adverbs of frequency include always, usually, often, sometimes, rarely, and never.
- Always - Indicates an action happens 100% of the time or every time.
- Usually - Refers to an action that occurs most of the time, around 80-90%.
- Often - Describes an action happening frequently but not as consistently as usually.
- Sometimes - Specifies an action that occurs occasionally or about 50% of the time.
- Never - Means an action does not occur at any time.
Adverbs of Manner
Adverbs of manner describe how an action is performed, providing more detail about the verb. Common examples include words like "quickly," "slowly," and "carefully." These adverbs often end in "-ly" and answer the question "How?"
Adverbs of Time and Place
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs to provide more information about how, when, where, or to what extent an action occurs. Adverbs of Time and Place specifically tell us when and where an action happens.
Understanding these adverbs improves sentence clarity and detail.
- Adverbs of Time - Indicate the timing of an action, such as "now," "yesterday," or "soon."
- Adverbs of Place - Describe the location of an action, such as "here," "everywhere," or "outside."
- Usage in Sentences - "She arrived early" uses an adverb of time, while "He waited outside" uses an adverb of place.
