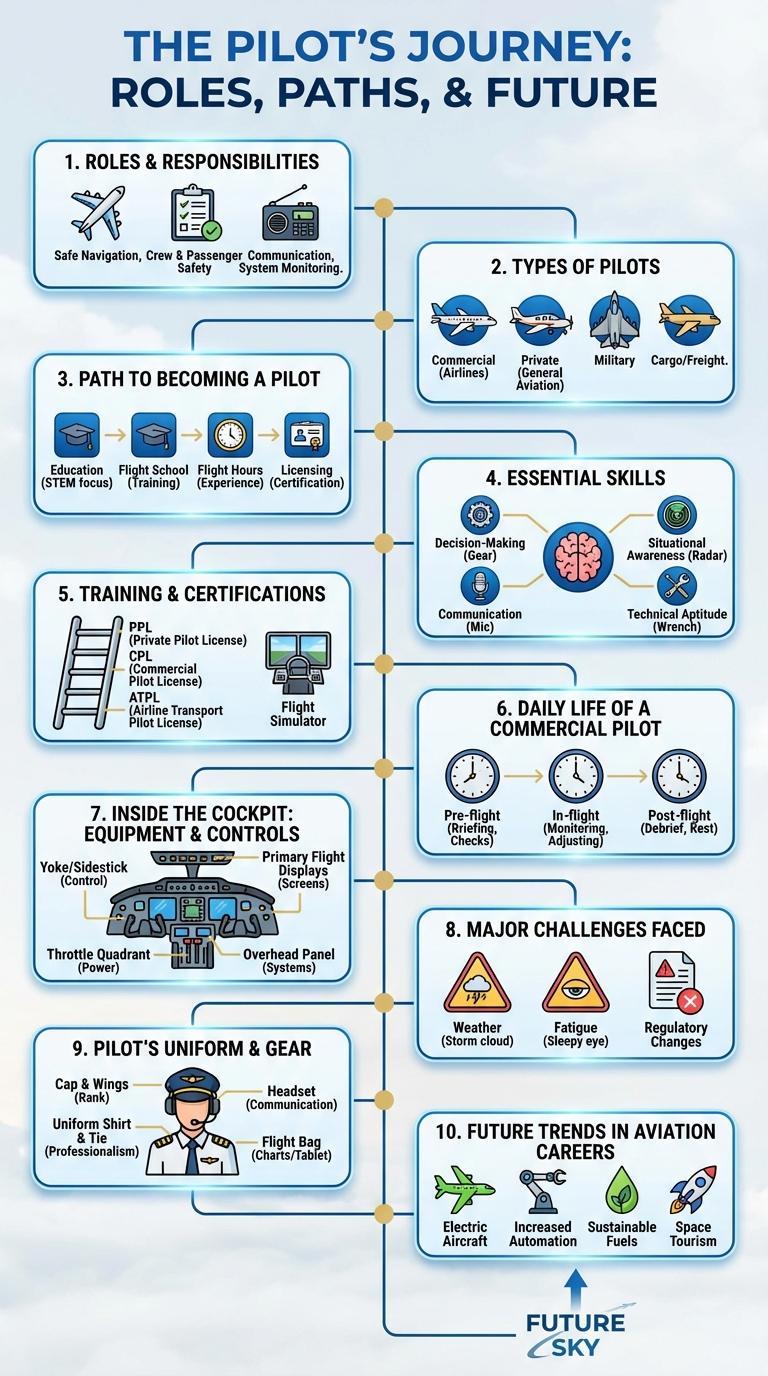
Pilots play a crucial role in aviation, expertly navigating aircraft through various weather conditions and complex airspace. Their extensive training and skills ensure the safety and efficiency of every flight, from takeoff to landing. This infographic highlights key facts and statistics about pilot responsibilities, training, and the challenges they face daily.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Pilot
Pilots are highly trained aviation professionals responsible for operating aircraft safely and efficiently. Their role encompasses navigation, communication, and decision-making during all flight phases.
- Flight Operation - Pilots control the aircraft, managing takeoff, cruising, and landing procedures to ensure safety.
- Navigation and Communication - They use instruments and radio systems to maintain course and coordinate with air traffic control.
- Safety Management - Pilots monitor weather conditions and aircraft performance to anticipate and mitigate risks.
- Pre-Flight Preparation - Conducting thorough inspections and reviewing flight plans before takeoff is essential.
- Emergency Handling - Pilots are trained to respond swiftly and effectively to in-flight emergencies.
Pilots play a critical role in maintaining aviation safety and passenger confidence throughout the journey.
Types of Pilots
Pilots operate various types of aircraft depending on their training and mission. Commercial pilots transport passengers and cargo on scheduled flights. Military pilots conduct defense and combat missions using specialized aircraft.
Path to Becoming a Pilot
Becoming a pilot requires extensive training and dedication. The journey begins with obtaining a private pilot license (PPL), which serves as the foundation.
After earning the PPL, pilots must accumulate flight hours and complete advanced certifications such as the commercial pilot license (CPL). Finally, aspiring pilots undergo specialized training for airline transport pilot (ATP) certification to qualify for airline careers.
Essential Skills for Pilots
Pilots require a unique combination of technical knowledge and physical coordination to operate aircraft safely. Mastery of navigation, communication, and problem-solving skills is critical for successful flights.
Essential skills include strong situational awareness and the ability to remain calm under pressure. Continuous training ensures pilots adapt to new technologies and changing weather conditions effectively.
Pilot Training and Certifications
Pilot training and certifications are essential steps to ensure safety and proficiency in aviation. These processes combine theoretical knowledge with practical flight experience to prepare pilots for various flying conditions.
Pilot certifications vary by type and complexity, reflecting different levels of expertise and aircraft operations.
- Private Pilot License (PPL) - Allows individuals to fly small aircraft for personal use after completing ground school and flight hours.
- Commercial Pilot License (CPL) - Enables pilots to operate aircraft for compensation or hire following advanced training and rigorous testing.
- Airline Transport Pilot License (ATPL) - The highest level of pilot certification required to act as a captain on commercial airliners, demanding extensive flight experience.
Daily Life of a Commercial Pilot
| Pre-Flight Preparation | Review weather conditions, flight plans, and aircraft systems before departure |
| Briefing and Coordination | Communicate with co-pilots, cabin crew, and air traffic control for flight details |
| Flight Operation | Handle takeoff, cruising, navigation, and landing while monitoring instruments |
| Post-Flight Tasks | Complete flight logs, report any technical issues, and debrief with crew |
| Rest and Training | Attend training sessions, simulator practices, and ensure adequate rest between flights |
Inside the Cockpit: Equipment and Controls
What equipment and controls are found inside a pilot's cockpit? The cockpit houses essential instruments like the yoke, throttle, and avionics systems that enable precise aircraft control. Pilots rely on displays such as the Primary Flight Display (PFD) and Multi-Function Display (MFD) to monitor flight data and navigation.
Major Challenges Faced by Pilots
Pilots navigate complex environments to ensure safe and efficient flights. Their roles demand high levels of skill, concentration, and adaptability to changing conditions.
Major challenges faced by pilots include dealing with adverse weather conditions, maintaining situational awareness, and managing fatigue during long-haul flights. Communication with air traffic control requires precision and clarity to prevent misunderstandings. Technical issues with aircraft systems add another layer of complexity to their responsibilities.
Pilot's Uniform and Gear
Pilot uniforms and gear are designed for functionality, safety, and professionalism. These elements play a crucial role in a pilot's daily routine and operational effectiveness.
- Pilot Uniform - Consists of a navy or black jacket, tie, and insignia that denote rank and airline affiliation.
- Flight Jacket - Provides warmth and protection in varying cockpit temperatures during flights.
- Headset - Essential for clear communication with air traffic control and co-pilots, featuring noise-canceling technology.
- Flight Gloves - Enhances grip and protects hands from extreme temperatures and sudden cabin pressure changes.
- Navigation Tools - Includes electronic devices and charts integrated into gear for flight planning and in-flight adjustments.
