Breast cancer remains one of the most prevalent cancers worldwide, affecting millions of individuals each year. Infographics provide a clear and concise way to understand critical data such as risk factors, symptoms, and survival rates. Visual representation of this information helps raise awareness and promotes early detection efforts.
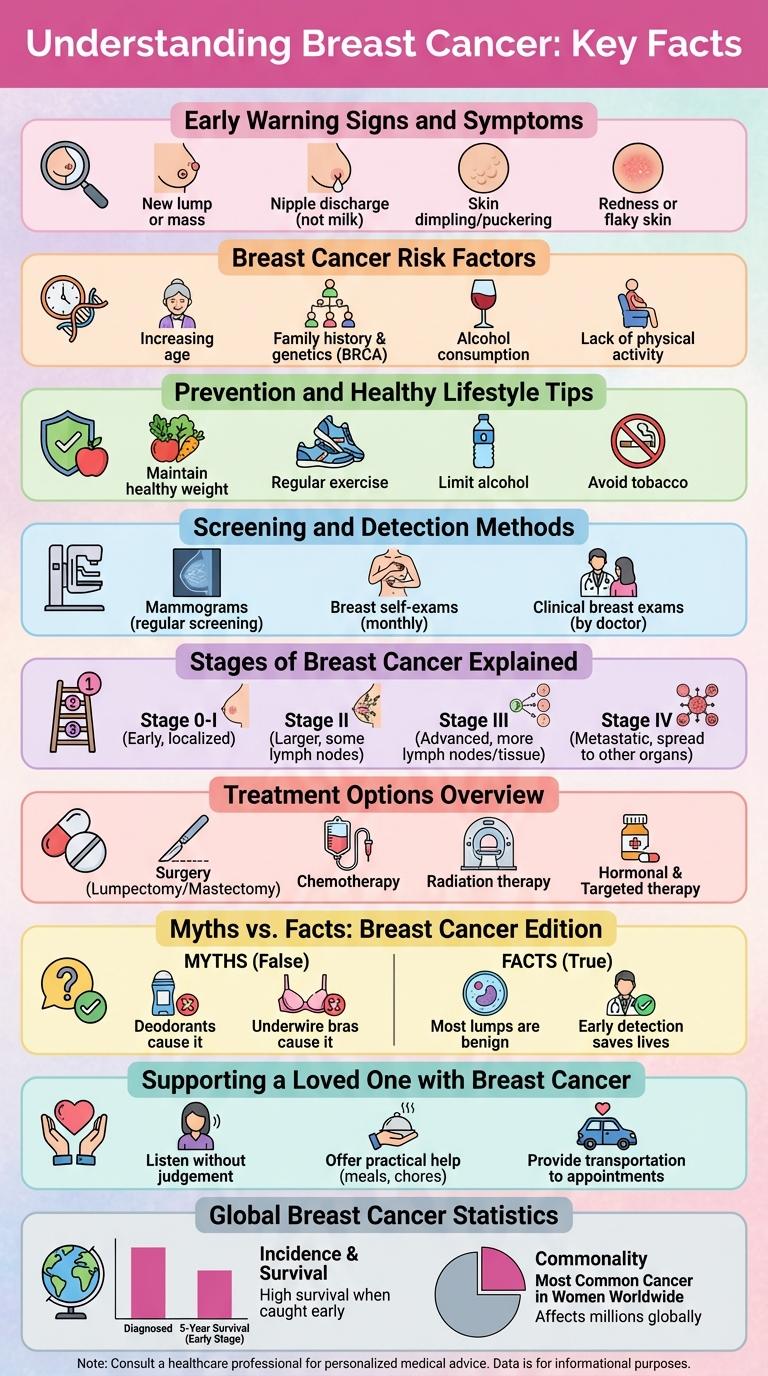
Understanding Breast Cancer: Key Facts
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide. Early detection through regular screening significantly improves treatment outcomes.
Risk factors include age, genetic mutations, family history, and lifestyle choices. Awareness of symptoms like lumps, changes in breast shape, and nipple discharge can lead to timely medical consultation.
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms
Breast cancer early detection significantly increases the chances of successful treatment and survival. Recognizing the warning signs and symptoms can prompt timely medical consultation and intervention.
Awareness of physical changes in breast tissue plays a crucial role in identifying potential breast cancer at an early stage.
- Lump or Thickening in the Breast - A new lump or area of thickened tissue in the breast, often painless, may indicate cancerous growth.
- Changes in Breast Size or Shape - Noticeable distortion or swelling in one breast can signal underlying breast cancer.
- Skin Changes - Dimpling, puckering, redness, or scaliness of the breast skin may be a symptom of breast cancer.
- Nipple Abnormalities - Inversion, redness, or unusual discharge from the nipple might be early warning signs.
- Pain in the Breast or Nipple - Persistent pain or discomfort without an obvious cause could indicate breast abnormalities including cancer.
Breast Cancer Risk Factors
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide. Understanding the risk factors can help in early detection and prevention.
- Age - The risk of breast cancer increases with age, especially after 50 years old.
- Genetics - Inherited mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes significantly raise breast cancer risk.
- Lifestyle - Factors such as obesity, alcohol consumption, and lack of physical activity contribute to higher risk.
Regular screenings and awareness of these risk factors can improve breast cancer outcomes.
Prevention and Healthy Lifestyle Tips
What are effective ways to prevent breast cancer through lifestyle changes? Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular physical activity reduce the risk of developing breast cancer. Limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding tobacco further support breast health.
How does diet impact breast cancer prevention? A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides antioxidants that protect breast tissue. Reducing intake of processed and high-fat foods contributes to lowering cancer risk.
Why is breast cancer screening important for prevention? Early detection through mammograms increases treatment success and survival rates. Women should consult healthcare providers about screening schedules based on age and family history.
What role does hormonal balance play in breast cancer risk? Minimizing prolonged exposure to estrogen by limiting hormone replacement therapy lowers the chance of cancer development. Breastfeeding also helps regulate hormones and offers protective benefits.
How can managing stress influence breast cancer prevention? Chronic stress affects immune function and hormone levels, potentially increasing cancer risk. Practicing relaxation techniques and ensuring sufficient sleep promote overall breast health.
Screening and Detection Methods
| Screening Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Mammography | Low-dose X-ray imaging to detect early signs of breast cancer, recommended annually for women aged 40 and above. |
| Breast MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging used for high-risk individuals or when mammography results are inconclusive, providing detailed breast tissue images. |
| Ultrasound | Sound wave imaging to differentiate between solid tumors and cysts, commonly used as a follow-up to abnormal mammograms. |
| Clinical Breast Exam (CBE) | Physical examination performed by healthcare providers to feel for lumps or abnormalities in breast tissue. |
| Breast Self-Exam (BSE) | Regular self-check by individuals to identify changes such as lumps, skin alterations, or nipple discharge. |
Stages of Breast Cancer Explained
Breast cancer is categorized into stages that describe its size and spread within the body. Understanding these stages helps guide treatment decisions and predict outcomes.
- Stage 0 - Non-invasive cancer confined to milk ducts without spreading.
- Stage I - Small tumor up to 2 cm with no lymph node involvement.
- Stage II - Tumor size between 2 and 5 cm or small tumor with limited lymph node spread.
- Stage III - Larger tumor or extensive lymph node involvement indicating locally advanced cancer.
- Stage IV - Cancer has metastasized to distant organs beyond the breast and nearby lymph nodes.
Treatment Options Overview
Breast cancer treatment options vary based on cancer type, stage, and patient health. Common approaches include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy. Personalized treatment plans aim to maximize effectiveness while minimizing side effects.
Myths vs. Facts: Breast Cancer Edition
Breast cancer is surrounded by many myths that can cause unnecessary fear and misunderstanding. Understanding the facts helps in early detection and effective treatment. This infographic highlights common misconceptions vs. the reality of breast cancer.
| Myths | Facts |
|---|---|
| Only women with a family history get breast cancer. | Most breast cancer cases occur in women without a family history. |
| A lump is the only sign of breast cancer. | Other signs include changes in breast shape, skin texture, or nipple discharge. |
| Breast cancer always causes pain. | Breast cancer can be painless, especially in early stages. |
| Men cannot get breast cancer. | Men can develop breast cancer, though it is rare. |
| Mammograms cause cancer to spread. | Mammograms use low-dose radiation and help detect cancer early. |
Supporting a Loved One with Breast Cancer
Supporting a loved one with breast cancer requires empathy and understanding. Emotional support can significantly impact their recovery journey.
Offer practical help like accompanying them to appointments or assisting with daily tasks. Being present and listening fosters a strong support system during treatment.
