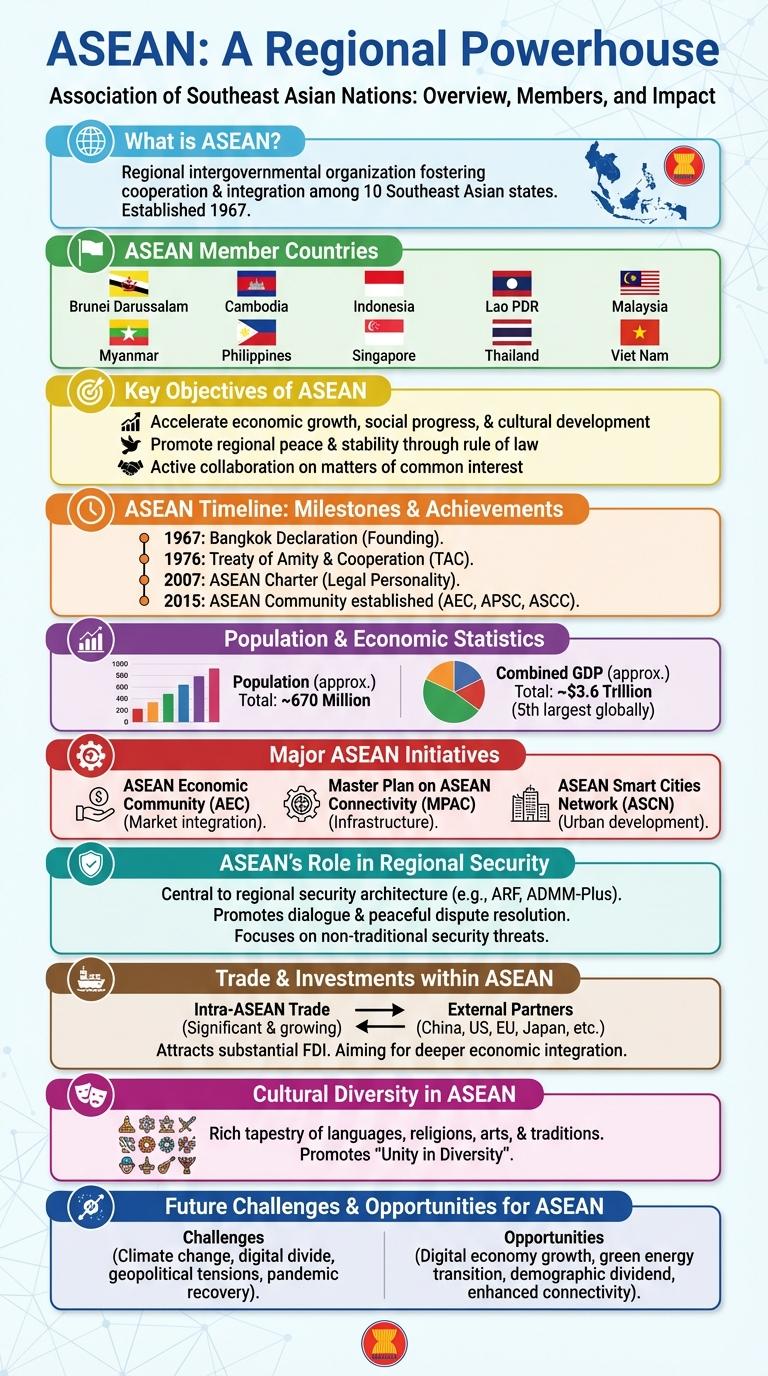
The infographic provides a detailed overview of ASEAN, highlighting its member countries, economic integration, and key initiatives. It illustrates the organization's role in fostering regional cooperation, trade, and cultural exchange among Southeast Asian nations. Visual data emphasizes ASEAN's impact on economic growth and geopolitical stability in the region.
What is ASEAN?
ASEAN, or the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, is a regional intergovernmental organization comprising ten Southeast Asian countries. It promotes political and economic cooperation and regional stability among its members.
- Formation - Established on August 8, 1967, by Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand.
- Member Countries - Includes Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- Objectives - Focuses on accelerating economic growth, social progress, cultural development, and maintaining peace in the region.
ASEAN serves as a platform for member states to collaborate on issues ranging from trade and security to environmental sustainability.
ASEAN Member Countries
| ASEAN Member Countries | Year Joined |
|---|---|
| Indonesia | 1967 |
| Malaysia | 1967 |
| Philippines | 1967 |
| Singapore | 1967 |
| Thailand | 1967 |
| Brunei Darussalam | 1984 |
| Vietnam | 1995 |
| Laos | 1997 |
| Myanmar | 1997 |
| Cambodia | 1999 |
Key Objectives of ASEAN
ASEAN, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, aims to promote regional peace, stability, and economic growth among its member countries. It focuses on enhancing cooperation in political, economic, and socio-cultural fields to create a resilient and integrated region.
Key objectives include accelerating economic development, encouraging regional trade and investment, and fostering sustainable development. ASEAN also strives to strengthen social progress, cultural development, and maintain regional security through collaborative efforts.
ASEAN Timeline: Milestones & Achievements
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) was established in 1967 to promote regional stability and economic growth among its member states. Key milestones include the adoption of the ASEAN Charter in 2007, which formalized its legal and organizational structure. ASEAN has achieved significant progress in regional integration, trade facilitation, and political cooperation, making it a vital player in the Asia-Pacific region.
Population & Economic Statistics
ASEAN, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, comprises 10 member countries with a combined population exceeding 670 million people, representing around 8.5% of the world's total population. The region boasts a dynamic economic landscape, ranking as the fifth-largest economy globally with a GDP surpassing $3.6 trillion in 2023.
Indonesia leads ASEAN in both population, with over 270 million residents, and GDP, contributing more than 40% to the bloc's economic output. The combined trade volume of ASEAN member states exceeded $4 trillion in 2023, making it a pivotal hub for global commerce and investment.
Major ASEAN Initiatives
What are the major initiatives driving ASEAN's regional integration? ASEAN promotes economic growth, social progress, and cultural development through strategic frameworks. Key initiatives focus on enhancing connectivity, environmental sustainability, and security cooperation.
| Initiative | Description |
|---|---|
| ASEAN Economic Community (AEC) | Creates a single market for goods, services, investment, and skilled labor within ASEAN countries. |
| Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity (MPAC) | Improves physical, institutional, and people-to-people connections across the region to boost trade and integration. |
| ASEAN Smart Cities Network (ASCN) | Encourages sustainable urban development and smart technology adoption in member cities. |
| ASEAN Political-Security Community (APSC) | Strengthens peace, stability, and cooperation in security among member nations. |
| ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community (ASCC) | Focuses on social welfare, environmental protection, and cultural development in the region. |
ASEAN's Role in Regional Security
ASEAN plays a pivotal role in maintaining regional security in Southeast Asia by promoting diplomatic dialogue and conflict resolution among member states. The organization facilitates cooperation on transnational threats such as terrorism, piracy, and human trafficking through joint initiatives and information sharing. ASEAN's regional security framework, including the ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF), enhances stability by encouraging collaboration between Southeast Asian countries and external powers.
Trade & Investments within ASEAN
ASEAN is a dynamic economic bloc driving significant trade and investment growth among member states. The region's integrated market fosters seamless cross-border commerce and capital flows.
- Intra-ASEAN Trade Volume - ASEAN accounts for nearly 25% of total trade flowing within its member countries, highlighting strong regional interconnectivity.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) - ASEAN attracted over $150 billion in FDI in recent years, with member states prioritizing infrastructure and manufacturing sectors.
- ASEAN Economic Community (AEC) Impact - The AEC framework has reduced trade barriers, increasing intra-regional investments and enhancing economic integration across 10 member states.
Cultural Diversity in ASEAN
ASEAN is home to a rich tapestry of cultural diversity, reflecting the unique traditions, languages, and religions of its member countries. This cultural variety fosters mutual respect and strengthens regional identity.
Understanding ASEAN's cultural diversity highlights the importance of preserving heritage while promoting unity and cooperation.
- Multilingual Population - Over 100 languages are spoken across ASEAN, with each country featuring its own official and regional languages.
- Religious Diversity - ASEAN hosts multiple major religions, including Buddhism, Islam, Christianity, Hinduism, and indigenous beliefs, shaping cultural practices.
- Traditional Arts and Festivals - Each member state celebrates unique festivals and traditional arts that showcase their historical and cultural heritage.
