Visual representations clarify complex data on gender, highlighting disparities and trends across demographics. Infographics distill information into easily digestible visuals that reveal patterns in workforce participation, education, and social dynamics. These graphics enhance understanding by presenting gender statistics clearly, fostering informed discussions and encouraging equality initiatives.
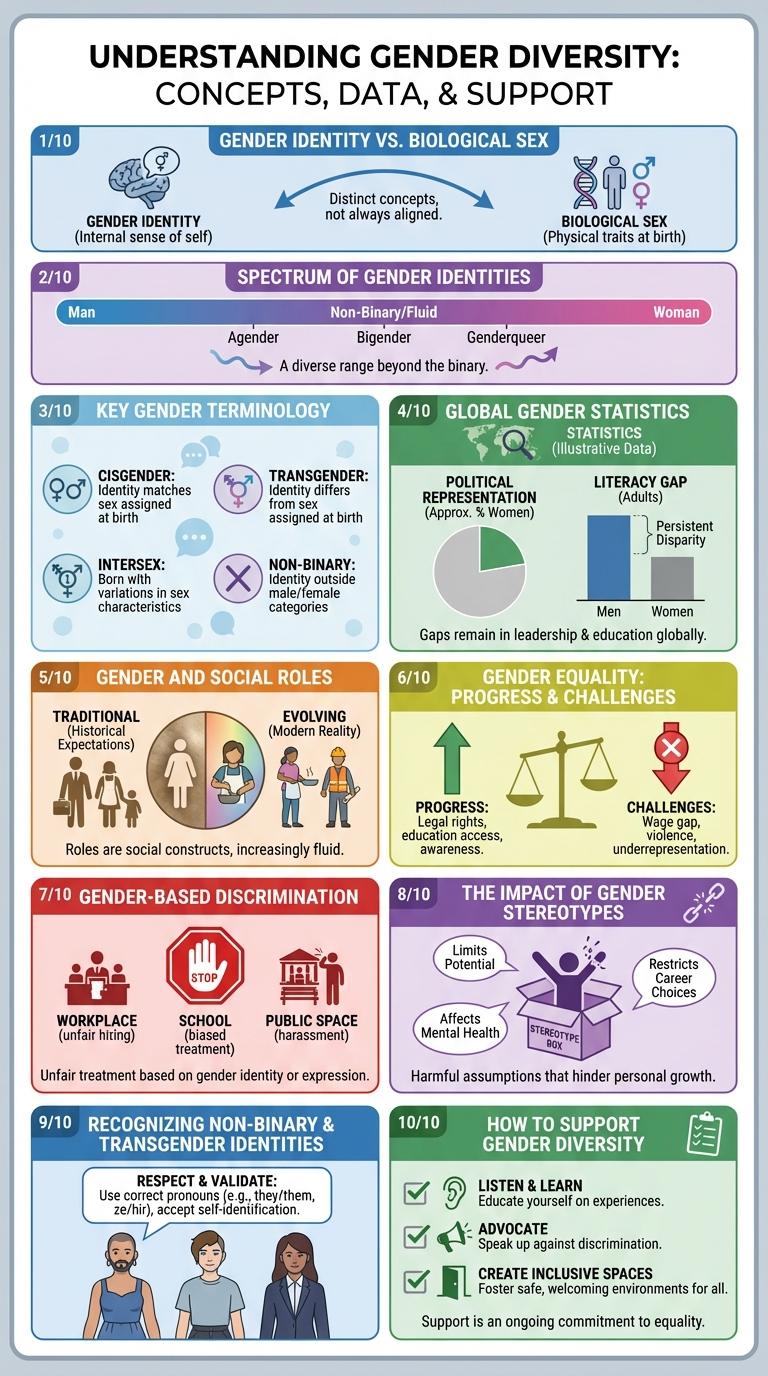
Gender Identity vs. Biological Sex
Gender Identity and Biological Sex represent distinct concepts influencing individual experiences and societal roles. Understanding their differences promotes respect and inclusivity for all people.
- Biological Sex - Refers to physical attributes including chromosomes, hormone levels, and reproductive anatomy typically categorized as male, female, or intersex.
- Gender Identity - Describes a person's deeply-felt internal sense of being male, female, a blend of both, neither, or another gender altogether.
- Non-Alignment - Biological sex does not always predict gender identity, as many individuals experience a disconnect between the two aspects.
- Social Recognition - Gender identity influences legal status, social roles, and personal relationships beyond biological characteristics.
- Respect and Inclusion - Recognizing the difference supports mental health and affirms diverse gender expressions and identities.
Spectrum of Gender Identities
The spectrum of gender identities includes a wide range of experiences beyond the traditional binary of male and female. People may identify as non-binary, genderqueer, genderfluid, agender, or other identities that reflect a personal understanding of gender. Recognizing this diversity promotes inclusivity and respect for individual expression.
Key Gender Terminology
Understanding key gender terminology is essential for fostering inclusivity and respect. These terms help clarify identities and experiences beyond traditional male and female categories.
Gender identity refers to a person's internal sense of their gender, which may differ from their assigned sex at birth. Gender expression involves the outward presentation of gender through clothing, behavior, and appearance.
Global Gender Statistics
Global gender statistics reveal significant disparities in education, employment, and political representation. Understanding these differences is key to promoting gender equality worldwide.
- Education Gap - Approximately 129 million girls worldwide are out of school, highlighting persistent educational inequalities.
- Labor Force Participation - Women's participation in the global labor force stands at 47%, compared to 74% for men, showing a substantial gender gap.
- Political Representation - Women hold 26% of parliamentary seats globally, indicating underrepresentation in political decision-making.
Gender and Social Roles
Gender plays a crucial role in shaping social expectations and responsibilities. Social roles often prescribe behaviors and duties based on perceived gender norms.
- Gender Socialization - Individuals learn gender roles through family, education, and media influences from an early age.
- Workplace Dynamics - Gender roles affect career choices and opportunities, often leading to occupational segregation.
- Household Responsibilities - Traditional gender roles frequently assign caregiving and domestic tasks predominantly to women.
Understanding gender and social roles is essential to promoting equality and challenging stereotypes.
Gender Equality: Progress and Challenges
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Global Gender Gap Index 2023 | 68.1% closed; indicates progress toward equality in health, education, economy, and politics |
| Women in Leadership | 28% of managerial positions worldwide held by women; gender disparity persists |
| Education Access | Gender parity achieved in primary education; gaps remain in secondary and tertiary levels |
| Economic Participation | Global female labor force participation rate at 47%, compared to 74% for men |
| Challenges | Gender-based violence, wage gap averaging 16%, underrepresentation in politics |
Gender-Based Discrimination
Gender-based discrimination refers to unfair treatment of individuals based on their gender identity or expression. It manifests in various settings including workplaces, education, and social interactions, limiting opportunities and perpetuating inequality. Addressing this issue requires awareness, legal protections, and inclusive policies to ensure equal rights for all genders.
The Impact of Gender Stereotypes
Gender stereotypes categorize individuals based on societal expectations related to their gender. These preconceived notions often limit personal freedom and professional opportunities.
The impact of gender stereotypes manifests in educational choices, workplace dynamics, and social interactions. Breaking these stereotypes promotes equality and fosters a more inclusive society.
Recognizing Non-Binary and Transgender Identities
Understanding gender diversity is essential in fostering inclusivity and respect. Recognizing non-binary and transgender identities highlights the spectrum of gender beyond traditional categories.
Non-binary individuals do not exclusively identify as male or female, embracing a range of gender expressions. Transgender people have a gender identity different from the sex assigned at birth, often seeking recognition and support. Respecting pronouns and using inclusive language creates a supportive environment for all gender identities.
