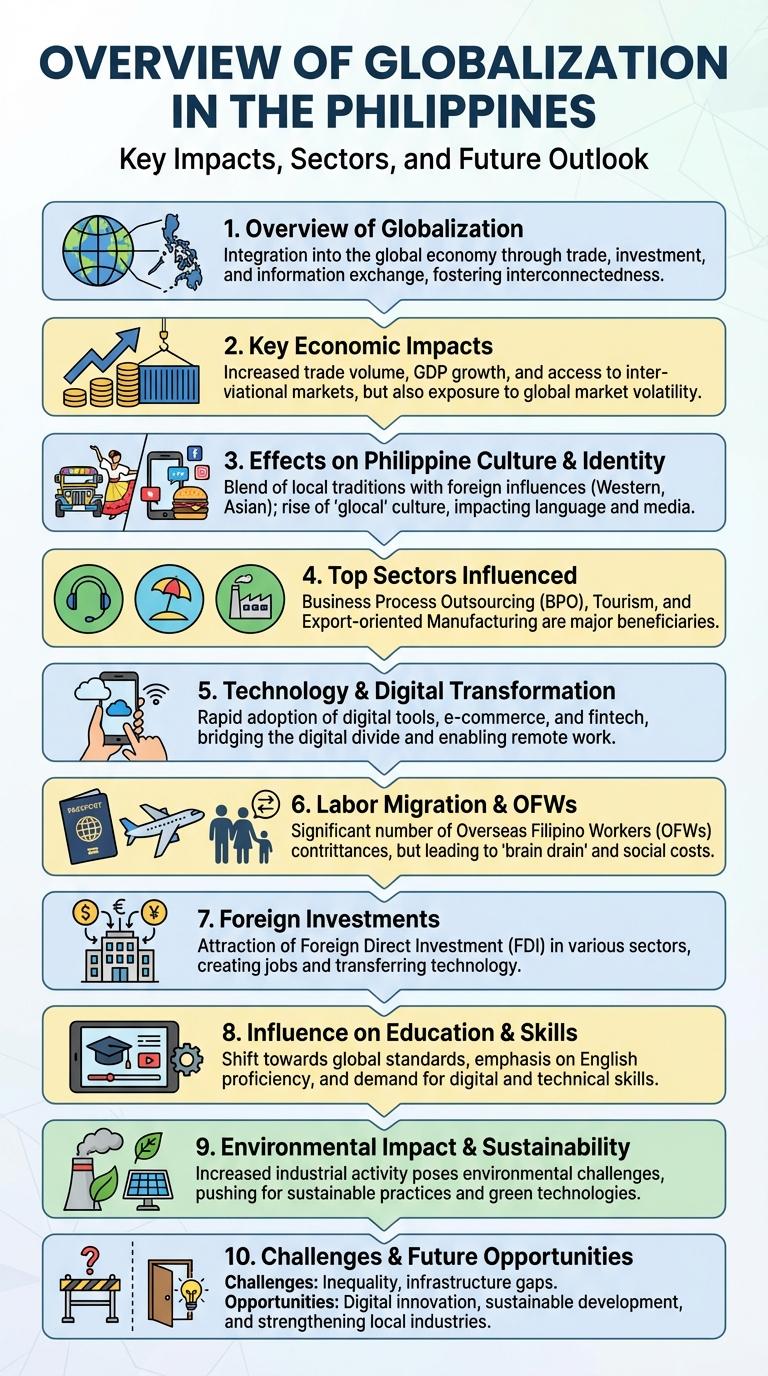
Globalization in the Philippines has significantly reshaped the nation's economy, culture, and social dynamics, fostering increased connectivity with the global market. The infographic highlights key trends such as foreign investment growth, the rise of the overseas Filipino workforce, and the expansion of digital technology access. Understanding these elements provides insights into how globalization influences development and everyday life in the Philippines.
Overview of Globalization in the Philippines
Globalization in the Philippines represents the increasing integration of the country into the global economy through trade, technology, and culture. The nation experiences growth and challenges as it connects with international markets and influence.
- Economic Growth - The Philippines benefits from foreign investment and export-driven industries that boost GDP.
- Labor Migration - Millions of Overseas Filipino Workers (OFWs) contribute significantly to remittances and global workforce mobility.
- Cultural Exchange - Global media and communication technologies foster cultural diversity and awareness.
The ongoing process of globalization shapes the Philippines' economic development and social dynamics in a globally connected world.
Key Economic Impacts of Globalization
Globalization has significantly transformed the Philippine economy by integrating it into the global market. This integration has boosted trade, foreign direct investment, and remittances from overseas Filipino workers (OFWs).
The rise in export-oriented industries like electronics and business process outsourcing (BPO) has created millions of jobs. However, economic disparities and dependency on global markets remain challenges for sustainable growth.
Effects on Philippine Culture and Identity
Globalization has significantly influenced Philippine culture and identity, blending traditional values with modern global trends. This dynamic interaction fosters both cultural preservation and transformation within Filipino society.
The influx of international media, technology, and consumer goods introduces new lifestyles and perspectives to Filipinos. While some traditional practices face challenges, many Filipino communities adapt by integrating these influences into their cultural expressions. This evolving cultural landscape highlights resilience and openness in maintaining a unique Filipino identity amid global changes.
Top Sectors Influenced by Globalization
Globalization has significantly impacted the Philippines, driving growth in key sectors such as information technology, manufacturing, and agriculture. The IT-BPO industry has flourished due to global demand for outsourcing services. Manufacturing benefits from international trade, while agriculture integrates into global markets through exports of products like coconut and bananas.
| Sector | Globalization Impact |
|---|---|
| Information Technology (IT-BPO) | Rapid growth fueled by outsourcing and global service contracts |
| Manufacturing | Expansion driven by foreign investment and export opportunities |
| Agriculture | Increased exports of tropical products like coconuts and bananas |
| Remittances | Significant contribution from overseas Filipino workers worldwide |
| Tourism | Growth supported by global travel and cultural exchange |
Technology and Digital Transformation
Globalization has significantly accelerated technology adoption and digital transformation in the Philippines, driving economic growth and innovation. The rise of internet penetration and mobile connectivity empowers businesses and individuals to access global markets and digital services seamlessly. Government initiatives and private sector investments continue to enhance digital infrastructure, fostering an inclusive digital economy and enabling smarter, more efficient public services.
Labor Migration and OFWs
Globalization has significantly influenced labor migration in the Philippines, leading to a large population of Overseas Filipino Workers (OFWs). These workers contribute to the country's economy through remittances and skills transfer.
The growth of OFWs highlights the Philippines' role in the global labor market and the social challenges faced by migrant workers.
- Remittances - OFWs sent over $38 billion in remittances in 2023, supporting millions of Filipino families and boosting national GDP.
- Labor Export Policy - The government actively promotes labor migration as a development strategy, regulating overseas employment to protect Filipino workers.
- Social Impact - Prolonged separation from families creates emotional and social challenges for OFWs and their relatives back home.
Foreign Investments in the Philippines
The Philippines has experienced significant growth in foreign investments, driving economic development and job creation. Globalization has enabled increased capital inflows from diverse international markets, enhancing the country's competitiveness.
Foreign investments focus on key sectors such as manufacturing, technology, and business process outsourcing (BPO), vital for sustainable growth.
- Growth in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) - The Philippines recorded a 14% increase in FDI inflows in 2023, reaching $11.7 billion, highlighting investor confidence.
- Top Investor Countries - Japan, the United States, and Singapore are the leading sources of foreign investments, accounting for over 60% of total FDI in the country.
- Sector Distribution - Manufacturing (40%), Real Estate (25%), and Services including BPO (20%) dominate foreign investment allocation.
Influence on Education and Skills Development
| Aspect | Impact on Education and Skills Development in the Philippines |
|---|---|
| Curriculum Modernization | Integration of global standards and digital literacy enhances competitiveness of Filipino students in international markets. |
| Language Proficiency | Increased emphasis on English and other foreign languages improves communication skills essential for global employment opportunities. |
| Access to Technology | Expansion of technology use in classrooms promotes innovative learning methods and fosters STEM education. |
| International Collaboration | Partnerships with foreign institutions enable student exchanges, scholarships, and exposure to diverse academic practices. |
| Skills Alignment | Skills training programs align with global labor market demands, enhancing employability in sectors like IT, healthcare, and business process outsourcing. |
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Globalization in the Philippines has significantly influenced environmental policies, driving both challenges and opportunities in sustainability. Rapid industrialization and urbanization have led to increased pollution and natural resource depletion.
Efforts to balance economic growth with environmental protection include adopting renewable energy and sustainable farming practices. These initiatives aim to reduce carbon footprints while promoting long-term ecological health.
