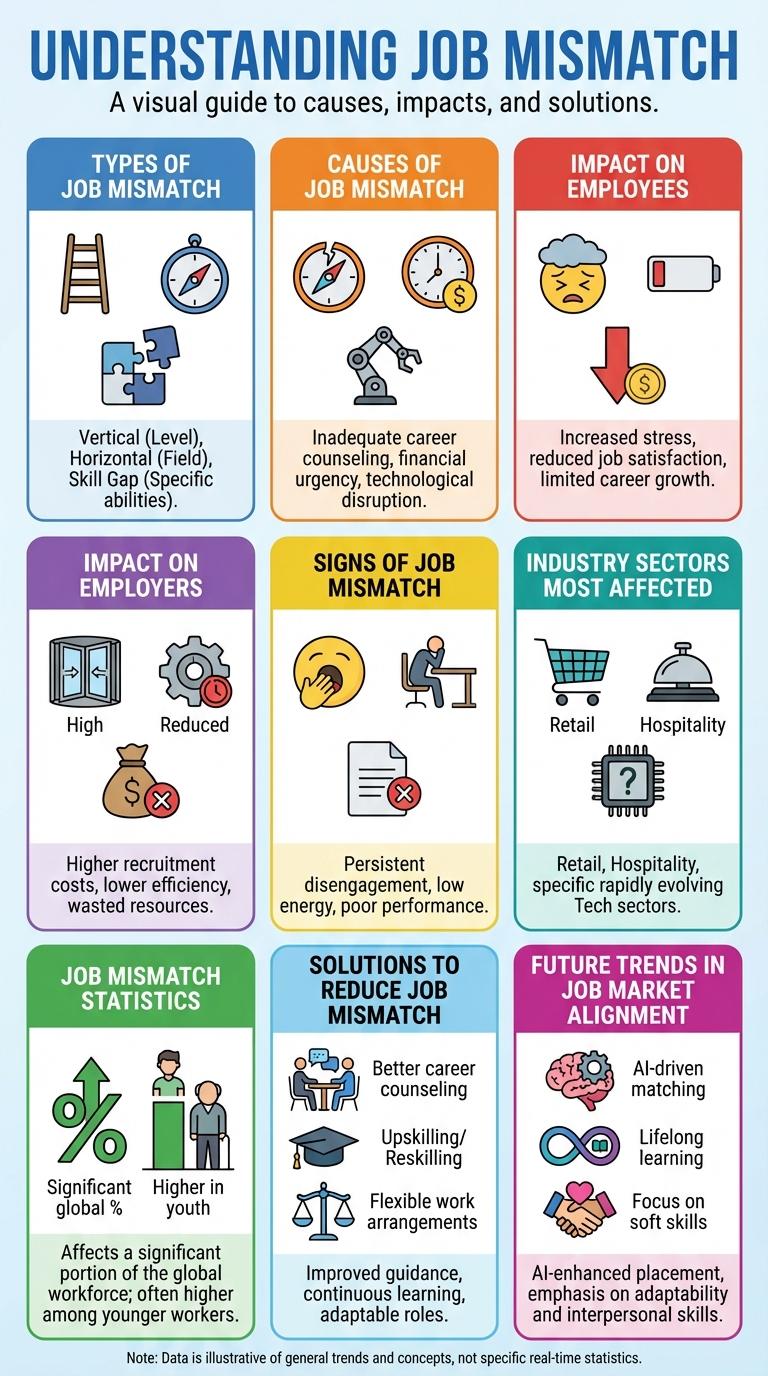
Job mismatch occurs when employees' skills, qualifications, or experiences do not align with their current roles, leading to decreased productivity and job dissatisfaction. Understanding the extent and causes of job mismatch can help organizations optimize workforce planning and improve employee engagement. Visualizing this data through an infographic highlights key trends and solutions for addressing skill gaps in the labor market.
Understanding Job Mismatch
Job mismatch occurs when there is a discrepancy between a worker's skills and the requirements of their job. This phenomenon affects productivity and can lead to employee dissatisfaction.
Understanding job mismatch involves analyzing the gaps between education, experience, and job demands. It includes both skill underutilization, where employees are overqualified, and skill gaps, where employees lack necessary competencies. Addressing job mismatch helps improve workforce efficiency and supports economic growth.
Types of Job Mismatch
Job mismatch occurs when employees' skills, education, or experiences do not align with the requirements of their jobs. Common types include skill mismatch, where workers lack necessary skills; overqualification, where employees have higher education or skills than required; and field mismatch, where workers are employed in sectors unrelated to their training. Understanding these mismatches helps organizations improve productivity and job satisfaction.
Causes of Job Mismatch
Job mismatch occurs when workers' skills do not align with the requirements of available jobs. This discrepancy affects productivity, career growth, and overall economic efficiency.
- Educational Gaps - Many workers lack the specific skills or qualifications demanded by current job markets.
- Rapid Technological Change - Emerging technologies outpace workers' ability to adapt and acquire new skills quickly.
- Labor Market Information Deficit - Insufficient access to accurate job market data leads to poor career choices and misaligned job placements.
Impact on Employees
Job mismatch occurs when employees' skills do not align with their job requirements, leading to various challenges. Its impact on employees affects job satisfaction, career growth, and overall well-being.
- Reduced Job Satisfaction - Employees in mismatched roles often experience frustration and disengagement, lowering their motivation and happiness at work.
- Stalled Career Development - Lack of skill alignment limits opportunities for professional growth and advancement within the organization.
- Increased Stress Levels - Performing tasks beyond or below employees' competencies can lead to workplace stress, affecting mental health and productivity.
Impact on Employers
Job mismatch significantly affects employer productivity by placing employees in roles that do not fully utilize their skills. This misalignment leads to increased training costs and lower overall performance.
Employers face higher turnover rates when job roles do not match employee capabilities, creating instability within the workforce. Addressing job mismatch helps reduce hiring expenses and fosters a more engaged, efficient team.
Signs of Job Mismatch
Job mismatch occurs when an employee's skills and job requirements are not aligned. Recognizing the signs helps improve job satisfaction and productivity.
- Underutilized Skills - Employees have skills that are not used in their current roles, leading to frustration and disengagement.
- Low Job Satisfaction - A mismatch often results in decreased motivation and overall dissatisfaction with the position.
- High Turnover Rates - Organizations experience frequent employee departures due to poor job fit and unmet expectations.
- Poor Performance - Employees struggle to meet job demands when their abilities do not match the required tasks.
- Lack of Career Growth - Limited opportunities for advancement can signal a misalignment between employee goals and job roles.
Identifying these signs early can enable corrective actions to align skills, improve job fit, and boost workforce effectiveness.
Industry Sectors Most Affected
| Industry Sector | Percentage of Job Mismatch |
|---|---|
| Information Technology | 28% |
| Healthcare | 22% |
| Manufacturing | 19% |
| Finance and Banking | 15% |
| Retail | 12% |
Job Mismatch Statistics
Job mismatch occurs when workers' skills do not align with the requirements of their current roles, affecting productivity and earnings. Studies show that approximately 25% of employees worldwide experience some form of job mismatch. The highest rates appear in sectors undergoing rapid technological change, highlighting the need for continuous skill development.
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Global job mismatch rate | 25% |
| Mismatch in tech-related jobs | 30% |
| Affected workforce segment | Younger professionals (age 20-35) |
| Impact on productivity | Up to 15% loss |
| Annual income reduction | 10-20% |
Solutions to Reduce Job Mismatch
How can job mismatch be effectively reduced in the workforce? Improving career guidance programs and enhancing skill development aligned with market demands are essential strategies. Employers and educational institutions must collaborate to bridge gaps between qualifications and job requirements.
| Solution | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Career Counseling | Providing accurate labor market information helps students and job seekers make informed career choices. |
| Skills Training Programs | Targeted training ensures workforce skills meet current and future industry needs. |
| Industry-Education Collaboration | Partnerships align curriculum with practical job requirements, reducing skill gaps. |
| Internship and Apprenticeships | Hands-on experience helps workers gain relevant skills and improves job placements. |
| Labor Market Data Analytics | Real-time data guides policy makers and educators to adjust to employment trends. |
