Loneliness affects millions worldwide, impacting mental and physical health significantly. Visualizing data on loneliness reveals patterns related to age, social connections, and geographic regions. Understanding these trends through an infographic helps raise awareness and promotes strategies to foster community and support networks.
Understanding Loneliness: Key Facts
| Key Fact | Details |
|---|---|
| Prevalence | Over 60% of adults report feeling lonely at some point in their lives. |
| Age Groups Affected | Young adults (18-29) and seniors (65+) experience the highest levels of loneliness. |
| Health Impact | Chronic loneliness increases risks of heart disease, depression, and cognitive decline. |
| Social Isolation | Social isolation is a major contributor to feelings of loneliness, especially after life changes. |
| Emotional Effects | Loneliness can lead to decreased self-esteem, anxiety, and poor sleep quality. |
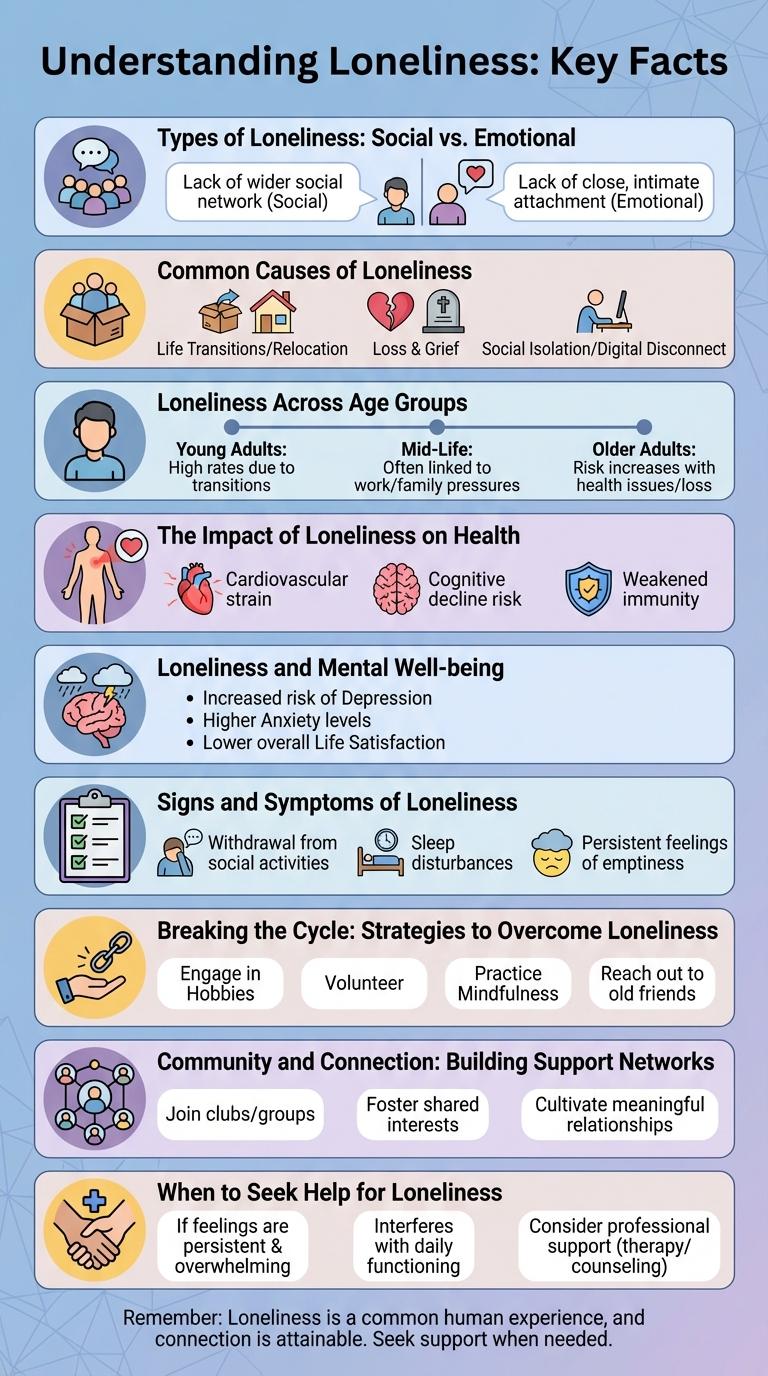
Types of Loneliness: Social vs. Emotional
Loneliness can be categorized into two main types: social loneliness and emotional loneliness. Social loneliness arises from the absence of a wider social network or community connections. Emotional loneliness stems from the lack of a close, intimate relationship or deep emotional bond with another person.
Common Causes of Loneliness
Loneliness affects millions worldwide and can emerge from various causes. Understanding these causes is crucial for addressing this emotional state effectively.
Common causes of loneliness include social isolation, where individuals lack regular social interactions. Life changes such as moving to a new city or losing a loved one can contribute significantly. Mental health issues like depression also play a key role in intensifying feelings of loneliness.
Loneliness Across Age Groups
Loneliness affects individuals of all ages but varies in intensity and causes across different age groups. Understanding these patterns helps develop targeted support strategies.
- Young Adults Experience High Loneliness - Studies show 18-29 year-olds report the highest levels of loneliness due to social transitions and digital interactions.
- Middle-Aged Adults Face Social Isolation - Adults aged 45-65 often experience loneliness linked to work stress and family responsibilities.
- Older Adults Have Increased Loneliness Risks - People over 65 encounter loneliness from loss of loved ones and reduced social engagement.
Addressing loneliness requires age-specific approaches to improve mental health and social connection.
The Impact of Loneliness on Health
Loneliness significantly affects both mental and physical health across all age groups. Understanding its impact is crucial to promoting overall well-being and preventing related health issues.
Research shows that loneliness can increase the risk of chronic diseases and mental health disorders.
- Increased Risk of Heart Disease - Chronic loneliness is linked to higher rates of cardiovascular problems and hypertension.
- Weakened Immune System - Loneliness reduces the body's ability to fight infections and recover from illness.
- Elevated Symptoms of Depression and Anxiety - Prolonged loneliness intensifies feelings of depression and anxiety, affecting mental health.
Loneliness and Mental Well-being
Loneliness significantly impacts mental well-being, leading to increased risks of depression and anxiety. Understanding these effects helps in developing strategies to improve emotional health.
Chronic loneliness triggers stress responses in the brain, affecting overall mood and cognitive function.
- Increased Risk of Depression - Persistent loneliness is linked to higher rates of depressive symptoms and mood disorders.
- Heightened Anxiety Levels - Social isolation intensifies feelings of anxiety and stress in affected individuals.
- Cognitive Decline - Loneliness can impair memory and executive functions, contributing to mental health deterioration.
Signs and Symptoms of Loneliness
Loneliness manifests through emotional and physical signs that impact overall well-being. Common symptoms include persistent sadness, social withdrawal, and feelings of emptiness. Recognizing these signs early can promote timely support and improve mental health outcomes.
Breaking the Cycle: Strategies to Overcome Loneliness
Loneliness affects millions worldwide, impacting mental and physical health significantly. Breaking the cycle requires intentional strategies to foster connection and well-being.
Engaging in community activities, pursuing hobbies, and seeking social support are proven methods to reduce feelings of isolation. Professional counseling and mindfulness practices also play crucial roles in overcoming loneliness.
Community and Connection: Building Support Networks
Loneliness affects mental and physical health, increasing risks of depression, anxiety, and cardiovascular issues. Building strong community connections offers vital support and combats social isolation.
Support networks foster a sense of belonging, enabling individuals to share experiences and find emotional comfort. Engaging in local groups, volunteer activities, and social events strengthens these essential bonds.
