Nonverbal cues play a crucial role in communication by conveying emotions and intentions without words. Understanding body language, facial expressions, and gestures enhances interpersonal connections and helps interpret unspoken messages accurately. This infographic highlights the key types of nonverbal communication and their significance in everyday interactions.
Understanding Non-Verbal Communication
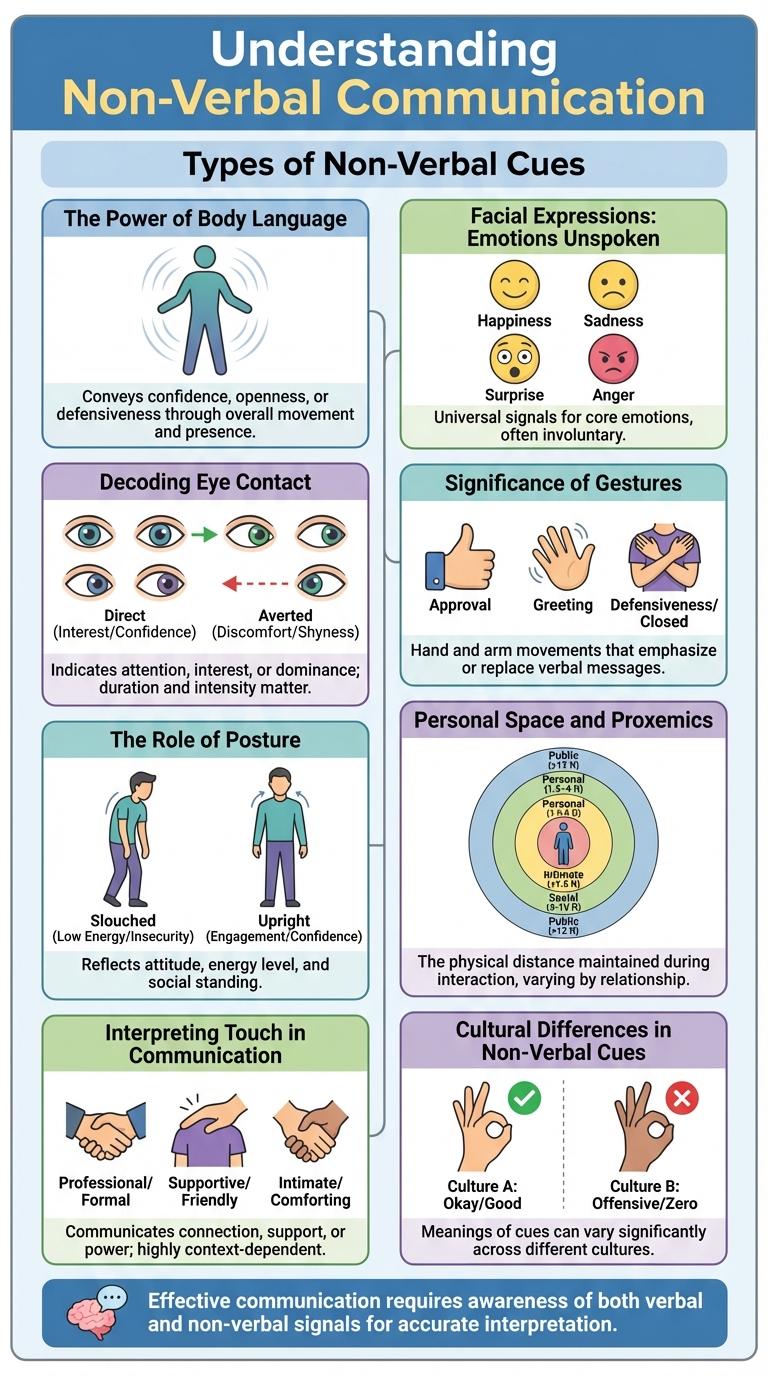
Non-verbal communication is a key element in understanding human interactions, involving facial expressions, gestures, posture, and eye contact. These cues reveal emotions and intentions beyond spoken words.
Recognizing non-verbal signals enhances effective communication in personal and professional settings. Awareness of body language helps interpret messages accurately and build stronger connections.
Types of Non-Verbal Cues
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Facial Expressions | Convey emotions such as happiness, anger, surprise, and sadness through movements of facial muscles. |
| Gestures | Hand and arm movements used to express ideas or feelings, including waving, pointing, and signaling. |
| Posture | Body stance or positioning that indicates confidence, openness, or defensiveness. |
| Eye Contact | Direct or indirect visual connection that communicates attention, interest, or dominance. |
| Proxemics | Use of personal space and physical distance to regulate interaction and convey intimacy or authority. |
The Power of Body Language
Body language conveys over 55% of communication, making it a crucial aspect of understanding others. Gestures, facial expressions, and posture reveal emotions and intentions beyond spoken words. Mastering non-verbal cues enhances personal and professional interactions by building trust and clarity.
Facial Expressions: Emotions Unspoken
Facial expressions communicate emotions without the use of words. They serve as a universal language understood across cultures and societies.
- Happiness - Smiling signals joy and positive feelings, often encouraging social bonding.
- Fear - Wide eyes and raised eyebrows reveal alertness and anticipation of potential threats.
- Anger - Furrowed brows and tight lips express displeasure and readiness to confront.
- Surprise - Open mouth and raised eyebrows indicate sudden awareness of unexpected events.
- Sadness - Downturned mouth and lowered eyes reflect emotional pain and withdrawal.
Understanding facial expressions enhances effective communication and emotional intelligence.
Decoding Eye Contact
Eye contact is a powerful non-verbal cue that reveals a person's attention and emotions. Understanding eye contact helps decode unspoken messages in communication.
Direct eye contact often signals confidence, interest, or honesty. Avoiding eye contact can indicate discomfort, nervousness, or deception. The duration and intensity of eye contact vary across cultures and social contexts.
Significance of Gestures
Non-verbal cues, especially gestures, play a crucial role in communication by conveying emotions and intentions without words. Gestures support verbal messages and enhance understanding in interpersonal interactions.
- Universal meaning - Some gestures, like a thumbs-up, have widespread recognition and clear interpretations across cultures.
- Emotional expression - Hand and body movements effectively communicate feelings such as anger, happiness, or confusion.
- Complement verbal communication - Gestures emphasize or clarify spoken words, improving message retention and engagement.
- Cultural variations - Interpretations of gestures differ, requiring cultural awareness to avoid misunderstandings.
- Regulate interaction - Gestures manage conversational flow, signaling when to speak or listen.
The Role of Posture
Non-verbal cues play a crucial role in communication, with posture being a key indicator of attitudes and emotions. Understanding posture helps decode unspoken messages in social and professional interactions.
- Confidence - Upright posture signals self-assurance and authority.
- Openness - Relaxed and open body positions indicate receptiveness and approachability.
- Discomfort - Closed or slouched postures often reveal anxiety or lack of confidence.
Personal Space and Proxemics
How does personal space influence communication? Personal space refers to the physical distance maintained between individuals during interactions. Proxemics studies these spatial relationships and their impact on social behavior.
Interpreting Touch in Communication
Touch is a powerful form of non-verbal communication that conveys emotions such as comfort, support, or authority. Different types of touch communicate distinct messages depending on context, culture, and relationship between individuals.
Interpreting touch requires awareness of factors like the duration, pressure, and location of contact on the body. Misunderstanding these cues can lead to confusion or offense in interpersonal interactions.
