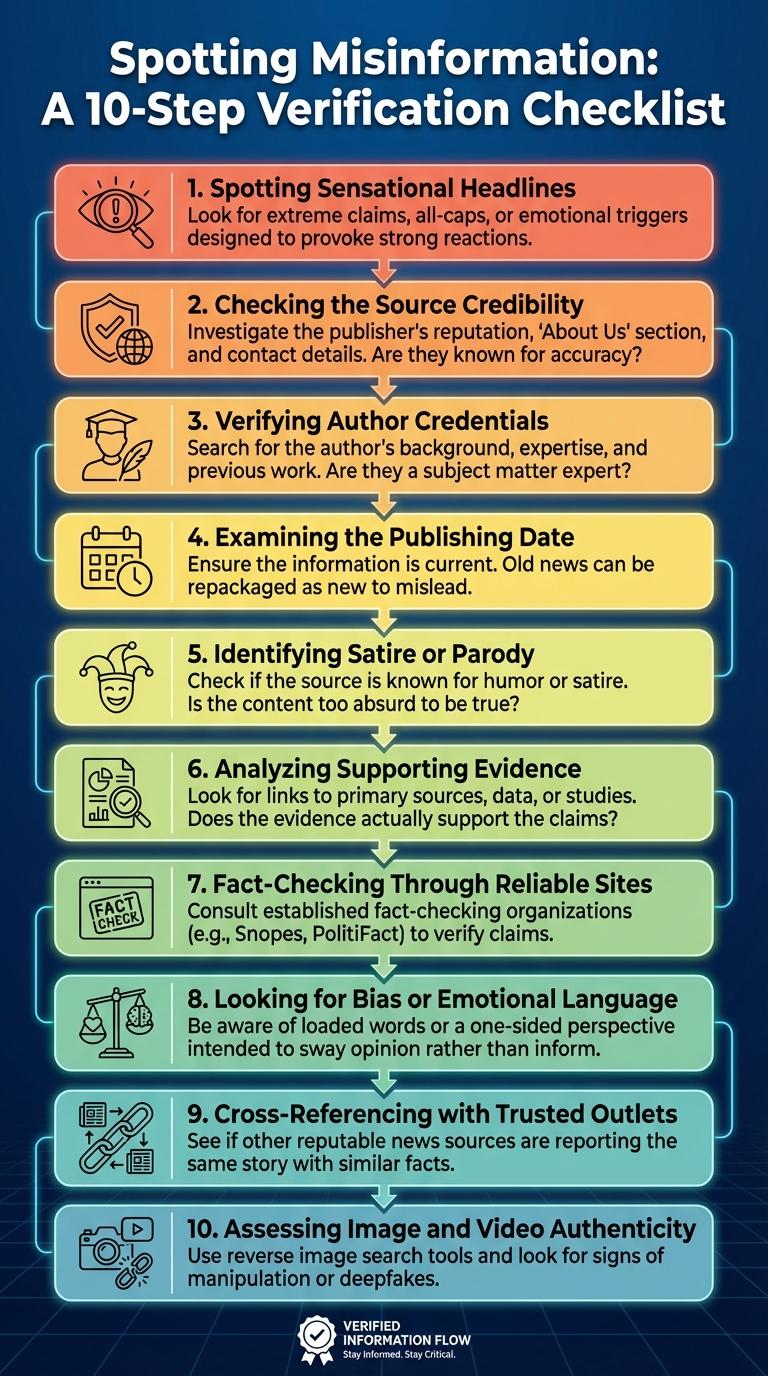
Identifying fake news requires keen observation of source credibility, verification of facts, and awareness of emotional language designed to mislead. Examining the author's credentials and cross-referencing information with trusted outlets help distinguish authentic reports from fabricated stories. Recognizing common signs like sensational headlines, lack of evidence, and biased content is crucial for critical media consumption.
Spotting Sensational Headlines
Sensational headlines often use exaggerated language to grab attention and provoke strong emotions. They may promise shocking revelations or urgent news without providing solid evidence.
Carefully analyze the headline for extreme or dramatic words that seem designed to incite fear or excitement. Verify the information by checking credible sources before trusting the claim. Headlines that seem too good or bad to be true usually require deeper investigation.
Checking the Source Credibility
How can you check the credibility of a news source? Verify the publisher's reputation by researching their history and expertise in the subject matter. Look for official websites or trusted media outlets with transparent editorial standards.
Verifying Author Credentials
| Step | How to Verify Author Credentials |
|---|---|
| Check Author Name | Search the author's full name online to find professional profiles, articles, or official pages linked to credible organizations. |
| Review Professional Background | Look for education, work experience, or affiliations with recognized institutions on LinkedIn or author biographies. |
| Assess Previous Publications | Identify if the author has published work in reputable journals, websites, or news outlets related to the topic. |
| Verify Social Media Presence | Confirm the author's official social media accounts for consistent professional activity and verified badges. |
| Check for Conflicts of Interest | Investigate whether the author has any biases or financial ties that could influence the reliability of the information. |
Examining the Publishing Date
Identifying fake news involves scrutinizing the publishing date to detect outdated or manipulated information. Fake news often exploits old events presented as current to mislead readers.
- Check for Recent Dates - Verify if the article's date aligns with the reported event's timeline for accuracy.
- Look for Date Inconsistencies - Multiple articles on the same topic with different dates may indicate misinformation.
- Beware of Republished Content - Old stories reposted without updates can spread false impressions of relevance.
Identifying Satire or Parody
Identifying satire or parody involves recognizing content that uses humor or exaggeration to critique or entertain rather than inform. Such articles often mimic real news but include absurd or exaggerated details that signal they are not factual.
Check the source website for disclaimers or clues indicating satirical intent. Headlines that seem outrageous or too bizarre to be true often point to parody rather than genuine news.
Analyzing Supporting Evidence
Analyzing supporting evidence is crucial in identifying fake news. Check if the claims are backed by credible sources or verifiable data.
Look for citations from reputable organizations, expert opinions, or original research. Absence of evidence or vague references often indicates unreliable information.
Fact-Checking Through Reliable Sites
Fact-checking through reliable sites is essential to identify fake news accurately. Using trusted sources helps verify claims and avoid misinformation.
- Use Established Fact-Checking Websites - Platforms like Snopes, FactCheck.org, and PolitiFact specialize in verifying news and debunking false claims.
- Cross-Reference Multiple Sources - Comparing information from various reputable sites ensures a balanced and accurate understanding.
- Check the Date and Context - Reliable sites provide timestamps and context to prevent outdated or misleading information from spreading.
Relying on credible fact-checking resources improves your ability to distinguish real news from fake stories.
Looking for Bias or Emotional Language
Identifying fake news requires careful attention to bias and emotional language. These elements often reveal the intent behind misleading content.
- Check for Emotional Triggers - Headlines or texts that use strong emotions like fear or anger can indicate manipulation.
- Detect One-Sided Reporting - Articles presenting only one viewpoint may lack objectivity and suggest bias.
- Analyze Word Choice - Loaded or subjective words often aim to influence your opinion rather than inform.
Cross-Referencing with Trusted Outlets
Cross-referencing with trusted outlets helps verify the accuracy of news by comparing information across reliable sources known for their journalistic integrity. Trusted outlets typically have established fact-checking processes and editorial standards that reduce the risk of misinformation. Confirming a story's presence in multiple reputable publications increases confidence in its authenticity and reduces the likelihood of encountering fake news.
