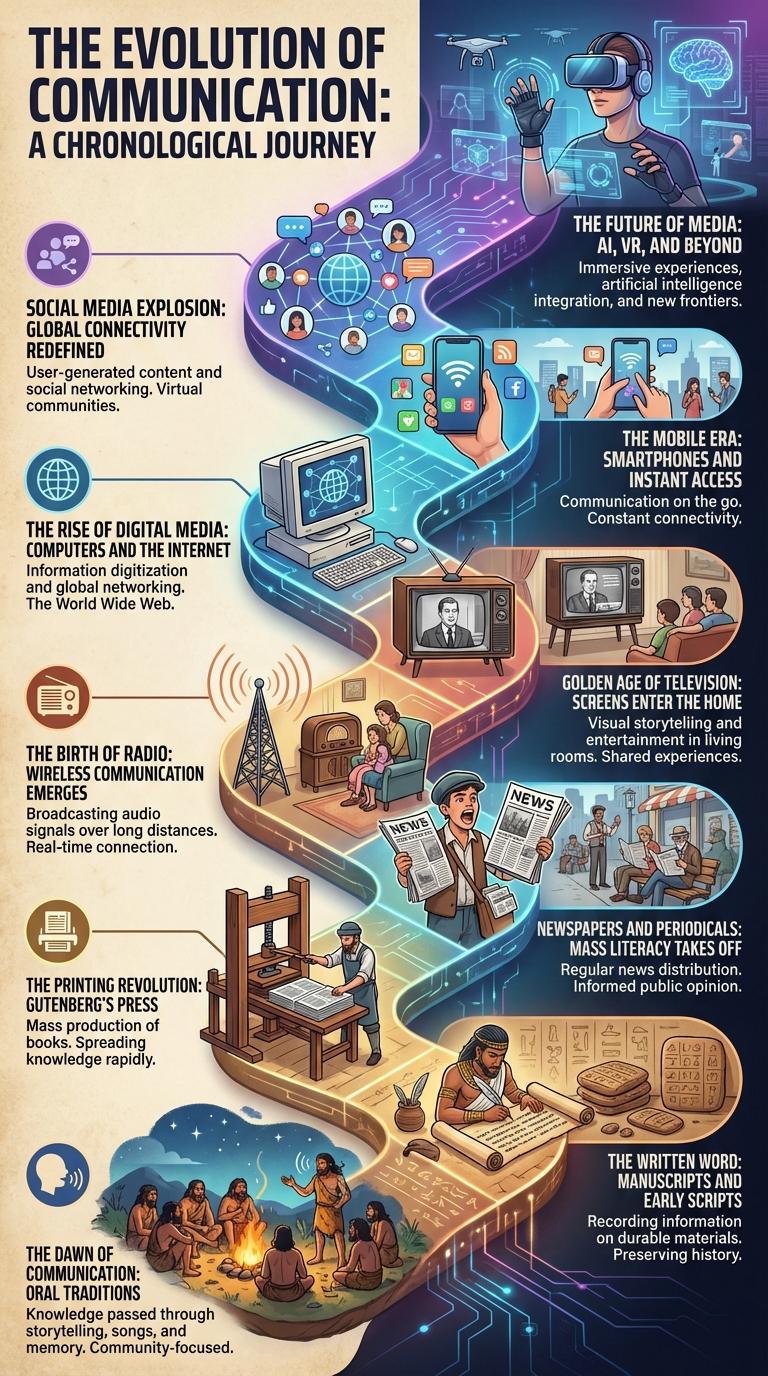
The evolution of media showcases a dynamic transformation from traditional print and broadcast formats to digital platforms and social media networks. This infographic highlights key milestones, technological advancements, and shifting consumption patterns that have redefined how information is created, shared, and accessed. Understanding this progression reveals the impact of media on communication, culture, and society over time.
The Dawn of Communication: Oral Traditions
The dawn of communication marks the beginning of human interaction through oral traditions. Early societies relied on spoken language to convey stories, knowledge, and cultural values across generations.
Oral traditions formed the foundation of communication long before written language emerged. Storytelling, songs, and chants preserved history and teachings within tribes and communities. These methods ensured the transmission of important information in the absence of physical media.
The Written Word: Manuscripts and Early Scripts
The evolution of media began with the written word, where manuscripts and early scripts served as the primary means of communication. These hand-crafted documents preserved knowledge, culture, and history for centuries before the invention of the printing press.
Manuscripts were typically written on materials like papyrus, parchment, and vellum, often produced by scribes in monasteries. Early scripts, such as cuneiform and hieroglyphics, represent some of the first attempts to capture language visually.
The Printing Revolution: Gutenberg's Press
The Printing Revolution began in the mid-15th century with Johannes Gutenberg's invention of the movable-type printing press. This breakthrough drastically reduced the cost and time required to produce books and written materials.
Gutenberg's press enabled the rapid spread of knowledge, contributing to increased literacy and the rise of the Renaissance and Reformation movements. This invention laid the foundation for mass communication and the evolution of modern media.
Newspapers and Periodicals: Mass Literacy Takes Off
The evolution of media witnessed a significant milestone with the rise of newspapers and periodicals, catalyzing the spread of mass literacy. Advances in printing technology and increased access to education in the 18th and 19th centuries made newspapers widely available to the growing public. This development transformed information dissemination, empowering societies with timely news and diverse viewpoints.
The Birth of Radio: Wireless Communication Emerges
The birth of radio marked the emergence of wireless communication, revolutionizing how information was transmitted across distances. Early 20th-century inventors like Guglielmo Marconi developed the first practical radio systems, enabling real-time audio broadcasts. This innovation laid the foundation for modern mass media, transforming news, entertainment, and emergency communications globally.
Golden Age of Television: Screens Enter the Home
When did the Golden Age of Television begin and what defined this era? The Golden Age of Television emerged in the late 1940s to early 1960s, marking the period when television screens became central to the home entertainment experience. This era introduced iconic shows, live broadcasts, and rapid advancements in TV technology that transformed media consumption.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Time Frame | Late 1940s to Early 1960s |
| Key Innovations | Live Broadcasting, Black-and-White to Color TV |
| Popular Shows | I Love Lucy, The Twilight Zone, The Ed Sullivan Show |
| Impact on Society | TV became a primary source for news, entertainment, and cultural influence |
| Technology | Adoption of cathode ray tube (CRT) TVs in households |
The Rise of Digital Media: Computers and the Internet
| Era | Key Developments |
|---|---|
| Pre-Digital Age | Print, Radio, Television dominate mass communication |
| 1970s - Early Computing | Introduction of personal computers; limited networking capabilities |
| 1990s - Internet Emergence | Expansion of World Wide Web; first websites and email services |
| 2000s - Broadband & Social Media | High-speed internet adoption; rise of platforms like Facebook, YouTube |
| 2010s - Mobile & Streaming Media | Smartphones popularize mobile access; streaming services transform content delivery |
The Mobile Era: Smartphones and Instant Access
The Mobile Era revolutionized media consumption through the widespread adoption of smartphones, enabling instant access to information and entertainment. This shift transformed how audiences interact with content, prioritizing convenience and mobility.
- Smartphone Penetration - Over 85% of adults globally own a smartphone, making mobile devices the primary medium for accessing digital content.
- Instant Access - Mobile internet technologies allow users to stream videos, read news, and engage on social platforms anytime, anywhere.
- App Ecosystem - Millions of mobile applications drive personalized media experiences, tailored to user preferences and real-time interactions.
Social Media Explosion: Global Connectivity Redefined
The evolution of media has been significantly shaped by the explosion of social media platforms, which transformed global communication. This transition redefined connectivity by enabling instant and widespread interaction across diverse demographics.
- Global Reach Expansion - Social media connects over 4.7 billion users worldwide, bridging geographic and cultural gaps instantly.
- User-Generated Content Surge - Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Twitter empower individuals to create and share content, democratizing information dissemination.
- Real-Time Interaction - Social networks facilitate immediate engagement, enhancing news distribution, marketing strategies, and social movements globally.
The social media explosion continues to evolve, shaping how societies communicate, influence, and create culture on a global scale.
