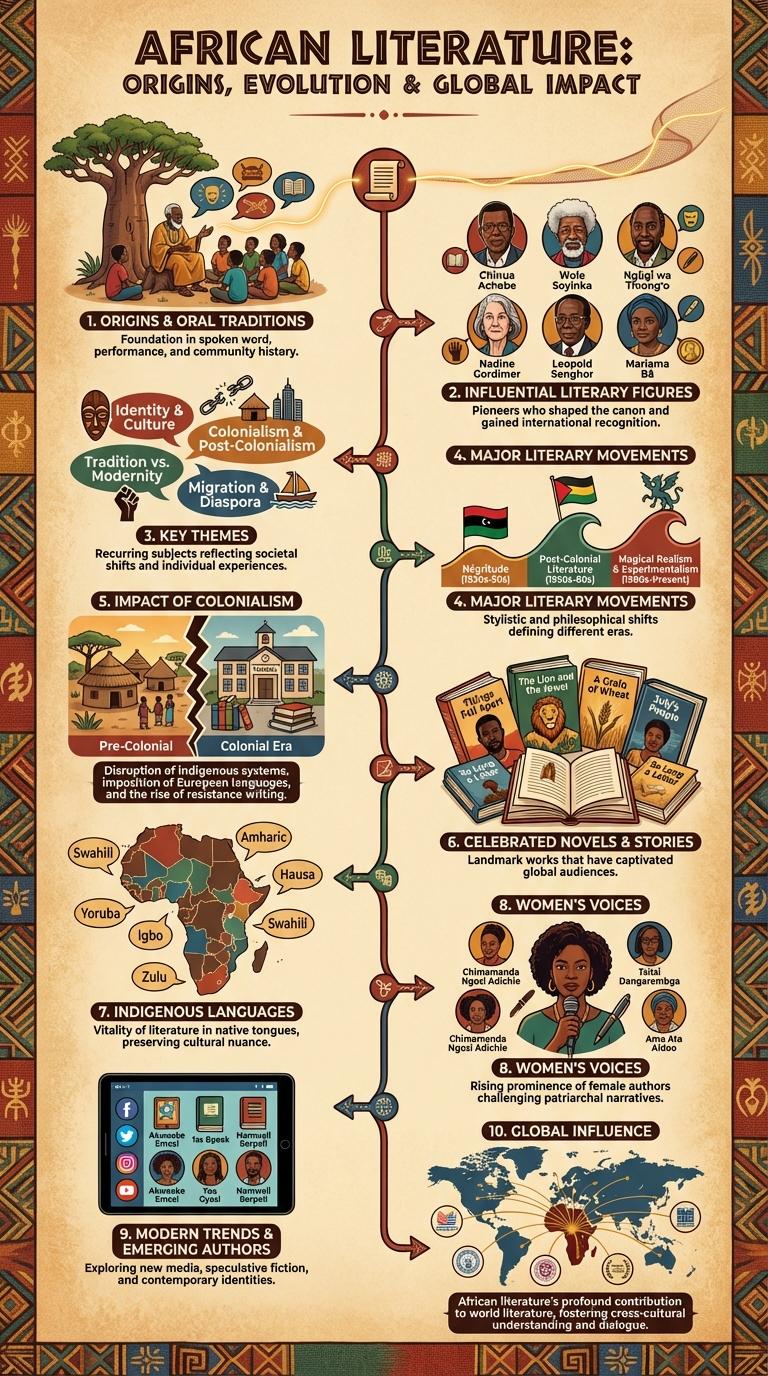
African literature showcases diverse narratives reflecting rich cultural heritage and complex histories across the continent. This infographic highlights key authors, literary genres, and influential movements that have shaped African storytelling. Explore how oral traditions blend with modern techniques to create powerful voices in global literature.
Origins and Oral Traditions of African Literature
African literature originates from diverse oral traditions passed down through generations, including storytelling, poetry, and song. These oral narratives serve as vital cultural repositories, preserving history, values, and social norms across African societies. Key forms include folktales, proverbs, and epics, which remain central to African literary identity and heritage.
Influential African Literary Figures
African literature boasts a rich tapestry of influential writers who have shaped global literary landscapes. Notable figures include Chinua Achebe, whose novel "Things Fall Apart" introduced African narratives to a worldwide audience. Wole Soyinka, Africa's first Nobel Prize in Literature laureate, and Nadine Gordimer, a champion of social justice in South African literature, stand out for their profound cultural impact.
Key Themes in African Literature
African literature explores a rich tapestry of themes reflecting the continent's diverse cultures, histories, and experiences. These themes offer insights into identity, struggle, and transformation within African societies.
Key themes in African literature highlight the complexities and vibrancy of African narratives, shaping global literary landscapes.
- Colonialism and Post-Colonialism - African literature often examines the impact of colonial rule and the challenges of independence on identity and society.
- Oral Traditions and Storytelling - Many works incorporate traditional oral narratives, emphasizing the importance of heritage and cultural continuity.
- Social Justice and Inequality - Themes of resistance, human rights, and social reform are prevalent, reflecting struggles against oppression.
- Identity and Diaspora - Explorations of personal and collective identity address themes of migration, displacement, and cultural hybridity.
- Spirituality and Mythology - African literature frequently weaves indigenous beliefs and myths, enriching the narrative fabric with symbolic meaning.
Major African Literary Movements
African literature has evolved through significant literary movements that reflect the continent's diverse cultures and histories. These movements highlight themes of identity, colonization, resistance, and post-colonial experience.
The Negritude movement, emerging in the 1930s, celebrates African heritage and black pride through poetry and prose. Postcolonial literature explores the effects of colonization and the struggle for independence across African nations.
Impact of Colonialism on African Writing
African literature has been profoundly shaped by the impact of colonialism, which introduced new languages, themes, and literary forms. The struggle for identity and cultural preservation remains central in postcolonial African writing.
- Language Shift - Colonial powers imposed European languages, leading many African writers to adopt English, French, or Portuguese in their works.
- Cultural Displacement - Colonialism disrupted indigenous traditions and storytelling methods, which writers often seek to reclaim or reinterpret.
- Resistance Themes - African literature commonly addresses the oppression and exploitation experienced under colonial rule.
- Hybrid Literary Forms - Writers merge oral traditions with Western literary structures to create unique narrative styles.
- Postcolonial Identity - African authors explore the complexities of national and personal identity in a society shaped by colonial legacies.
The ongoing dialogue in African literature reflects its evolution from colonial influence towards authentic self-expression and cultural revival.
Celebrated African Novels and Stories
What are some celebrated novels and stories in African literature? African literature boasts a rich collection of novels and stories that have garnered worldwide acclaim for their cultural depth and storytelling. These works explore themes of identity, colonialism, and resilience.
| Title | Author |
|---|---|
| "Things Fall Apart" | Chinua Achebe |
| "Nervous Conditions" | Tsitsi Dangarembga |
| "Half of a Yellow Sun" | Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie |
| "So Long a Letter" | Mariama Ba |
| "The Palm-Wine Drinkard" | Amos Tutuola |
African Literature in Indigenous Languages
African literature in indigenous languages preserves the rich cultural heritage and oral traditions of the continent. These works provide authentic insights into the values, beliefs, and histories of diverse African communities.
Indigenous languages such as Swahili, Yoruba, Zulu, and Amharic play a crucial role in the literary landscape of Africa. Writers use these languages to express identity, resist colonial influence, and promote local narratives. The rise of publications and digital media has increased the accessibility and appreciation of indigenous African literature worldwide.
Women's Voices in African Literature
Women's voices in African literature have significantly shaped the continent's narrative landscape, highlighting themes of resilience, identity, and social change. Prominent authors such as Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie and Tsitsi Dangarembga use storytelling to challenge traditional gender roles and amplify women's experiences.
The influence of female African writers extends across genres including novels, poetry, and drama, providing diverse perspectives on cultural and political issues. Their work fosters greater understanding of African societies, inspiring both local and global audiences through authentic representation.
Modern Trends and Emerging Authors
Modern African literature unveils a rich tapestry of diverse voices and innovative storytelling techniques. Emerging authors from the continent are reshaping narratives with fresh perspectives and global appeal.
Exploring themes of identity, migration, and technology, contemporary African writers engage both local and international audiences.
- Rise of Digital Publishing - New platforms enable African authors to reach wider audiences and challenge traditional publishing norms.
- Younger Writers Gaining Recognition - Authors in their 20s and 30s are winning major literary awards and critical acclaim worldwide.
- Fusion of Genres - Hybrid forms blending folklore, science fiction, and memoir are redefining African literary expression.
