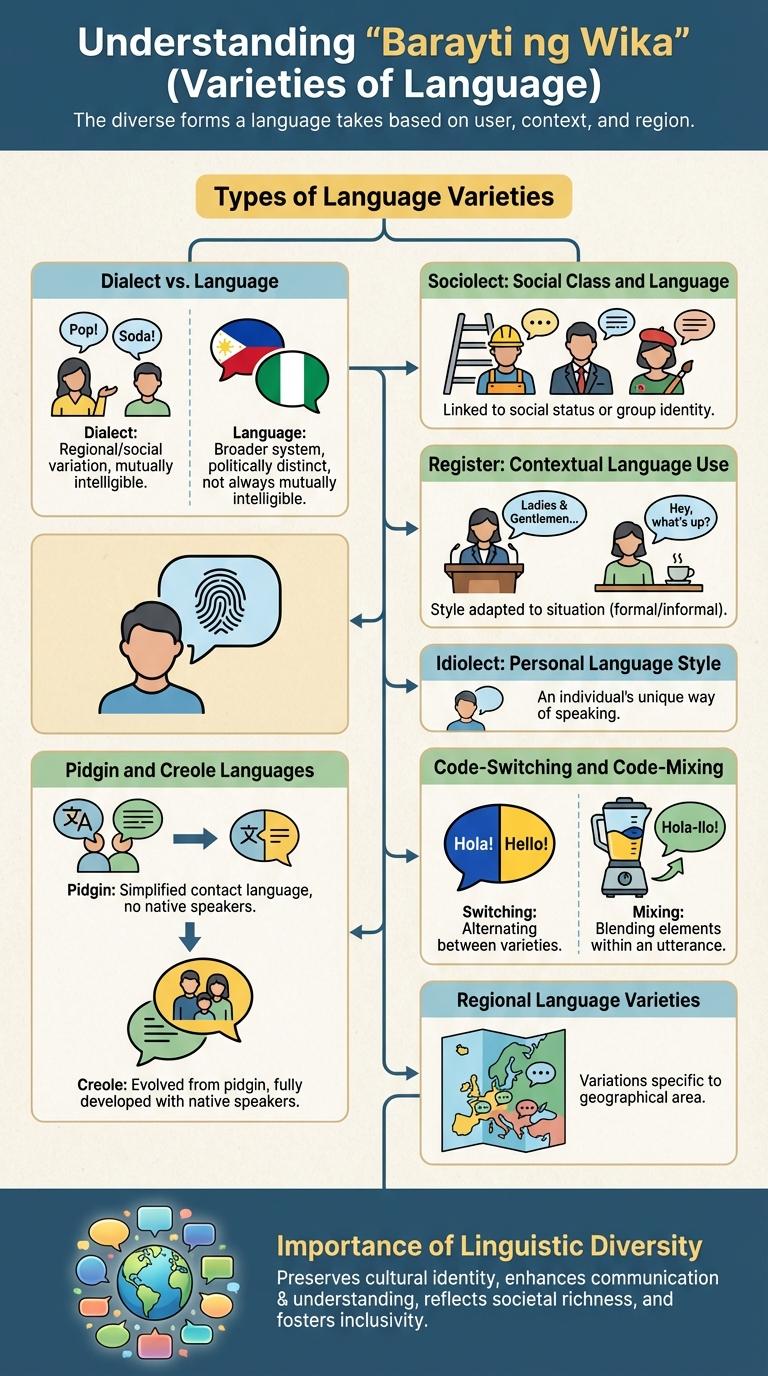
Barayti ng wika showcases the diverse forms and variations within a language, reflecting cultural identity and social context. Understanding these linguistic variations helps in appreciating the richness and adaptability of communication across different communities. This infographic visually represents the key types and examples of language varieties for better comprehension.
Understanding "Barayti ng Wika
Barayti ng wika refers to the different variations of a language used by speakers depending on region, social class, or context. These variations highlight the rich diversity within a single language system.
Understanding barayti ng wika helps in appreciating the cultural and social factors influencing language use. It also aids in effective communication by recognizing distinct dialects, sociolects, and idiolects across communities.
Types of Language Varieties
Language varieties reflect the diverse ways people communicate within different groups and contexts. Understanding these types enhances appreciation of linguistic richness and cultural identity.
- Dialect - A regional or social variety of a language with distinct vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation.
- Register - Language variation based on context, purpose, and audience, such as formal or informal speech.
- Slang - Informal and often ephemeral language used by particular social groups for in-group identity.
- Jargon - Specialized terminology used within specific professions or interest groups for precise communication.
- Pidgin and Creole - Simplified or fully developed languages arising from contact between different linguistic communities.
Exploring language varieties reveals the dynamic nature of human communication across regions and cultures.
Dialect vs. Language
Barayti ng wika ay tumutukoy sa iba't ibang anyo ng isang wika batay sa rehiyonal, sosyal, o sitwasyonal na pagkakaiba. Ang dialect ay isang baryasyon ng wika na ginagamit sa partikular na lugar o komunidad, na may kakaibang pagbigkas, bokabularyo, at grammar ngunit hindi ganap na magkahiwalay na wika. Ang language naman ay isang malawakang sistema ng komunikasyon na may sariling estruktura at ginagamit ng malaking populasyon, kaya ang dialect ay bahagi ng language ngunit may limitadong saklaw.
Sociolect: Social Class and Language
Sociolect refers to language variations influenced by social class, reflecting speakers' socioeconomic backgrounds. Social class impacts vocabulary, pronunciation, and grammar, creating distinct linguistic patterns within communities. Understanding sociolect helps reveal social identity and group membership through language use.
Register: Contextual Language Use
Barayti ng wika, or language varieties, refer to the different forms of a language used in various social contexts. Register is a key aspect that determines the appropriate language style based on the setting and audience.
Formal register is used in professional or academic environments where polite and precise language is essential. Informal register appears in casual conversations among friends and family, featuring relaxed and colloquial expressions.
Idiolect: Personal Language Style
What is idiolect in the context of language varieties? Idiolect refers to the unique, personal language style of an individual. It includes distinct vocabulary, pronunciation, and grammar patterns that differentiate one person's speech from another's.
Pidgin and Creole Languages
| Language Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Pidgin | A simplified form of language that develops as a means of communication between speakers of different native languages. Pidgin languages have limited vocabulary and simplified grammar. Commonly used in trade or colonial contexts. |
| Creole | An evolved, stable language that originates from a pidgin but becomes the native language of a community. Creoles have fully developed grammar and vocabulary, serving all communication needs of their speakers. |
| Examples of Pidgin Languages | Tok Pisin (Papua New Guinea), Nigerian Pidgin English, West African Pidgin English |
| Examples of Creole Languages | Haitian Creole, Jamaican Patois, Louisiana Creole |
| Significance | Pidgin and Creole languages illustrate linguistic adaptation and cultural exchange. They highlight language change in contact situations and reflect social identities. |
Code-Switching and Code-Mixing
Barayti ng wika ay nagpapakita ng iba't ibang anyo ng komunikasyon sa isang lipunan. Dalawang karaniwang anyo nito ay ang code-switching at code-mixing.
Ang code-switching ay ang pagsasanib ng dalawang wika sa pangungusap, kadalasan sa paglipat mula sa isang wika patungo sa isa pa. Sa kabilang banda, ang code-mixing ay ang paghalo ng mga salita o parirala mula sa dalawang wika sa loob ng isang pangungusap. Parehong ginagamit ito upang mas epektibong maipahayag ang ideya o makalikha ng mas natural na usapan sa pang-araw-araw na buhay.
Regional Language Varieties
Regional language varieties in the Philippines reflect the rich linguistic diversity across different provinces and islands. These varieties include distinct dialects and languages that carry unique cultural identities.
- Ilocano - Predominantly spoken in Northern Luzon, Ilocano is one of the most widely used regional languages.
- Cebuano - Spoken in the Central Visayas and parts of Mindanao, Cebuano has millions of native speakers.
- Hiligaynon - Common in Western Visayas, this language features its own vocabulary and pronunciation variations.
- Kapampangan - Native to Pampanga and surrounding areas, Kapampangan has a distinctive sound and grammar.
- Bikol - Used in the Bicol Region, Bikol contains several dialects that differ by locality.
