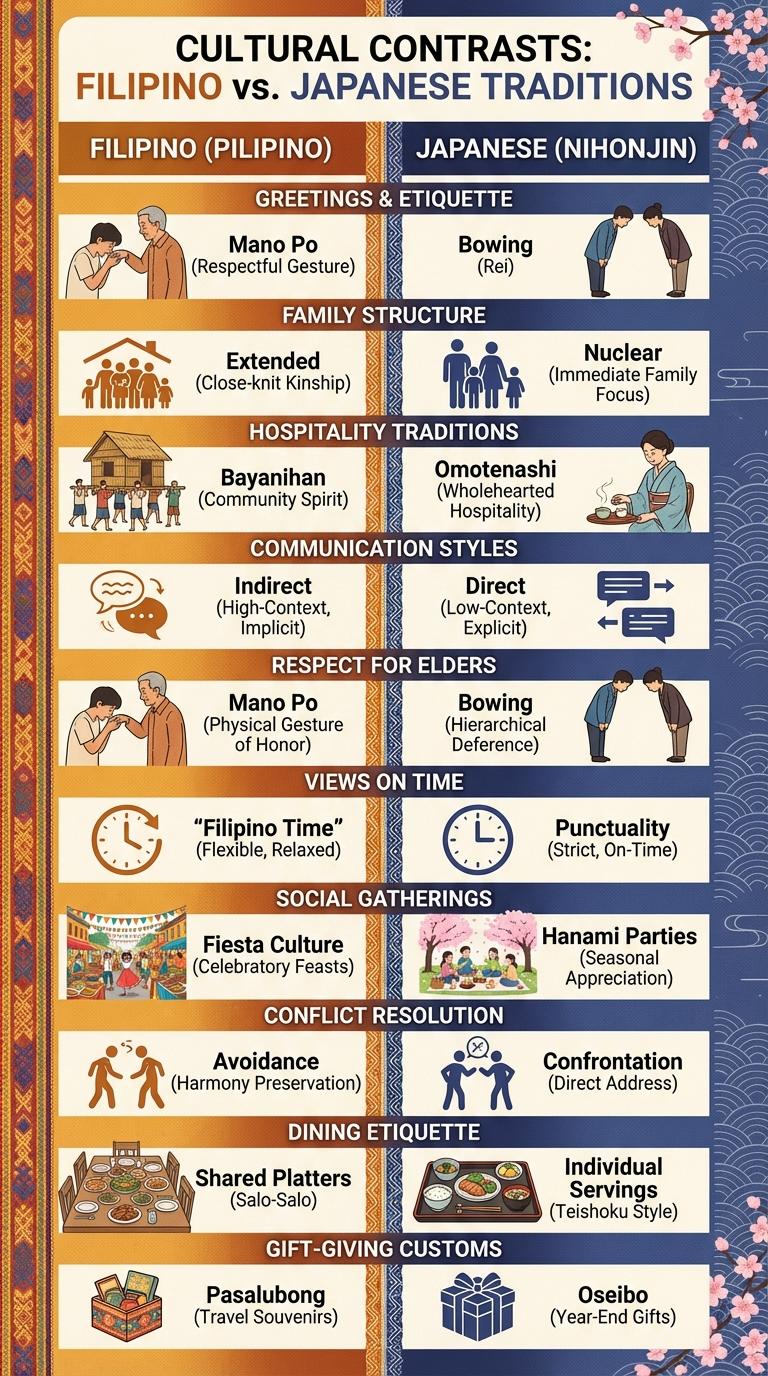
Filipino cultural norms emphasize strong family ties, hospitality, and respect for elders, creating a close-knit community atmosphere. In contrast, Japanese culture values punctuality, formality, and group harmony, reflecting its societal focus on order and collective well-being. Comparing these distinct traditions highlights the unique ways each culture shapes social interactions and daily life.
Greetings & Etiquette: Filipinos vs. Japanese
Filipino and Japanese cultures have distinct greetings and etiquette that reflect their social values and traditions. Understanding these differences helps foster respectful intercultural communication.
- Filipino Greetings - Filipinos commonly greet with a warm handshake or a cheek-to-cheek "beso" among family and close friends, emphasizing warmth and familiarity.
- Japanese Greetings - Japanese people traditionally bow to show respect during greetings, with different bow depths corresponding to varying degrees of formality.
- Etiquette in Social Interaction - Filipinos often use honorifics like "po" and "opo" to show respect when speaking to elders, while Japanese use formal language and titles to maintain politeness and hierarchy.
Family Structure: Extended vs. Nuclear
How do family structures differ between Filipinos and Americans?
Filipino families commonly embrace an extended family structure, including multiple generations living together or near each other. In contrast, American families primarily follow a nuclear family model, consisting of parents and their children living independently.
Hospitality Traditions: Bayanihan vs. Omotenashi
The Filipino cultural norm of Bayanihan emphasizes communal unity and helping neighbors through collective efforts, often demonstrated by physically moving a neighbor's house or supporting community projects. In contrast, Japan's Omotenashi tradition centers on meticulous hospitality, where hosts anticipate guests' needs with sincere care and attention to detail. Both practices reflect deep-rooted cultural values of kindness and respect, yet Bayanihan highlights communal cooperation while Omotenashi prioritizes individual guest experience.
| Bayanihan (Philippines) | Omotenashi (Japan) |
|---|---|
| Community-driven assistance | Personalized, anticipatory hospitality |
| Physical teamwork (e.g., moving houses) | Attention to detail in service |
| Focus on mutual support and cooperation | Focus on guest comfort and satisfaction |
| Rooted in Filipino Bayanihan spirit | Rooted in Japanese cultural refinement |
Communication Styles: Indirect (Filipino) vs. Direct (Japanese)
The communication style of Filipinos is predominantly indirect, emphasizing harmony and avoiding confrontation. In contrast, Japanese communication, while also valuing politeness, tends to be more direct and explicit in conveying messages.
Filipinos often use subtle hints, nonverbal cues, and context to express opinions and feelings, prioritizing the preservation of relationships. Japanese communication relies on clear and precise language, reflecting a cultural preference for honesty and efficiency during interactions. Both cultures highly value respect and social hierarchy but express these values differently through their communication styles.
Respect for Elders: Mano Po vs. Bowing
The Filipino cultural norm of "Mano Po" involves a respectful gesture where younger individuals take the hand of an elder and gently touch it to their forehead. This practice signifies deep respect and gratitude towards elders, commonly observed in family gatherings and social events.
In contrast, Japanese culture uses bowing as the primary gesture to show respect, especially toward elders and authority figures. The depth and duration of the bow reflect the level of respect being conveyed, highlighting a formal and hierarchical social structure.
Views on Time: Filipino “Filipino Time” vs. Japanese Punctuality
Filipino cultural norms about time, often called "Filipino Time," reflect a more relaxed attitude toward punctuality compared to Japan's strict adherence to exact timing. These differing views influence social and professional interactions in both countries.
Filipino Time showcases flexibility and a focus on relationships, while Japanese punctuality emphasizes respect and efficiency.
- Filipino Time - Being late is socially acceptable and linked to prioritizing personal connections over strict schedules.
- Japanese Punctuality - Arriving on time or early is a sign of respect and professionalism in Japan.
- Impact on Social Interactions - Filipinos often use time more fluidly in social contexts, whereas Japanese prefer precise scheduling to maintain harmony and order.
Social Gatherings: Fiesta Culture vs. Hanami Parties
| Cultural Norms | Filipinos: Fiesta Culture vs. Japanese: Hanami Parties |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Fiestas celebrate patron saints, community unity, and heritage through food, music, and dance. Hanami parties honor the beauty of cherry blossoms, symbolizing renewal and transient beauty. |
| Duration | Fiestas usually last several days to a week, featuring multiple events and rituals. Hanami gatherings occur mainly during a short cherry blossom blooming period, lasting 1-2 weeks. |
| Activities | Includes street parades, religious ceremonies, communal feasts, and traditional dances. Hanami involves outdoor picnics under blooming cherry trees with food, drinks, and socializing. |
| Community Involvement | Entire communities participate, often with neighborhood competitions, volunteer preparations, and collective hosting. Hanami parties are more informal, involving family, friends, and coworkers gathering in parks. |
| Symbolism | Emphasizes faith, gratitude, and cultural pride. Hanami symbolizes the fleeting nature of life and appreciation of natural beauty. |
Conflict Resolution: Avoidance vs. Confrontation
Filipino culture typically emphasizes conflict avoidance, prioritizing harmony and indirect communication to maintain relationships. In contrast, American culture often supports direct confrontation, encouraging open dialogue to resolve issues quickly and transparently. These differing approaches reflect deeper cultural values surrounding respect, individualism, and group cohesion.
Dining Etiquette: Shared Platters vs. Individual Servings
Dining etiquette varies significantly between Filipinos and Americans, especially regarding shared platters and individual servings. Understanding these differences highlights cultural values around community and personal space during meals.
- Filipino Shared Platters - Filipinos commonly enjoy meals by sharing multiple dishes served in the center of the table, promoting fellowship and connection.
- American Individual Servings - Americans typically prefer individual plates with personal portions, emphasizing convenience and personal preference.
- Respect and Adaptation - Visitors in either culture often adapt their dining habits to respect local customs and foster social harmony.
These contrasting dining practices reflect deeper cultural attitudes toward communal interaction and individualism.
