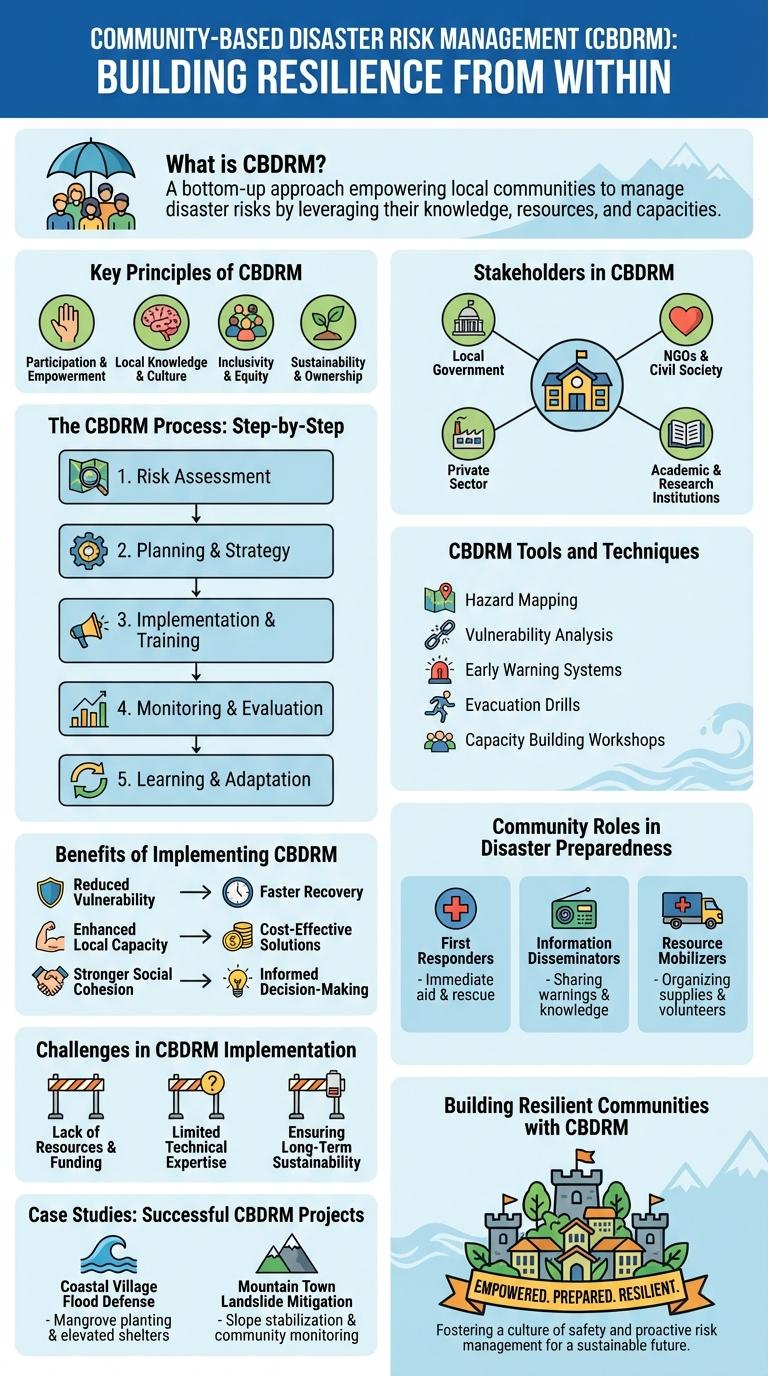
CBDRM infographics visually present critical steps for effective community-based disaster risk management, highlighting risk assessment, planning, and local engagement. Clear graphics emphasize the roles of preparedness, capacity building, and early warning systems in minimizing disaster impacts. These infographics serve as practical guides to empower communities in resilience and sustainable recovery efforts.
What is Community-Based Disaster Risk Management (CBDRM)?
Community-Based Disaster Risk Management (CBDRM) is a strategy that involves local communities in identifying, assessing, and managing disaster risks to reduce vulnerabilities and enhance resilience. It emphasizes participatory approaches tailored to the specific needs and capacities of the community.
CBDRM integrates local knowledge with scientific information to develop effective disaster preparedness and response plans. This method empowers communities to actively participate in disaster risk reduction and recovery processes, fostering sustainable development.
Key Principles of CBDRM
Community-Based Disaster Risk Management (CBDRM) empowers local communities to identify, assess, and reduce disaster risks through active participation and collaboration. It emphasizes inclusive decision-making, capacity building, and the integration of traditional knowledge with scientific approaches. CBDRM aims to enhance community resilience by fostering preparedness, resource management, and sustainable development practices.
The CBDRM Process: Step-by-Step
Community-Based Disaster Risk Management (CBDRM) empowers local populations to identify, assess, and reduce disaster risks effectively. This process enhances resilience through active community participation and localized strategies.
- Risk Assessment - Community members analyze hazards, vulnerabilities, and capacities to understand potential disaster impacts.
- Planning - Development of action plans tailored to reduce identified risks and strengthen preparedness measures.
- Implementation - Execution of risk reduction activities, including infrastructure improvements and awareness campaigns.
- Monitoring and Evaluation - Continuous review of outcomes to improve effectiveness and adapt strategies as needed.
- Capacity Building - Training and education efforts aimed at enhancing community skills and knowledge for disaster management.
The CBDRM process creates sustainable, community-driven solutions for disaster preparedness and resilience.
Stakeholders in CBDRM
Community-Based Disaster Risk Management (CBDRM) involves multiple key stakeholders working collaboratively to enhance disaster resilience. Understanding these stakeholders helps optimize risk reduction and emergency response strategies.
- Local Communities - Residents actively participate in identifying hazards and implementing risk reduction measures.
- Government Agencies - Authorities provide policy support, resources, and coordination for disaster preparedness and response.
- Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) - NGOs facilitate training, awareness campaigns, and mobilize community resources.
CBDRM Tools and Techniques
Community-Based Disaster Risk Management (CBDRM) employs various tools and techniques to enhance local resilience. Key methods include hazard mapping, risk assessment, and early warning systems tailored to community needs. Participatory approaches ensure inclusive planning and effective disaster response.
Benefits of Implementing CBDRM
What are the benefits of implementing Community-Based Disaster Risk Management (CBDRM)? CBDRM empowers local communities to identify, assess, and mitigate disaster risks effectively. This approach enhances resilience by promoting local knowledge, participation, and resource mobilization for disaster preparedness and response.
How does CBDRM improve disaster response time and effectiveness? By engaging community members in planning and decision-making, CBDRM ensures quicker mobilization and tailored interventions during emergencies. It fosters collaboration between local authorities and residents, reducing vulnerability and minimizing disaster impacts.
In what ways does CBDRM contribute to sustainable development? CBDRM integrates disaster risk reduction into local development processes, protecting livelihoods and infrastructure. It supports long-term resilience by addressing environmental, social, and economic factors that increase community vulnerability.
Can CBDRM reduce economic losses from disasters? Implementing CBDRM helps communities develop risk-aware strategies that lower damage to property and assets. Preventive measures and early warnings decrease recovery costs and support faster economic stability after disasters.
How does CBDRM enhance social cohesion within communities? Participatory risk management builds trust and cooperation among community members. Shared responsibility and knowledge exchange strengthen social networks, which are crucial for effective disaster preparedness and recovery.
Community Roles in Disaster Preparedness
Community-Based Disaster Risk Management (CBDRM) empowers local populations to actively participate in reducing disaster risks. It enhances resilience by integrating community knowledge and resources into preparedness efforts.
- Risk Identification - Local residents identify hazards and vulnerabilities specific to their community to prioritize preparedness actions.
- Resource Mobilization - Communities organize and allocate local resources such as manpower, materials, and information for effective disaster response.
- Capacity Building - Training and education programs strengthen community skills in emergency management and first aid.
- Early Warning Systems - Community members establish locally tailored warning mechanisms to ensure timely alerts before disasters strike.
- Recovery Planning - Planning involving community input ensures sustainable and culturally appropriate post-disaster recovery strategies.
Challenges in CBDRM Implementation
Community-Based Disaster Risk Management (CBDRM) faces significant challenges during implementation that can hinder its effectiveness. Limited resources and insufficient local capacity often restrict the ability to conduct thorough risk assessments and preparedness activities.
Engaging diverse community members and sustaining long-term participation is difficult due to varying levels of awareness and interest. Coordination between local authorities, NGOs, and community groups remains a persistent hurdle in streamlining disaster management efforts.
Case Studies: Successful CBDRM Projects
Community-Based Disaster Risk Management (CBDRM) empowers local communities to actively participate in disaster preparedness and resilience building. Successful CBDRM projects demonstrate the effectiveness of grassroots engagement in reducing vulnerability.
Case studies reveal that integrating local knowledge with scientific expertise enhances early warning systems and disaster response. In the Philippines, a CBDRM initiative reduced flood damage by 40% through community-led infrastructure improvements. Similarly, in Nepal, community mapping and training decreased landslide casualties by 30% during the monsoon season.
