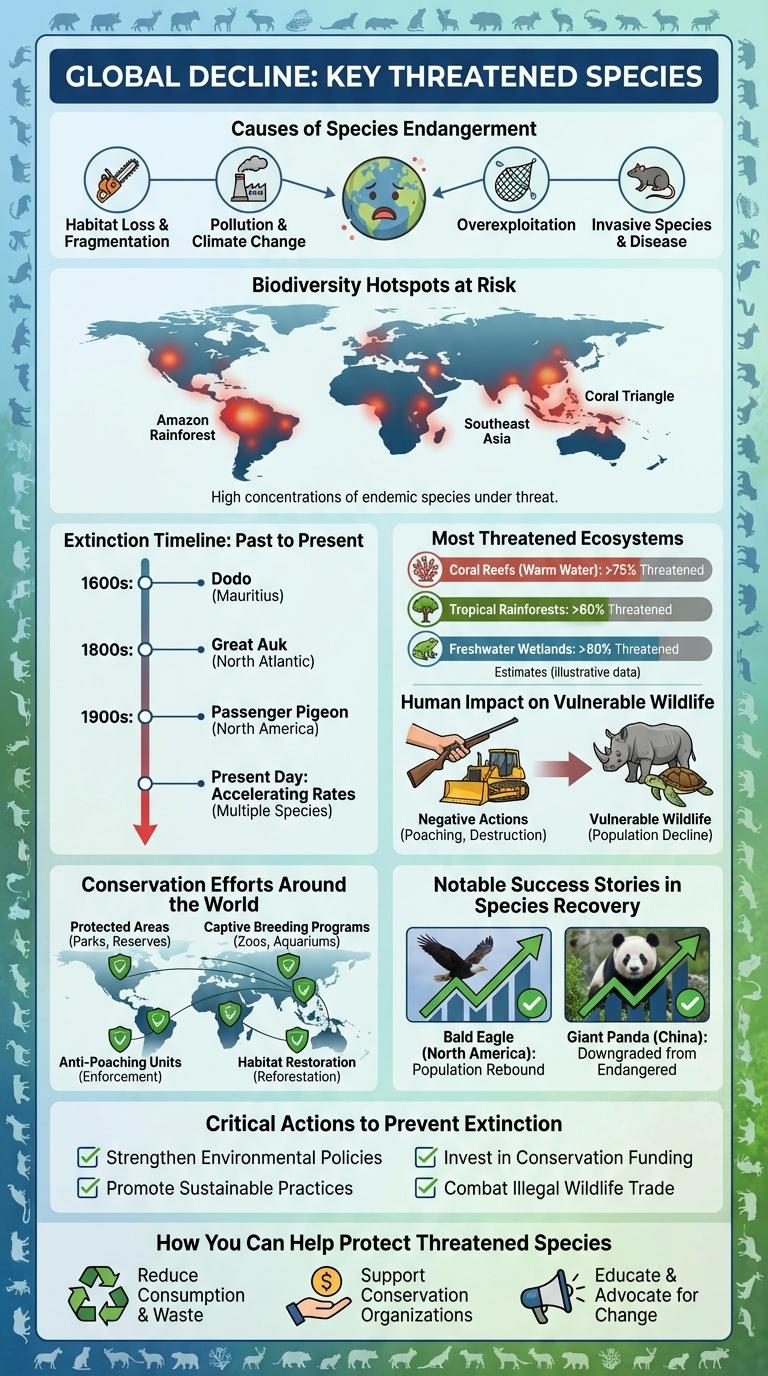
The infographic highlights various threatened organisms, emphasizing their endangered status and the urgent need for conservation efforts. Visual data presents critical factors contributing to habitat loss, climate change, and human activities affecting biodiversity. Understanding these challenges supports global initiatives aimed at protecting vulnerable species and preserving ecosystems.
Global Decline: Key Threatened Species
The world is witnessing a significant decline in biodiversity, with numerous species facing heightened risks of extinction. Habitat loss, climate change, and human activities are the main drivers behind the global decline of threatened organisms.
Key threatened species highlight urgent conservation priorities and reflect broader environmental challenges.
- Amur Leopard - Critically endangered with fewer than 100 individuals remaining in the wild, primarily due to poaching and habitat fragmentation.
- Vaquita - The rarest marine mammal faces imminent extinction with an estimated population below 10, caused by bycatch in illegal fishing nets.
- Javan Rhino - Only around 80 survive within Ujung Kulon National Park, threatened by habitat loss and small population size vulnerability.
Causes of Species Endangerment
Species endangerment occurs when populations face threats that disrupt their natural habitats and reproductive cycles. Major causes include habitat destruction, pollution, climate change, overexploitation, and invasive species.
Habitat destruction from deforestation and urban development eliminates crucial living spaces for many organisms. Pollution contaminates air, water, and soil, harming species' health and reducing survival rates.
Biodiversity Hotspots at Risk
Biodiversity hotspots are regions with exceptionally high levels of endemic species facing significant threats from habitat loss and climate change. These areas contain over half of the world's plant species as endemics but cover only 2.4% of Earth's land surface. Urgent conservation efforts are critical to protect the diverse organisms that maintain ecological balance within these hotspots.
Extinction Timeline: Past to Present
The extinction timeline of threatened organisms reveals critical patterns from the past to the present. Species such as the Dodo, Passenger Pigeon, and Tasmanian Tiger have vanished due to habitat loss, hunting, and environmental changes. Current threats place thousands of species at risk, emphasizing urgent conservation efforts worldwide.
Most Threatened Ecosystems
Most threatened ecosystems around the world face severe challenges due to habitat loss, climate change, and human activities. These ecosystems support a vast number of species that are at risk of extinction.
Rainforests, coral reefs, wetlands, mangroves, and grasslands are among the most endangered ecosystems globally. Rainforests are vital for biodiversity, providing habitat for over half of all terrestrial species. Coral reefs face bleaching and degradation, threatening marine life and coastal protection.
Human Impact on Vulnerable Wildlife
How does human activity threaten vulnerable wildlife species?
Human activities such as deforestation, pollution, and urban expansion severely disrupt the natural habitats of many species. These actions lead to reduced biodiversity and increase the risk of extinction for numerous organisms worldwide.
Which human-induced factors cause the most harm to wildlife populations?
Habitat destruction, climate change, and poaching are among the leading causes of wildlife declines. Overexploitation of resources and introduction of invasive species also contribute significantly to threatening vulnerable species.
What are the effects of habitat fragmentation on wildlife?
Habitat fragmentation isolates animal populations, limiting their ability to find food, mates, and shelter. This results in decreased genetic diversity and makes populations more susceptible to disease and environmental changes.
How does pollution impact aquatic wildlife species?
Pollutants like heavy metals, plastics, and chemicals contaminate water bodies, harming fish, amphibians, and other aquatic life. These toxic substances disrupt reproductive systems and can cause long-term population declines.
What role does climate change play in endangering wildlife?
Climate change alters temperature and weather patterns, affecting species' migration, breeding, and food availability. Many vulnerable wildlife species struggle to adapt quickly enough, increasing their risk of extinction.
Conservation Efforts Around the World
Conservation efforts worldwide aim to protect threatened organisms and preserve biodiversity. These initiatives involve collaboration between governments, NGOs, and local communities to create sustainable solutions.
- Protected Areas - Establishing national parks and wildlife reserves safeguards critical habitats for endangered species.
- Species Recovery Programs - Captive breeding and reintroduction programs help boost populations of critically threatened animals.
- Legislation and Policies - Enforcing laws like CITES regulates trade and combats illegal poaching of vulnerable species.
Notable Success Stories in Species Recovery
| Species | Recovery Highlights |
|---|---|
| Bald Eagle | Population rebound after DDT ban; removed from U.S. Endangered Species list in 2007 |
| Giant Panda | Habitat protection and breeding programs increased wild population by over 17% by 2021 |
| Gray Wolf | Reintroduction efforts in Yellowstone National Park restored ecological balance |
| Humpback Whale | International protections led to significant population growth worldwide |
| California Condor | Captive breeding and release programs increased wild numbers from 22 to over 300 |
Critical Actions to Prevent Extinction
Threatened organisms face extinction due to habitat loss, climate change, and poaching. Immediate, targeted conservation efforts are essential to halt these declines.
Critical actions include habitat restoration, strict anti-poaching laws, and captive breeding programs. Public awareness and sustainable development practices support long-term species survival.
