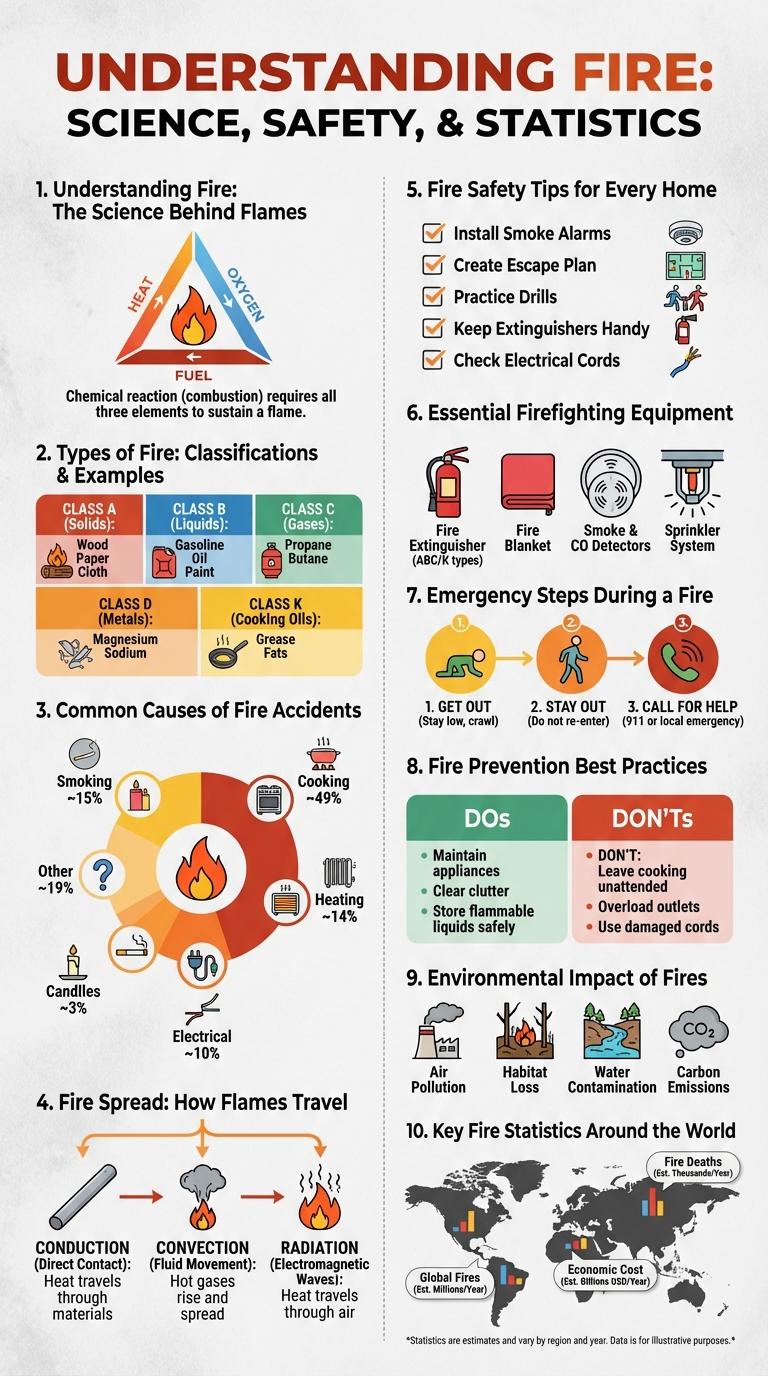
Fire is a powerful element that shapes ecosystems, provides warmth, and fuels industry, but it also poses significant risks. Understanding the science of fire, its causes, and safety measures is essential for prevention and control. This infographic visualizes key fire facts, types, and safety tips for better awareness and preparedness.
Understanding Fire: The Science Behind Flames
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Fire Triangle | Three elements required for fire: Heat, Fuel, and Oxygen |
| Combustion | A chemical reaction between oxygen and a fuel producing heat and light |
| Flame Structure | Includes the inner core (unburned gases) and outer luminous part (combustion zone) |
| Heat Transfer | Occurs through conduction, convection, and radiation to sustain fire |
| Fire Behavior | Influenced by fuel type, oxygen availability, and environmental conditions |
Types of Fire: Classifications & Examples
Fires are classified into different types based on the fuel causing the combustion and the nature of the fire. Common classifications include Class A for ordinary combustibles like wood and paper, Class B for flammable liquids such as gasoline, Class C for electrical fires, Class D for combustible metals, and Class K for kitchen fires involving oils and fats. Understanding these classifications helps in selecting the proper extinguishing method to effectively control and prevent fire damage.
Common Causes of Fire Accidents
Fire accidents pose significant risks to life and property, often resulting from preventable causes. Understanding common triggers helps in reducing fire hazards effectively.
- Electrical Faults - Faulty wiring and overloaded circuits frequently spark unintended fires in homes and businesses.
- Cooking Fires - Unattended cooking equipment is a leading cause of residential fires worldwide.
- Heating Equipment - Improper use or malfunction of heaters can ignite nearby combustible materials.
- Smoking Materials - Neglected cigarettes and matches are major contributors to accidental fires.
- Open Flames - Candles and fireplaces left unattended often cause accidental fire outbreaks.
Fire Spread: How Flames Travel
Fire spreads through a combination of heat, fuel, and oxygen. Understanding how flames travel helps improve fire prevention and safety measures.
- Conduction - Heat transfers through solid materials, igniting adjacent areas.
- Convection - Hot air rises, carrying flames and embers to new locations.
- Radiation - Heat radiates outward, preheating fuels ahead of the fire front.
Effective fire control requires managing each mode of fire spread to limit damage and protect lives.
Fire Safety Tips for Every Home
Fire safety in every home is essential to protect lives and property. Smoke alarms should be installed on every floor and tested monthly to ensure functionality. Create and practice a fire escape plan with all household members to respond quickly in an emergency.
Essential Firefighting Equipment
Firefighting requires specialized equipment to ensure safety and effectiveness in extinguishing fires. Proper tools help firefighters control flames and rescue individuals quickly.
- Fire Extinguisher - Portable device that releases agents to suppress small fires before they spread.
- Fire Hose - Flexible tube used to deliver water or foam to extinguish large fires rapidly.
- Protective Gear - Includes helmets, fire-resistant suits, gloves, and boots designed to shield firefighters from heat and smoke.
Emergency Steps During a Fire
Fires can spread rapidly, making it crucial to act immediately. Knowing the correct emergency steps increases the chances of safety for everyone involved.
First, alert everyone in the building and activate the fire alarm if available. Secondly, evacuate the premises quickly using the nearest safe exit, avoiding elevators. Lastly, call emergency services from a safe location once outside the building.
Fire Prevention Best Practices
Fire prevention is essential for protecting lives and properties from devastating damage. Understanding and implementing basic safety measures significantly reduce the risk of fire incidents.
Regularly inspect electrical wiring and appliances to prevent electrical fires. Keep flammable materials away from heat sources and ensure smoke detectors are installed and maintained properly.
Environmental Impact of Fires
Fires release large amounts of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing significantly to climate change. The loss of vegetation during fires disrupts local ecosystems and reduces biodiversity.
Smoke from fires contains harmful particulate matter that affects air quality and public health. Soil erosion and water contamination often follow fires, further impacting the environment and surrounding communities.
