Organic agriculture promotes sustainable farming by avoiding synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, enhancing soil health and biodiversity. This method supports environmental conservation and produces healthier, chemical-free food options. Growing consumer demand for organic products drives the expansion of eco-friendly farming practices worldwide.
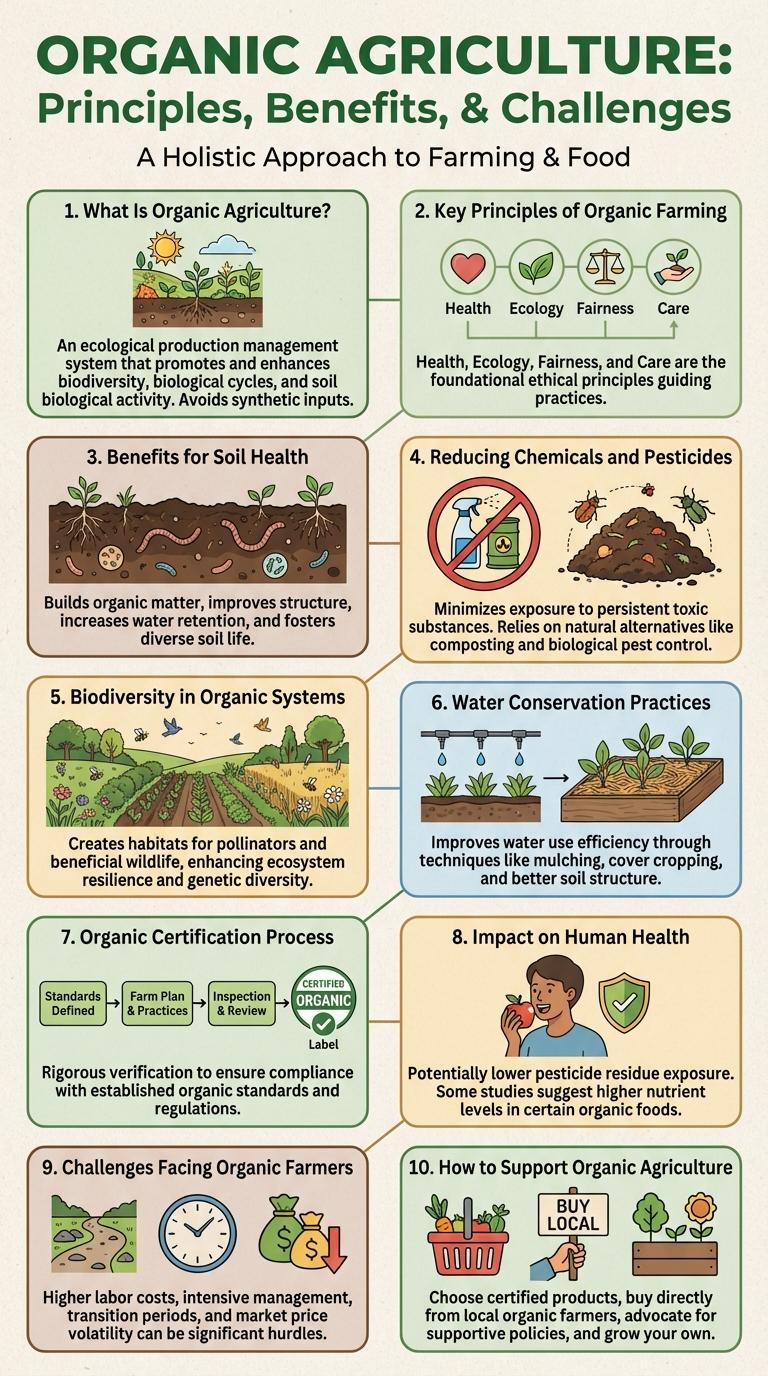
What Is Organic Agriculture?
Organic agriculture is a farming method that relies on natural processes and minimizes the use of synthetic chemicals. It aims to maintain soil health, biodiversity, and ecological balance.
Farmers use organic seeds, natural fertilizers like compost, and biological pest control to grow crops sustainably. Organic agriculture promotes environmental conservation and produces healthier food products.
Key Principles of Organic Farming
Organic agriculture relies on natural processes, biodiversity, and cycles adapted to local conditions instead of synthetic inputs. It emphasizes soil health, ecological balance, and conserving biodiversity to produce sustainable and resilient food systems.
Key principles include maintaining soil fertility through crop rotation, composting, and green manures. Organic farming prohibits synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, promoting pest control through natural predators and habitat preservation.
Benefits for Soil Health
Organic agriculture enhances soil health by promoting natural nutrient cycles and reducing chemical input. This sustainable approach supports long-term fertility and ecosystem balance.
- Improved Soil Structure - Organic farming increases organic matter, enhancing soil aeration and water retention.
- Enhanced Microbial Activity - Natural inputs boost beneficial microbes that aid nutrient availability and disease resistance.
- Reduced Soil Erosion - Cover crops and crop rotation protect soil from erosion and improve surface stability.
Reducing Chemicals and Pesticides
Organic agriculture minimizes the use of synthetic chemicals and pesticides, promoting healthier ecosystems. By relying on natural pest control methods, such as crop rotation and beneficial insects, it reduces harmful chemical residues in soil and water. This approach supports biodiversity and fosters sustainable farming practices for long-term environmental health.
Biodiversity in Organic Systems
Organic agriculture promotes biodiversity by creating diverse habitats that support various plant and animal species. It avoids synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, preserving soil microorganisms and beneficial insects. These practices lead to healthier ecosystems and enhanced resilience against pests and diseases.
Water Conservation Practices
Organic agriculture employs water conservation practices that enhance soil moisture retention and reduce water waste. Techniques such as mulching and crop rotation help maintain healthy soil structure and improve water efficiency.
Mulching covers the soil with organic matter, which reduces evaporation and keeps the soil cool, minimizing water loss. Crop rotation prevents soil degradation and increases organic matter, enhancing the soil's ability to retain water. Additionally, organic farms often use drip irrigation systems that target water directly to plant roots, maximizing water use efficiency.
Organic Certification Process
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Application | Farmers or producers submit detailed documentation about farming practices and inputs used. |
| On-site Inspection | Certified inspectors visit the farm to verify organic practices and compliance with standards. |
| Review of Documentation | Certification bodies evaluate submitted records and inspection reports for adherence to organic criteria. |
| Certification Decision | The certification agency grants or denies organic status based on compliance evidence. |
| Annual Renewal | Producers undergo yearly inspections and updates to maintain certification status. |
Impact on Human Health
How does organic agriculture impact human health? Organic agriculture reduces exposure to synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, leading to lower risks of health issues such as cancer and neurological disorders. It enhances the nutrient content of food, providing higher levels of antioxidants and essential vitamins.
Challenges Facing Organic Farmers
Organic agriculture promotes sustainable farming by avoiding synthetic chemicals and focusing on natural processes. Despite its benefits, organic farmers face significant challenges that impact productivity and market growth.
- Pest and Disease Management - Organic farmers rely on natural pest control methods, which can be less effective and more labor-intensive than synthetic alternatives.
- Soil Fertility Maintenance - Maintaining soil health without chemical fertilizers requires complex crop rotations and organic amendments, demanding careful planning.
- Higher Production Costs - Organic farming often involves increased labor and certification expenses, leading to higher overall costs for farmers.
