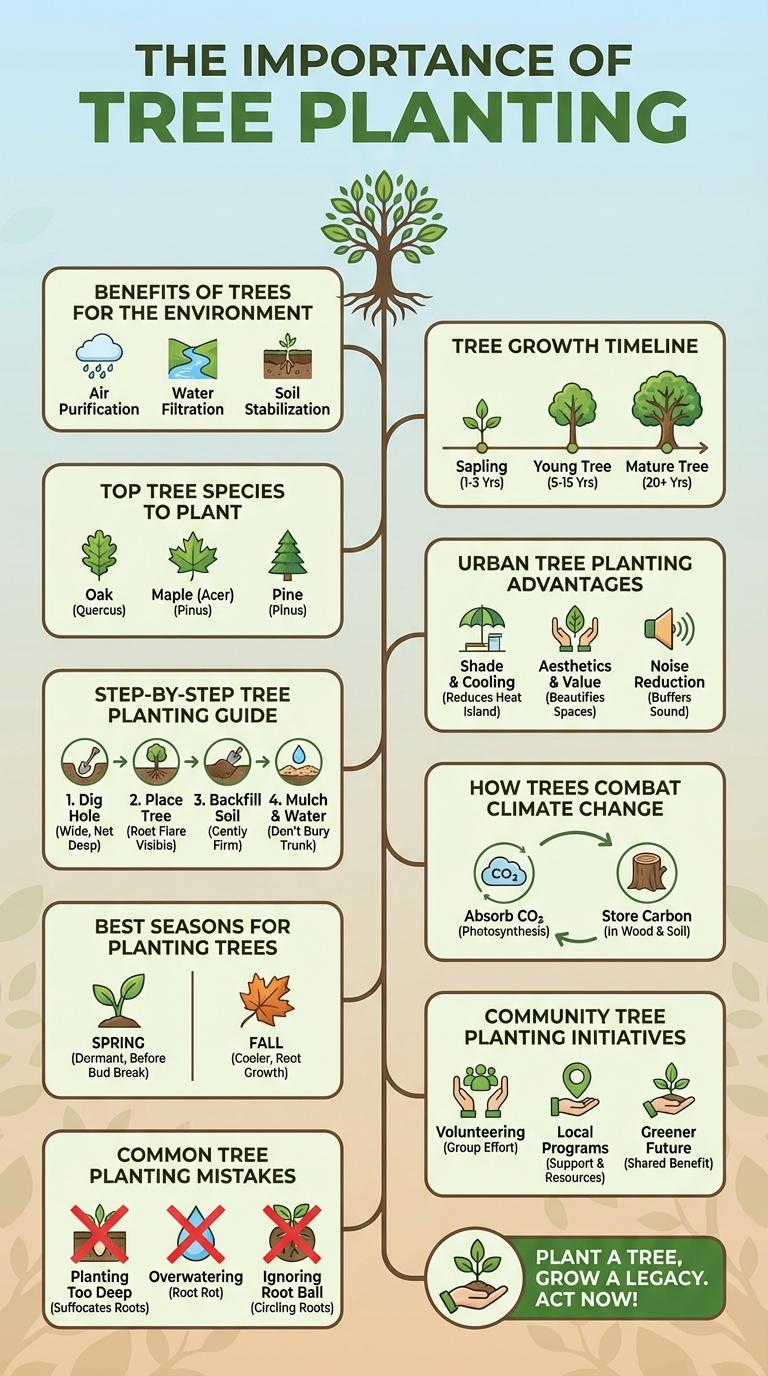
Tree planting plays a crucial role in combating climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide and improving air quality. This infographic highlights key benefits, techniques, and statistics that demonstrate the environmental and social impact of reforestation efforts worldwide. Understanding these facts encourages communities to engage in sustainable tree planting initiatives for a greener future.
The Importance of Tree Planting
Tree planting plays a crucial role in combating climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen. It helps restore natural habitats, supporting biodiversity and improving ecosystem health.
Trees reduce air pollution and mitigate the urban heat island effect by providing shade and cooling the environment. Planting trees also enhances soil quality, prevents erosion, and improves water retention.
Benefits of Trees for the Environment
Trees play a crucial role in maintaining environmental balance. They absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, improving air quality.
Trees help reduce soil erosion by stabilizing the ground with their roots. They provide habitats for numerous species, supporting biodiversity. Trees also regulate temperature by providing shade and cooling the air through evapotranspiration.
Top Tree Species to Plant
Tree planting plays a crucial role in enhancing biodiversity and combating climate change. Selecting the right tree species ensures maximum environmental impact and sustainability.
- Oak Trees - Known for their longevity and ability to support wildlife, oaks improve soil health and provide shade.
- Maple Trees - Popular for their vibrant foliage, maples contribute to carbon sequestration and urban cooling.
- Pine Trees - Evergreens like pines are excellent for erosion control and provide year-round habitat for various species.
Step-by-Step Tree Planting Guide
Planting trees supports environmental health and boosts local biodiversity. A clear, step-by-step guide ensures successful growth and sustainability.
Choose a suitable tree species based on your climate and soil type. Prepare the planting site by clearing debris and digging a hole twice as wide as the root ball.
Remove the tree from its container carefully to avoid root damage. Place the tree in the hole, ensuring the root collar is level with the soil surface.
Fill the hole with soil, gently firming it to eliminate air pockets. Water thoroughly to settle the soil and provide moisture for the roots.
Apply a 2-3 inch layer of mulch around the base, keeping it away from the trunk. Monitor watering regularly, especially during the first year, to support healthy establishment.
Best Seasons for Planting Trees
Planting trees during optimal seasons enhances their growth and survival rate. Spring and fall provide ideal conditions with moderate temperatures and adequate rainfall. Avoid extreme heat or frost to ensure young trees establish strong roots.
Common Tree Planting Mistakes
| Mistake | Description |
|---|---|
| Planting Too Deep | Placing the tree too deep restricts root growth and causes oxygen deficiency. |
| Improper Site Selection | Choosing unsuitable soil or climate leads to poor tree health and growth. |
| Poor Watering Practices | Overwatering or underwatering stresses the tree and increases mortality risk. |
| Neglecting Soil Preparation | Failure to loosen and enrich soil reduces nutrient availability for roots. |
| Ignoring Tree Spacing | Crowding trees limits sunlight, inhibits growth, and increases disease risk. |
Tree Growth Timeline
Tree planting initiates a natural growth cycle essential for environmental health. Understanding the timeline of tree growth helps optimize care and conservation efforts.
- Germination (0-4 weeks) - Seeds sprout and develop roots establishing the foundation for growth.
- Seedling Stage (1 month - 1 year) - Trees grow small leaves and stems while adapting to their environment.
- Sapling Stage (1-5 years) - Significant height increase occurs as woody tissues strengthen.
- Juvenile Stage (5-15 years) - Trees focus on rapid growth and branch expansion for structural stability.
- Mature Stage (15+ years) - Trees reach full height, start producing seeds, and contribute to ecosystem balance.
Monitoring these stages ensures trees develop healthily and support biodiversity over time.
Urban Tree Planting Advantages
Why is urban tree planting important for cities? Trees in urban areas improve air quality by filtering pollutants and producing oxygen. They also help reduce urban heat by providing shade and cooling the environment.
What environmental benefits do urban trees offer? Urban trees increase biodiversity by creating habitats for birds and insects. They contribute to stormwater management by absorbing rainwater and reducing runoff.
How do trees impact the social well-being of city residents? Trees enhance mental health by offering green spaces for relaxation and recreation. Neighborhoods with more trees often experience lower crime rates and stronger community bonds.
In what ways do urban trees affect economic factors? Property values tend to rise in areas with more mature trees and greenery. Businesses benefit from increased foot traffic as tree-lined streets attract more customers.
What role do trees play in urban climate resilience? Trees help mitigate the effects of climate change by capturing carbon dioxide. They reduce energy costs by lowering the need for air conditioning during hot months.
How Trees Combat Climate Change
Trees absorb carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas, helping to reduce the overall concentration in the atmosphere. Their leaves release oxygen through photosynthesis, improving air quality and supporting life. Planting trees also cools the environment by providing shade and releasing moisture, mitigating the urban heat island effect.
