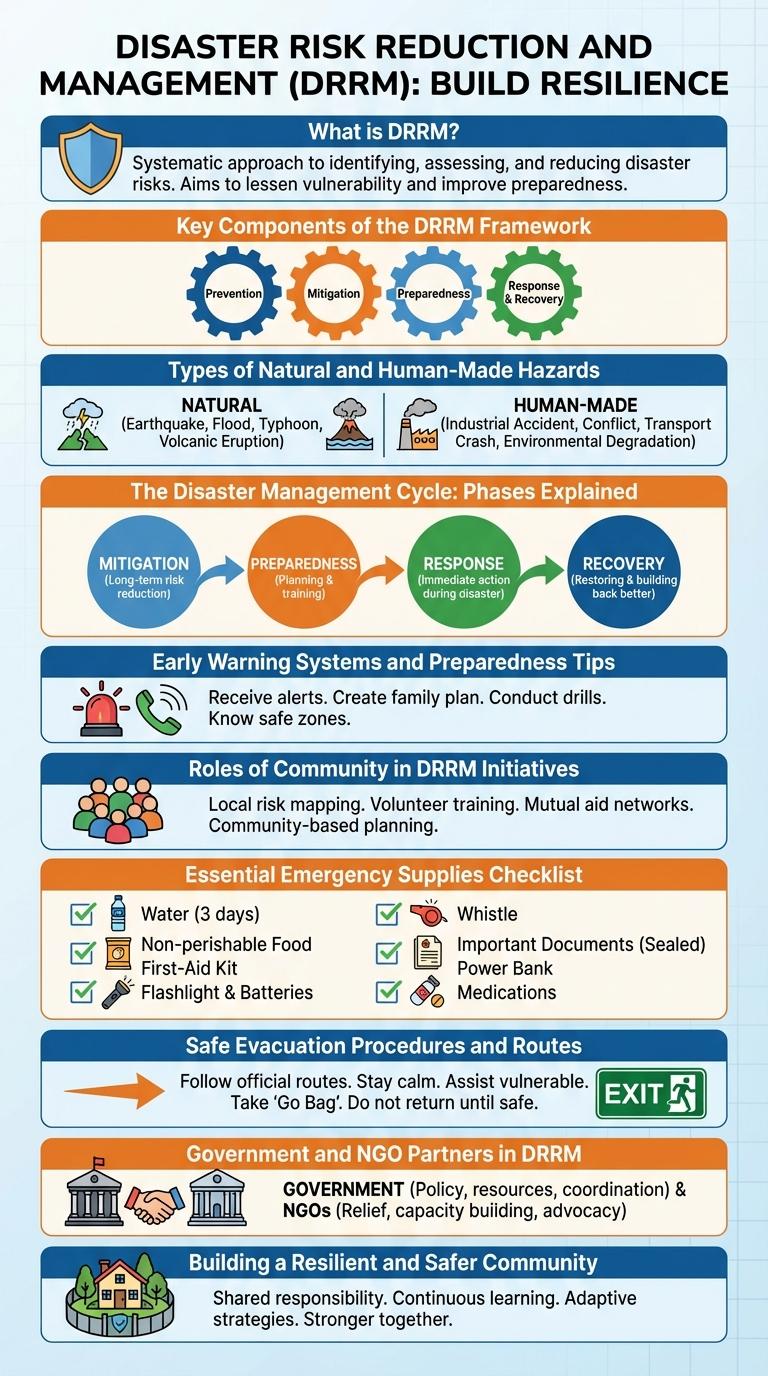
Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (DRRM) focuses on identifying hazards and building community resilience to minimize damage and loss during emergencies. This infographic breaks down key components such as preparedness, response, recovery, and mitigation strategies that are essential for effective DRRM. Visualizing these elements helps stakeholders understand roles, processes, and best practices to enhance safety and disaster readiness.
What is Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (DRRM)?
Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (DRRM) is a comprehensive approach aimed at minimizing the risks and impacts of disasters through effective strategies, policies, and actions. It focuses on building resilient communities by enhancing preparedness, reducing vulnerabilities, and promoting sustainable development.
DRRM involves risk assessment, early warning systems, and community engagement to mitigate disaster effects. It integrates disaster risk prevention, mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery in a continuous cycle. The goal is to protect lives, property, and the environment while ensuring faster recovery and sustainable growth.
Key Components of the DRRM Framework
Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (DRRM) framework consists of key components that ensure effective disaster preparedness, response, and recovery. These components include disaster prevention and mitigation, preparedness and early warning systems, response and relief operations, and rehabilitation and recovery efforts. Together, they build resilient communities capable of minimizing disaster impacts and promoting sustainable development.
Types of Natural and Human-Made Hazards
Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (DRRM) addresses both natural and human-made hazards to protect communities and infrastructure. Understanding these hazards is crucial for effective preparedness and response.
Natural hazards include earthquakes, floods, typhoons, volcanic eruptions, and landslides, originating from environmental forces. Human-made hazards involve industrial accidents, chemical spills, fires, armed conflicts, and technological failures caused by human activity.
The Disaster Management Cycle: Phases Explained
Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (DRRM) follows a continuous cycle aimed at minimizing the impact of hazards. Understanding the phases of this cycle enhances preparedness and resilience in communities.
- Prevention and Mitigation - Actions taken to avoid or reduce the severity of disasters before they occur.
- Preparedness - Planning and training to strengthen response capabilities for potential emergencies.
- Response - Immediate actions during and after a disaster to protect lives and property.
- Recovery - Efforts to restore normalcy and rebuild affected areas following a disaster.
The Disaster Management Cycle ensures a proactive approach to managing risks and enhancing community safety.
Early Warning Systems and Preparedness Tips
Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (DRRM) emphasizes the importance of Early Warning Systems (EWS) to minimize the impact of natural hazards. Preparedness tips enhance community resilience by promoting quick response and safety measures before disasters occur.
- Early Warning Systems provide timely alerts - These systems use technology and communication networks to inform communities about imminent threats.
- Evacuation plans are critical - Well-established routes and safe zones ensure orderly and safe movement during emergencies.
- Emergency kits improve survival - Having supplies like food, water, and first aid ready supports families during disaster events.
Roles of Community in DRRM Initiatives
The community plays a critical role in Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (DRRM) initiatives by actively participating in hazard identification, risk assessment, and resource mobilization. Community members enhance early warning systems through local knowledge and coordinated communication networks. Their involvement ensures sustainable preparedness, effective response, and quicker recovery during disasters.
Essential Emergency Supplies Checklist
Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (DRRM) emphasizes preparedness through essential emergency supplies. Having a well-stocked emergency kit is crucial for survival during natural disasters.
This checklist includes water, non-perishable food, first aid supplies, flashlights with batteries, and important documents. Regularly updating and personalizing the kit ensures readiness for various emergency situations.
Safe Evacuation Procedures and Routes
| Safe Evacuation Procedures | Evacuation Routes |
|---|---|
| Stay calm and listen to official alerts. | Identify nearest emergency exits in buildings. |
| Follow designated evacuation signs and instructions. | Use pre-planned community evacuation routes. |
| Assist children, elderly, and persons with disabilities. | Avoid main roads prone to congestion during disasters. |
| Do not use elevators during emergencies. | Move quickly but safely to assembly points. |
| Prepare an emergency kit with essentials. | Regularly review and practice evacuation plans. |
Government and NGO Partners in DRRM
Who are the key government and NGO partners involved in Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (DRRM)? Government agencies such as the National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council (NDRRMC) coordinate efforts nationwide. Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) like the Philippine Red Cross provide vital support in emergency response and community resilience building.
How do these partners collaborate in DRRM? They share resources, expertise, and information to enhance preparedness, response, and recovery operations. Joint training programs and disaster drills are commonly conducted to ensure coordinated action during emergencies.
What are the main roles of government agencies in DRRM? Agencies are responsible for policy-making, resource allocation, and overall disaster management coordination. Local government units implement localized risk reduction strategies and conduct community awareness campaigns.
What contributions do NGOs make to DRRM efforts? NGOs often focus on grassroots-level risk assessment, capacity building, and providing humanitarian aid. They mobilize volunteers and offer specialized services such as medical assistance and psychosocial support.
Why is partnership between government and NGOs essential in DRRM? Collaborative partnerships maximize resource efficiency and disaster response effectiveness. Such alliances build community resilience and ensure timely and comprehensive disaster relief operations.
