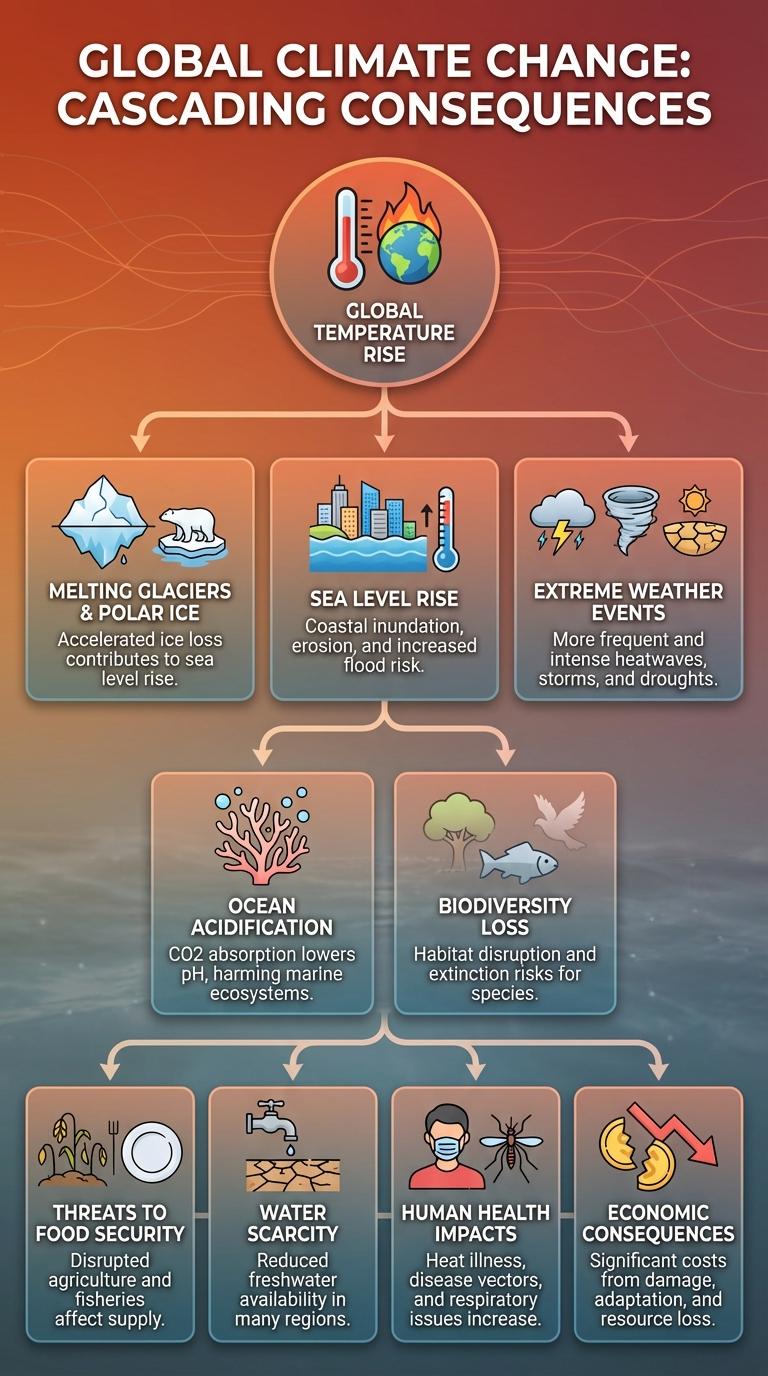
Rising global temperatures intensify extreme weather events, causing widespread ecological damage and threatening biodiversity. Melting ice caps and glaciers lead to sea level rise, increasing the risk of coastal flooding and habitat loss. Shifts in climate patterns disrupt agriculture, water resources, and human health worldwide.
Global Temperature Rise
The global temperature has increased by approximately 1.2degC since the pre-industrial era, significantly altering weather patterns worldwide. This rise accelerates the effects of climate change, impacting ecosystems, sea levels, and human health.
- Record-Breaking Heatwaves - Increased global temperatures cause more frequent and intense heatwaves affecting millions.
- Melting Polar Ice - Rising temperatures accelerate the loss of polar ice caps, contributing to rising sea levels.
- Ecosystem Disruption - Temperature rise alters habitats, threatening species survival and biodiversity.
Melting Glaciers & Polar Ice
Melting glaciers and polar ice significantly contribute to rising sea levels worldwide. This accelerates coastal erosion and increases the risk of flooding in low-lying areas.
The loss of reflective ice surfaces reduces Earth's albedo, causing more solar energy to be absorbed by the oceans. This intensifies global warming and disrupts marine ecosystems dependent on stable temperatures.
Sea Level Rise
Sea level rise is a direct consequence of climate change, driven by melting glaciers and the thermal expansion of seawater. This phenomenon threatens coastal communities and ecosystems worldwide.
Rising sea levels increase the frequency and severity of coastal flooding, leading to habitat loss for plants, animals, and humans. Saltwater intrusion into freshwater resources affects agriculture and drinking water supplies. Increased erosion damages infrastructure and disrupts local economies dependent on coastal tourism and fisheries.
Extreme Weather Events
Climate change significantly increases the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events worldwide. These changes disrupt ecosystems, endanger lives, and cause substantial economic damage.
Extreme weather events linked to climate change include hurricanes, heatwaves, floods, droughts, and wildfires.
- Hurricanes - Warmer ocean temperatures fuel stronger and more destructive hurricanes, resulting in increased coastal damage and flooding.
- Heatwaves - Rising global temperatures lead to more frequent and severe heatwaves, posing serious health risks and straining energy systems.
- Floods - Increased precipitation intensity and rising sea levels cause more frequent and severe flooding in vulnerable regions.
Ocean Acidification
What is ocean acidification and how does it affect marine life?
Ocean acidification occurs when seawater absorbs excess carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere, lowering its pH. This process harms marine organisms, especially those with calcium carbonate shells, such as corals, mollusks, and some plankton species.
| Effect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Coral Reefs | Reduced calcification rates lead to weaker coral structures and loss of biodiversity. |
| Shellfish | Difficulty in shell formation causes population declines in oysters, clams, and mussels. |
| Plankton | Altered development affects the marine food web and fish populations. |
| Marine Ecosystems | Disruption of habitats results in loss of species and ecological imbalance. |
| Fisheries | Decreased fish stocks impact food security and coastal economies worldwide. |
Biodiversity Loss
Climate change accelerates biodiversity loss by altering habitats, leading to the extinction of numerous plant and animal species. Rising temperatures and shifting weather patterns disrupt ecosystems, making it difficult for species to adapt. Conservation efforts face significant challenges as the natural balance of life is increasingly destabilized worldwide.
Threats to Food Security
Climate change significantly threatens global food security by altering agricultural productivity and disrupting supply chains. Increasing temperatures, unpredictable rainfall, and extreme weather events challenge crop growth and food distribution systems.
- Reduced Crop Yields - Rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns limit the growth of staple crops like wheat, rice, and maize.
- Soil Degradation - Increased frequency of droughts and floods leads to nutrient loss and decreased soil fertility, impacting farm productivity.
- Supply Chain Disruptions - Extreme weather events damage infrastructure and transport routes, delaying food delivery and increasing waste.
Addressing these threats requires adaptive farming techniques and sustainable resource management to ensure future food availability.
Water Scarcity
Climate change intensifies water scarcity by altering precipitation patterns and increasing evaporation rates. Regions already vulnerable to drought face prolonged dry spells, reducing freshwater availability.
Water scarcity affects agriculture, drinking water supplies, and sanitation, impacting millions globally. Sustainable water management and conservation efforts are critical to address these growing challenges.
Human Health Impacts
| Effect | Impact on Human Health |
|---|---|
| Heatwaves | Increased cases of heat-related illnesses and fatalities, especially among elderly and vulnerable populations |
| Air Quality | Higher levels of air pollution and allergens contribute to respiratory diseases such as asthma and bronchitis |
| Vector-borne Diseases | Expanded habitats for mosquitoes and ticks increase the spread of diseases like malaria, dengue, and Lyme disease |
| Water Quality | Contaminated water sources lead to higher incidences of waterborne illnesses including cholera and diarrhea |
| Mental Health | Stress, anxiety, and trauma rise due to extreme weather events and displacement |
