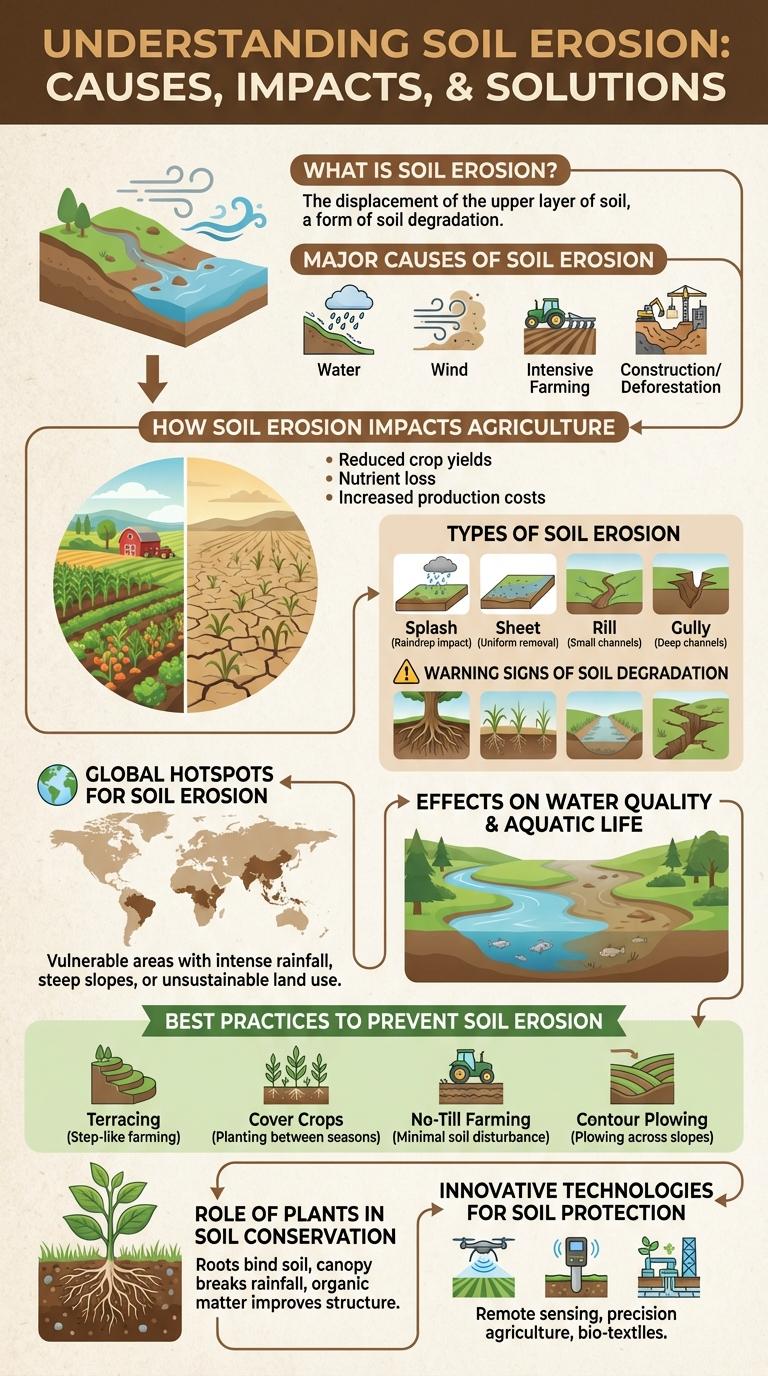
Soil erosion significantly impacts agricultural productivity and environmental health by removing the fertile top layer of soil. Understanding the causes, effects, and prevention methods of soil erosion helps promote sustainable land management practices. This infographic visually presents key data and strategies to combat soil degradation effectively.
What is Soil Erosion?
Soil erosion is the process by which the top layer of soil is removed by natural forces such as wind and water. This degradation reduces soil fertility and disrupts ecosystems.
It occurs when protective vegetation cover is lost due to activities like deforestation, overgrazing, and poor agricultural practices. Soil erosion contributes to sedimentation in waterways, impacting water quality and aquatic life.
Major Causes of Soil Erosion
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Water Runoff | Heavy rainfall and improper water management cause soil particles to be washed away. |
| Wind | Strong wind velocities lift and remove topsoil, especially in dry, barren areas. |
| Deforestation | Removal of trees leaves soil exposed, reducing organic matter and root protection. |
| Agricultural Practices | Intensive farming, overgrazing, and lack of crop rotation degrade soil structure. |
| Construction Activities | Land clearing and excavation disrupt soil layers and increase susceptibility to erosion. |
How Soil Erosion Impacts Agriculture
Soil erosion significantly reduces the productivity of agricultural land by removing the nutrient-rich topsoil. This process undermines crop yields and increases vulnerability to drought and flooding.
- Soil Nutrient Loss - Erosion strips away essential nutrients, depleting soil fertility and hindering plant growth.
- Reduced Water Retention - Eroded soils retain less water, leading to increased irrigation needs and crop stress.
- Crop Yield Decline - Loss of topsoil directly correlates with lower agricultural output and economic losses for farmers.
Implementing soil conservation techniques is crucial to sustaining agricultural productivity and food security.
Types of Soil Erosion
What are the main types of soil erosion that impact land quality? Soil erosion primarily occurs in four types: water erosion, wind erosion, tillage erosion, and mass movement. Each type affects the soil differently, leading to loss of fertile topsoil and reduced agricultural productivity.
Warning Signs of Soil Degradation
Soil erosion is a critical environmental issue that leads to the loss of fertile topsoil, reducing agricultural productivity and harming ecosystems. Recognizing early warning signs of soil degradation helps prevent long-term damage and supports sustainable land management.
Key warning signs include increased surface runoff after rainfall, noticeable loss of soil depth, and the presence of gullies or rills on land surfaces. Vegetation decline and reduced soil organic matter also indicate soil health deterioration. These signs signal the need for immediate conservation efforts to protect and restore soil quality.
Global Hotspots for Soil Erosion
Soil erosion is a critical environmental issue affecting agricultural productivity and ecosystem stability worldwide. Certain regions experience higher rates of soil degradation, known as global hotspots for soil erosion.
Major hotspots include parts of Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, Southeast Asia, and Latin America, where deforestation, overgrazing, and unsustainable farming practices accelerate soil loss. These areas face severe impacts on food security, water quality, and biodiversity.
Effects on Water Quality and Aquatic Life
Soil erosion significantly decreases water quality by increasing sedimentation and introducing pollutants into water bodies. Sediment runoff clouds water, disrupts photosynthesis, and smothers aquatic habitats, leading to reduced biodiversity. Contaminants such as pesticides and fertilizers attached to eroded soil further harm fish and other aquatic organisms, disrupting ecosystems.
Best Practices to Prevent Soil Erosion
Soil erosion threatens agricultural productivity and environmental health worldwide. Implementing effective prevention techniques can significantly reduce soil loss and improve land sustainability.
- Contour Farming - Plowing along the natural contours of the land helps slow water runoff and minimize soil erosion.
- Cover Crops - Planting cover crops protects soil from erosion by maintaining ground cover and improving soil structure.
- Terracing - Creating stepped levels on slopes reduces water flow speed and prevents soil displacement.
Role of Plants in Soil Conservation
Plants play a crucial role in soil conservation by stabilizing the soil with their root systems, which reduce erosion caused by wind and water. Vegetation cover acts as a natural barrier, slowing down surface runoff and allowing water to infiltrate the soil more effectively. Diverse plant species enhance soil structure and fertility, promoting long-term soil health and preventing degradation.
