Waste segregation enhances recycling efficiency and reduces environmental impact by separating materials like plastics, paper, and organic waste. Proper sorting minimizes landfill overflow and promotes the reuse of valuable resources. Clear guidelines in an infographic help individuals and communities adopt sustainable waste management practices effectively.
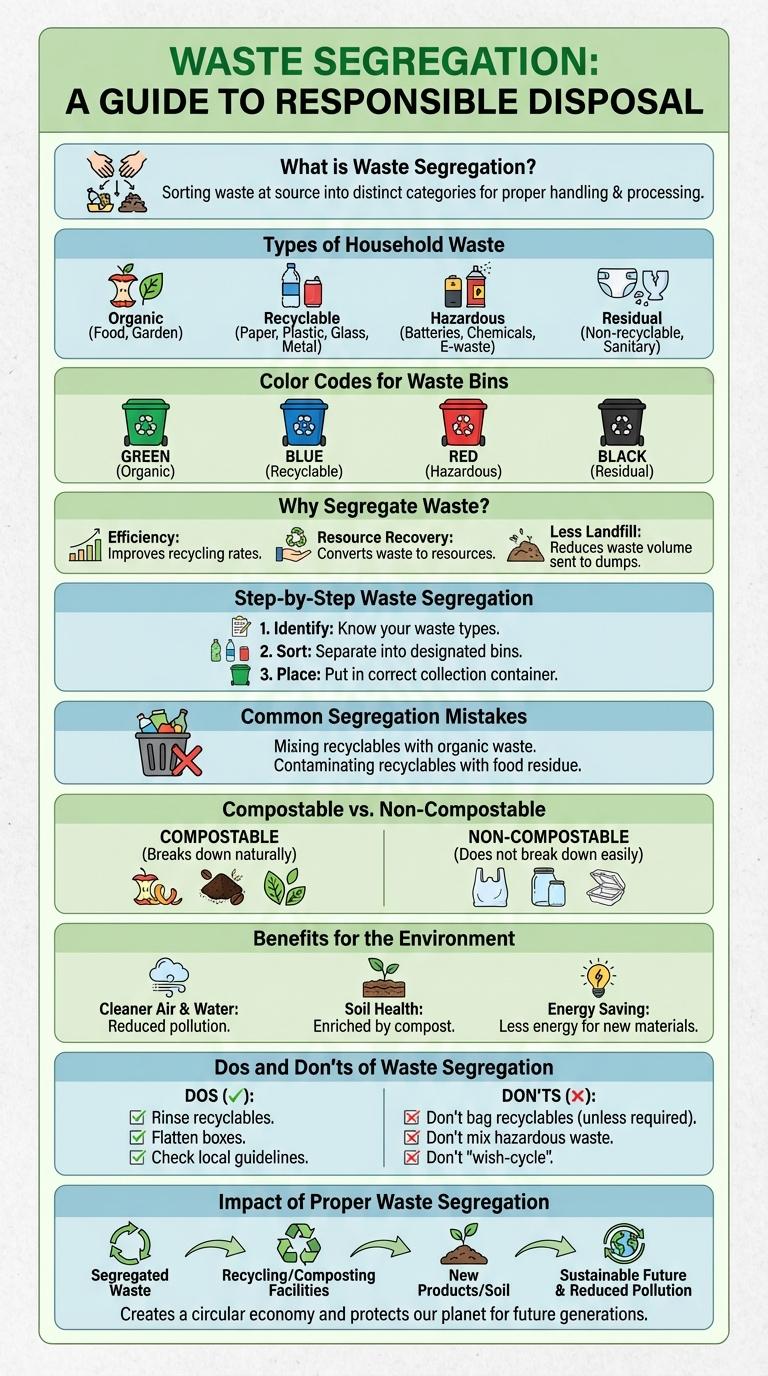
What is Waste Segregation?
Waste segregation is the process of separating waste into different categories based on material type. It helps in efficient recycling, reducing landfill use, and minimizing environmental pollution. Proper segregation ensures that organic, recyclable, hazardous, and general wastes are managed appropriately for sustainable waste disposal.
Types of Household Waste
What are the main types of household waste that require segregation? Proper segregation helps in efficient recycling and waste management. Separating waste reduces environmental impact and conserves resources.
| Type of Waste | Description |
|---|---|
| Organic Waste | Food scraps, garden waste, and biodegradable materials suitable for composting. |
| Recyclable Waste | Paper, cardboard, plastics, glass, and metals that can be processed and reused. |
| Hazardous Waste | Items like batteries, chemicals, paints, and electronic waste needing special disposal. |
| General Waste | Non-recyclable and non-hazardous items, usually destined for landfills. |
| E-waste | Electronic devices such as phones, computers, and appliances requiring specialized recycling. |
Color Codes for Waste Bins
Waste segregation is essential for effective recycling and environmental conservation. Using color-coded bins helps in the easy identification and proper disposal of different types of waste.
Each color represents a specific category: green for organic waste, blue for recyclables like paper and plastics, red for hazardous waste, black for general or non-recyclable waste, and yellow for metals and glass. Proper use of these bins reduces contamination, making recycling processes more efficient. Clear labeling and public awareness enhance compliance with waste segregation guidelines.
Why Segregate Waste?
Waste segregation separates waste into categories to improve recycling and reduce landfill use. Proper segregation helps protect the environment and conserve natural resources.
- Reduces Pollution - Sorting waste prevents hazardous materials from contaminating soil and water.
- Enhances Recycling Efficiency - Segregated waste allows recyclers to process materials more effectively.
- Conserves Resources - Recycling materials means fewer raw materials need to be extracted from nature.
Effective waste segregation supports sustainable waste management and a cleaner planet.
Step-by-Step Waste Segregation
| Step | Action for Waste Segregation |
|---|---|
| Step 1: Identify Waste Types | Separate waste into categories such as organic, recyclable, hazardous, and landfill. |
| Step 2: Use Designated Bins | Place waste in color-coded bins: green for organic, blue for recyclables, red for hazardous, and black for landfill. |
| Step 3: Clean Recyclables | Rinse containers and remove food residues to avoid contamination in recycling streams. |
| Step 4: Compost Organic Waste | Collect food scraps and garden waste separately for composting to reduce landfill use. |
| Step 5: Dispose Hazardous Waste Properly | Store batteries, chemicals, and electronic waste safely and deliver them to authorized disposal centers. |
Common Segregation Mistakes
Waste segregation is essential for efficient recycling and environmental protection. Incorrect sorting can lead to contamination, reducing the effectiveness of recycling programs.
Common segregation mistakes include mixing recyclables with organic waste and disposing of hazardous materials in general trash. Properly separating waste ensures materials are processed correctly and reduces landfill overflow.
Compostable vs. Non-Compostable
Waste segregation is crucial for effective composting and reducing landfill waste. Differentiating compostable from non-compostable materials helps improve recycling efficiency and environmental health.
- Compostable Waste - Organic materials like fruit peels, coffee grounds, and vegetable scraps break down naturally into nutrient-rich compost.
- Non-Compostable Waste - Items such as plastics, metals, and synthetic fabrics do not decompose biologically and must be disposed of separately.
- Environmental Impact - Proper segregation reduces greenhouse gas emissions and supports soil regeneration through compost use.
Benefits for the Environment
Waste segregation separates recyclable, compostable, and landfill materials at the source, reducing environmental pollution. Proper sorting minimizes hazardous waste contamination and conserves natural resources by enabling material recovery.
This process decreases landfill overflow and lowers greenhouse gas emissions by diverting organic waste from landfills. Efficient waste segregation supports sustainable waste management and protects ecosystems from harmful pollutants.
Dos and Don'ts of Waste Segregation
Effective waste segregation reduces environmental pollution and promotes recycling. Following the right practices ensures proper disposal and resource recovery.
- Do separate biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste - Sorting waste at the source helps streamline recycling and composting processes.
- Do use color-coded bins for different waste types - Using designated bins reduces contamination and simplifies waste management.
- Do rinse containers before recycling - Cleaning recyclable items prevents odor and pests, improving recycling quality.
- Don't mix hazardous waste with regular trash - Hazardous materials require special handling to avoid health risks and environmental damage.
- Don't dispose of electronic waste in general bins - E-waste should be collected separately to enable proper recycling of valuable components.
