Taal Volcano, located in the Philippines, is one of the most active and complex volcanoes in the world, renowned for its stunning crater lake and frequent eruptions. This infographic highlights its geological features, eruption history, and the impact on surrounding communities. Understanding Taal's behavior is essential for disaster preparedness and risk management in the region.
Taal Volcano: An Overview
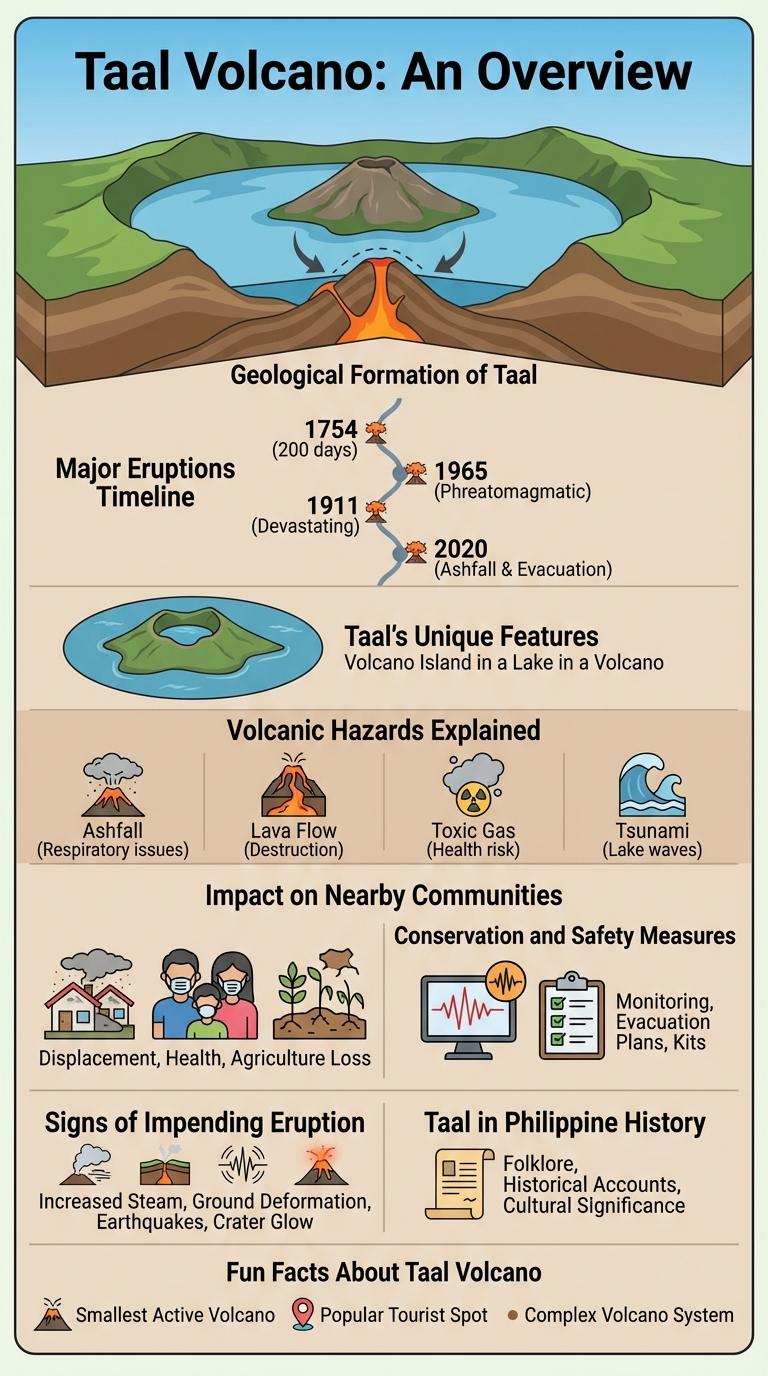
Taal Volcano is one of the most active volcanoes in the Philippines, located on the island of Luzon within Batangas province. It features a unique volcanic lake surrounding a crater lake, forming a complex volcanic island system. Taal's eruptions have historically caused significant impact due to its proximity to densely populated areas.
Geological Formation of Taal
Taal Volcano, located on Luzon Island in the Philippines, is one of the most active volcanoes in the country. It consists of a complex caldera filled by Taal Lake, formed from previous massive eruptions.
The geological formation began around 500,000 years ago, shaped by multiple explosive eruptions and lava dome collapses. The current caldera measures approximately 25 kilometers in diameter, featuring a lake and a central volcanic island known as Volcano Island.
Major Eruptions Timeline
Taal Volcano, located in the Philippines, is one of the country's most active and dangerous volcanoes. Its eruptions have significantly impacted local communities and the environment throughout history.
- 1754 Eruption - A major eruption that lasted nearly a year, causing widespread ashfall and volcanic activity in Luzon.
- 1911 Eruption - This eruption resulted in pyroclastic flows and the deaths of over 1,300 people.
- 1965 Eruption - Produced lava fountains and ash plumes prompting evacuations in surrounding areas.
- 2020 Eruption - A sudden phreatomagmatic eruption led to volcanic earthquakes and ashfall over nearby provinces.
- 2021 Activity - Continued unrest with steam emissions and ground deformation signaling potential future eruptions.
Taal's eruption history highlights the need for continuous monitoring and preparedness in the region.
Taal's Unique Features
What makes Taal Volcano unique among the world's volcanoes? Taal Volcano is a complex volcano located on Luzon Island in the Philippines, famous for its nested caldera structure. It features a lake-filled caldera with a smaller volcanic island at its center, creating a rare "volcano within a volcano" phenomenon.
Why is Taal's volcanic activity significant? Taal is one of the most active volcanoes in the Philippines, with historical eruptions affecting surrounding communities and ecosystems. Its frequent eruptions provide valuable data for volcanologists studying volcanic behavior and risk mitigation.
How does Taal's geology contribute to its uniqueness? Taal's caldera formed from a massive eruption thousands of years ago, followed by subsequent smaller eruptions that shaped its current structure. The presence of the crater lake and volcanic island combination is a distinctive geological feature rarely seen in active volcanoes.
What ecological aspects does Taal Volcano support? The caldera lake surrounding the volcano island hosts diverse aquatic species, while the island itself supports unique terrestrial flora and fauna adapted to volcanic conditions. This biodiversity highlights the ecological importance of volcanic landscapes.
How does Taal Volcano impact local culture and tourism? Taal is a popular destination for eco-tourism and scientific study, attracting visitors fascinated by its dramatic scenery and volcanic activity. The volcano holds cultural significance for local communities, symbolizing natural power and resilience.
Volcanic Hazards Explained
| Volcanic Hazard | Description |
|---|---|
| Phreatic Eruptions | Sudden steam-driven explosions caused by groundwater heating, ejecting ash and rock fragments without new magma. |
| Tephra Falls | Layers of ash, lapilli, and volcanic bombs fall from eruption columns, impacting air quality and structures around Taal Volcano. |
| Lava Flows | Molten rock flows from the volcano's vents, destroying vegetation and infrastructure near the crater lake. |
| Volcanic Gas Emissions | Release of gases such as sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide can cause respiratory problems and contribute to acid rain. |
| Base Surges | Rapid lateral blasts of hot gas and tephra from phreatomagmatic explosions that can impact areas close to the eruption site. |
Impact on Nearby Communities
Taal Volcano, located in the Philippines, is one of the most active volcanoes in the region. Its eruptions have significantly impacted the lives of nearby communities.
The 2020 eruption caused widespread ashfall, affecting thousands of residents in Batangas and Cavite provinces. Many families were forced to evacuate due to volcanic ash and lava flows, leading to temporary displacement. The local economy, heavily reliant on agriculture and tourism, experienced substantial disruption from the volcanic activity.
Conservation and Safety Measures
Taal Volcano, located in the Philippines, is one of the most active volcanoes in the region, necessitating rigorous conservation and safety measures. Efforts focus on preserving the surrounding natural environment while ensuring the safety of residents and tourists.
Monitoring systems track volcanic activity continuously to provide early warnings and reduce risk. Evacuation plans and restricted zones are implemented to minimize exposure to volcanic hazards.
Signs of Impending Eruption
Taal Volcano exhibits several signs of impending eruption, including increased seismic activity such as frequent volcanic earthquakes. Ground deformation and swelling around the volcano indicate magma movement beneath the surface. Gas emissions, particularly sulfur dioxide, surge significantly before an eruption, signaling volcanic unrest.
Taal in Philippine History
Taal Volcano is a significant natural feature in the Philippines with a rich history that has influenced local culture and events. Its eruptions have been recorded throughout Philippine history, affecting communities and the development of the region.
Located on the island of Luzon, Taal is one of the most active volcanoes in the country and a key part of Philippine heritage.
- Historical Eruptions - Taal Volcano has erupted over 30 times since the 16th century, impacting the lives and settlements around it.
- Colonial Era - The volcano played a role during Spanish colonization, serving as a natural barrier and influencing local resistance efforts.
- Cultural Significance - Taal is embedded in local folklore and traditions, symbolizing both destruction and rebirth for communities.
