Climate change results from the accumulation of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane in the atmosphere, primarily caused by human activities such as fossil fuel combustion and deforestation. These changes lead to effects including rising global temperatures, melting polar ice, and increased frequency of extreme weather events. Understanding the cause-and-effect relationships depicted in the infographic helps reveal the urgent need for sustainable actions to mitigate environmental impact.
Unveiling Climate Change: Causes & Effects
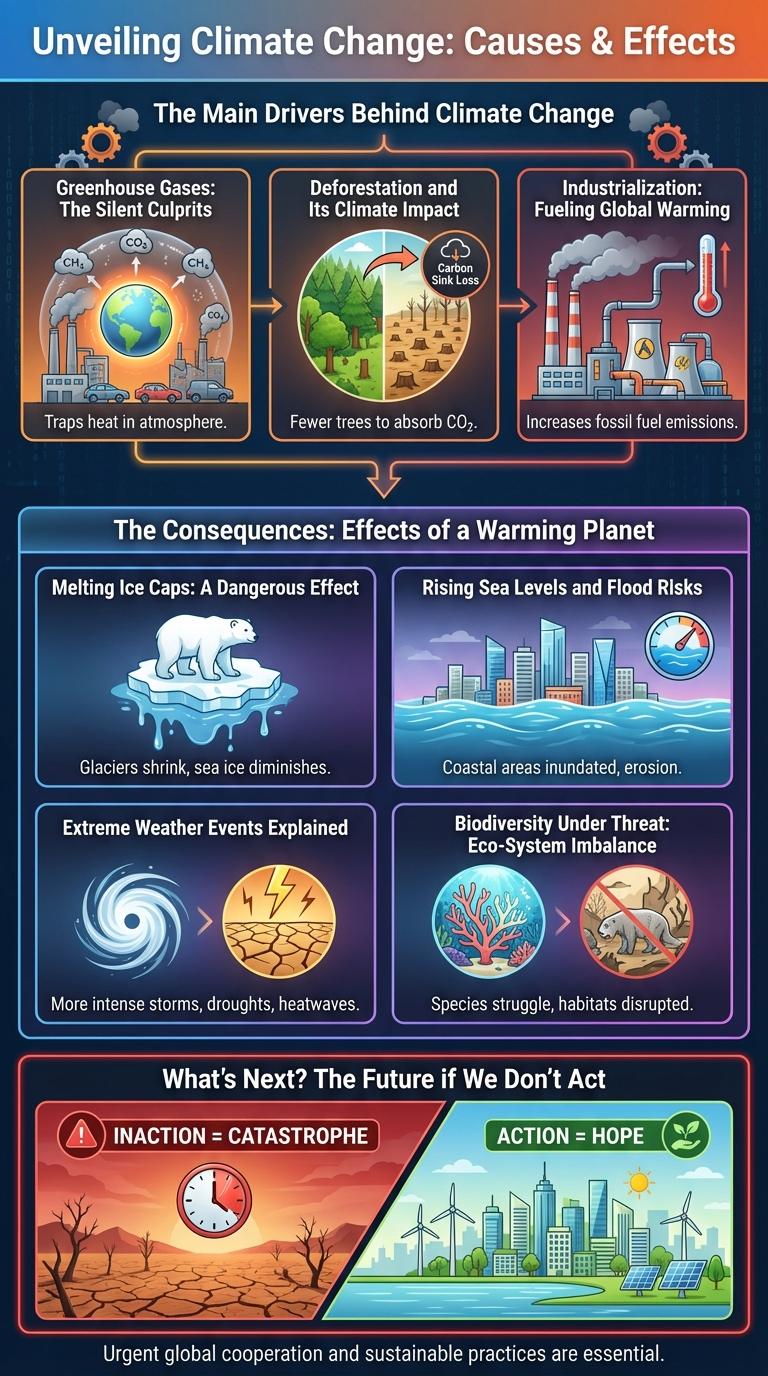
Unveiling Climate Change reveals the primary causes driving global temperature rise, including greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial activities. These changes result in severe environmental effects such as rising sea levels, increased frequency of extreme weather events, and loss of biodiversity. Understanding the intricate link between human actions and climate impacts is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies.
The Main Drivers Behind Climate Change
What are the main drivers behind climate change? Human activities, especially the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes, significantly increase greenhouse gas emissions. These emissions trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to global warming and dramatic shifts in climate patterns.
Greenhouse Gases: The Silent Culprits
Greenhouse gases are invisible agents driving global climate change by trapping heat in the Earth's atmosphere. These gases originate from both natural processes and human activities, significantly altering weather patterns and ecosystems.
- Carbon Dioxide Emissions - Primarily from burning fossil fuels, carbon dioxide is the largest contributor to the greenhouse effect, increasing global temperatures.
- Methane Release - Produced by agriculture and landfills, methane has a heat-trapping ability over 25 times greater than carbon dioxide over 100 years.
- Nitrous Oxide Sources - Emitted from agricultural fertilizers and industrial processes, nitrous oxide contributes to ozone layer depletion and climate warming.
Deforestation and Its Climate Impact
Deforestation contributes significantly to climate change by reducing the number of trees that absorb carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas. This process increases atmospheric CO2 levels, accelerating global warming.
The removal of forests disrupts local weather patterns and reduces biodiversity, weakening ecosystems' resilience. It also releases stored carbon from trees and soil, further intensifying climate change effects.
Industrialization: Fueling Global Warming
Industrialization has significantly increased the emission of greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide and methane, contributing to global warming. The widespread use of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas in factories and transportation accelerates the accumulation of heat-trapping gases in the atmosphere.
Since the Industrial Revolution, carbon dioxide levels have risen from approximately 280 parts per million (ppm) to over 420 ppm today. This increase intensifies the greenhouse effect, causing global temperatures to rise. Consequences include more frequent heatwaves, melting polar ice, and disruptions to ecosystems worldwide.
Melting Ice Caps: A Dangerous Effect
Climate change is accelerating the melting of ice caps, posing a significant threat to global ecosystems. This phenomenon leads to rising sea levels and disrupts weather patterns worldwide.
- Rising Sea Levels - Melting ice caps contribute to higher sea levels, increasing the risk of coastal flooding and habitat loss.
- Loss of Habitat - Polar species like polar bears and seals lose their natural habitats due to shrinking ice caps.
- Climate Feedback Loops - Reduced ice cover decreases Earth's albedo, causing more heat absorption and faster melting.
The ongoing melting of ice caps demands urgent global action to mitigate climate change impacts.
Rising Sea Levels and Flood Risks
Climate change accelerates the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers, leading to rising sea levels worldwide. This increase threatens coastal communities with higher flood risks and more frequent storm surges.
Rising sea levels exacerbate coastal erosion and disrupt marine ecosystems. Flood risks endanger infrastructure, displace populations, and cause significant economic losses in vulnerable regions.
Extreme Weather Events Explained
| Cause | Effect |
|---|---|
| Rising Global Temperatures | Increased frequency of heatwaves |
| Higher Ocean Temperatures | More intense hurricanes and typhoons |
| Melting Polar Ice Caps | Rising sea levels causing coastal flooding |
| Changes in Atmospheric Circulation | Unpredictable storm patterns and longer droughts |
| Increased Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Amplified extreme weather events worldwide |
Biodiversity Under Threat: Eco-System Imbalance
Climate change significantly disrupts biodiversity by altering habitats and threatening species survival. These changes create an imbalanced ecosystem, reducing its resilience and function.
- Habitat Loss - Rising temperatures and extreme weather events destroy natural habitats essential for diverse species.
- Species Extinction - Altered environmental conditions lead to increased extinction rates, impacting ecosystem stability.
- Disrupted Food Chains - Changes in species populations disturb predator-prey relationships, causing ecological imbalance.
