Global climatic phenomena significantly influence Earth's ecosystems, weather patterns, and biodiversity. Understanding these effects through clear visual data highlights the urgency of addressing climate change. Infographics effectively communicate complex interactions between phenomena like El Nino, La Nina, and global warming on our planet's health.
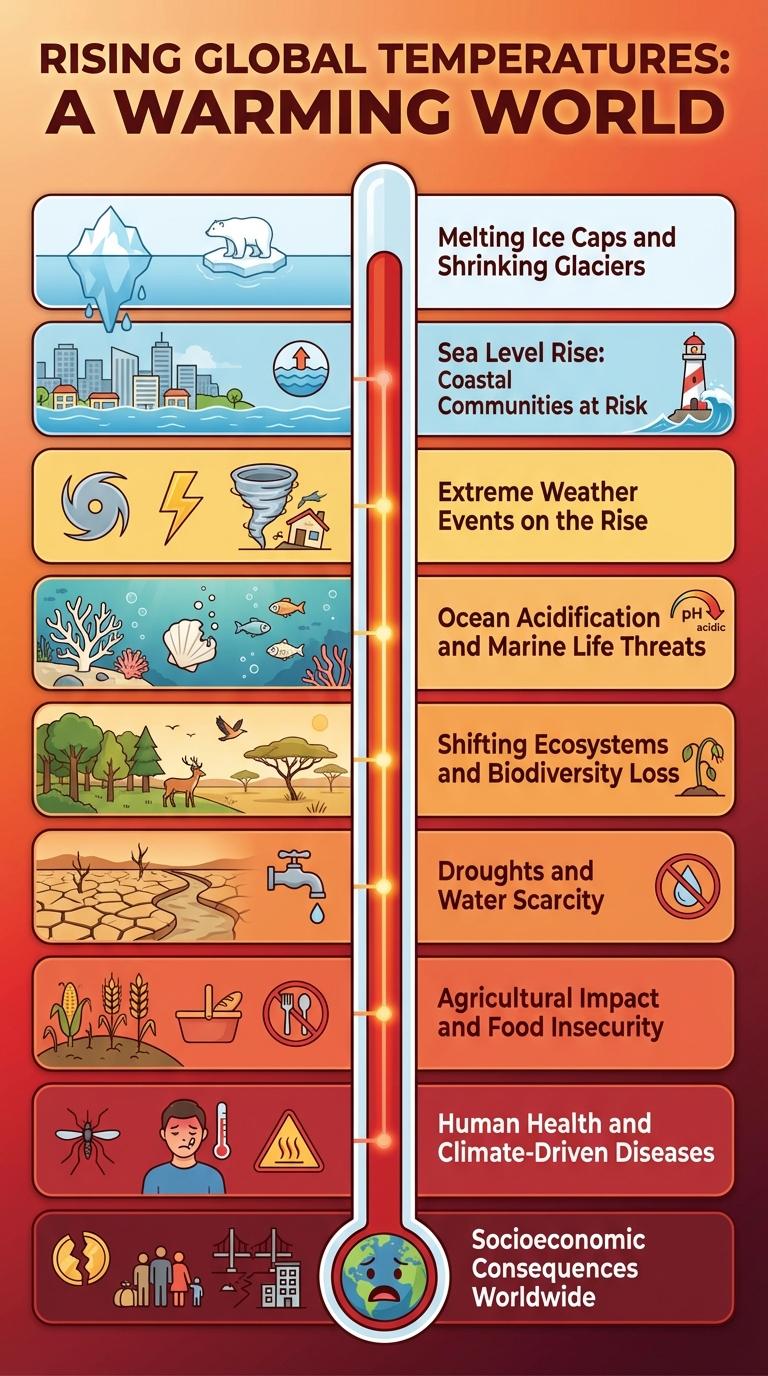
Rising Global Temperatures: A Warming World
How do rising global temperatures affect our planet? Increasing global temperatures cause glaciers to melt and sea levels to rise. These changes disrupt ecosystems and threaten biodiversity worldwide.
What drives the rise in Earth's temperature? Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities trap heat in the atmosphere, creating a warming effect. This intensifies climate-related events and shifts weather patterns.
Which regions experience the most impact? Polar areas warm faster than the global average, accelerating ice sheet loss in Antarctica and the Arctic. Meanwhile, tropical regions face stronger heatwaves and droughts.
How does warming influence ocean health? Higher temperatures lead to coral bleaching and reduced marine biodiversity. Ocean currents and chemistry alter, affecting fish populations and coastal communities.
What are the consequences for human societies? Rising temperatures increase heat-related illnesses and reduce agricultural productivity. Water scarcity and extreme weather events pose growing risks to livelihoods worldwide.
Melting Ice Caps and Shrinking Glaciers
Global climatic phenomena are profoundly impacting Earth's natural systems, with melting ice caps and shrinking glaciers serving as critical indicators of climate change. These transformations threaten ecosystems, sea levels, and human communities worldwide.
- Rising Temperatures Accelerate Ice Melt - Average global temperatures have increased by approximately 1.1degC since pre-industrial times, driving rapid melting of polar ice caps and mountain glaciers.
- Sea Level Rise Increases Flood Risks - Melting ice contributes to an estimated 3.3 millimeters of sea-level rise annually, raising the threat of coastal flooding and erosion.
- Loss of Freshwater Resources - Shrinking glaciers reduce freshwater availability for over 1 billion people relying on glacial melt for drinking, agriculture, and hydropower.
Sea Level Rise: Coastal Communities at Risk
Sea level rise is a direct consequence of global climatic phenomena such as melting polar ice caps and thermal expansion of seawater. This gradual increase threatens coastal communities by increasing the frequency and severity of flooding events.
Many low-lying areas face displacement risks, affecting millions of people worldwide. Infrastructure damage and loss of habitat for marine and terrestrial species further exacerbate the socio-economic challenges in these vulnerable regions.
Extreme Weather Events on the Rise
Global climatic phenomena are intensifying extreme weather events worldwide. These events severely impact ecosystems, economies, and human lives.
- Increased Frequency - The number of hurricanes, heatwaves, and floods has significantly risen in the last two decades.
- Stronger Storms - Warmer ocean temperatures fuel more powerful tropical cyclones and hurricanes.
- Unpredictable Patterns - Climate change disrupts historical weather patterns, causing extreme droughts and heavy rainfall.
Addressing the rise in extreme weather requires urgent global climate action and adaptation strategies.
Ocean Acidification and Marine Life Threats
Global climatic phenomena significantly impact Earth's oceans, causing ocean acidification that threatens marine ecosystems. Increased carbon dioxide levels dissolve in seawater, lowering pH and disrupting marine life.
Ocean acidification harms coral reefs, leading to weakened structures and loss of biodiversity. Shell-forming organisms like mollusks and plankton struggle to maintain their shells, affecting the entire marine food web. This disruption endangers fish species vital for human food resources and marine biodiversity.
Shifting Ecosystems and Biodiversity Loss
Global climatic phenomena such as rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns are causing significant shifts in ecosystems across the planet. These changes disrupt habitat conditions, forcing species to migrate, adapt, or face extinction.
Biodiversity loss accelerates as specialized species lose their natural habitats and food sources. This imbalance threatens ecosystem stability, reducing nature's ability to provide essential services like pollination and carbon sequestration.
Droughts and Water Scarcity
Droughts and water scarcity are critical global climatic phenomena affecting millions of people and ecosystems. Reduced rainfall and rising temperatures lead to prolonged dry periods, severely impacting agriculture, drinking water supplies, and biodiversity. Regions such as Sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East, and parts of Australia face the most intense water shortages, threatening food security and health.
Agricultural Impact and Food Insecurity
Global climatic phenomena significantly disrupt agricultural productivity, leading to increased food insecurity worldwide. These changes challenge food systems and threaten the livelihood of millions dependent on farming.
- Reduced Crop Yields - Extreme weather events such as droughts and floods damage crops and lower harvest volumes.
- Soil Degradation - Rising temperatures and erratic rainfall accelerate soil erosion and nutrient depletion, undermining soil health.
- Increased Pest and Disease Pressure - Changing climate patterns expand the range and lifecycle of pests and plant diseases, harming crops.
Human Health and Climate-Driven Diseases
| Climate Phenomenon | Impact on Human Health & Diseases |
|---|---|
| Heatwaves | Increase in heat-related illnesses and mortality, especially among elderly and infants. |
| Flooding | Rise in waterborne diseases like cholera and leptospirosis due to contaminated water sources. |
| Drought | Malnutrition and respiratory problems caused by crop failures and dust exposure. |
| Vector Expansion | Spread of diseases such as malaria and dengue as mosquitoes and ticks inhabit new regions. |
| Extreme Storms | Increased injury, mental health disorders, and disruption of healthcare infrastructure. |
