The Sierra Madre mountain range stretches across multiple countries, offering stunning landscapes and diverse ecosystems. Rich in biodiversity, it hosts numerous endemic species and is crucial for regional climate regulation. This infographic highlights key geographical features, wildlife, and conservation efforts within the Sierra Madre.
Sierra Madre: A Biodiversity Hotspot
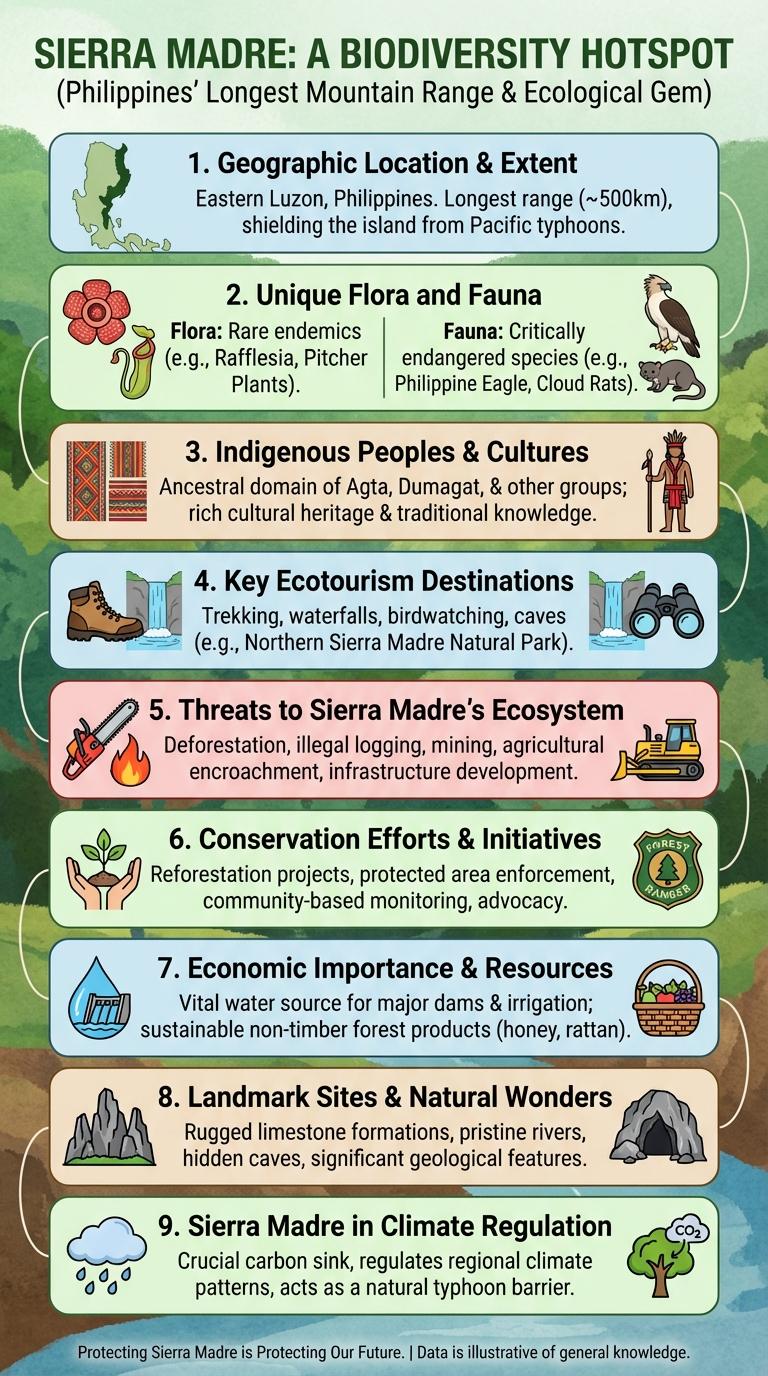
The Sierra Madre mountain range, spanning the Philippines, is a critical biodiversity hotspot boasting over 1,100 endemic species. It supports diverse ecosystems from lowland rainforests to montane forests, sheltering rare flora and fauna. Conservation efforts focus on protecting its unique habitats from deforestation and habitat fragmentation.
Geographic Location & Extent
The Sierra Madre is the longest mountain range in the Philippines, stretching approximately 540 kilometers along the eastern coast of Luzon Island. It runs from the province of Cagayan in the north to Quezon province in the south.
This mountain range acts as a natural barrier against typhoons from the Pacific Ocean, influencing the climate and ecology of surrounding regions. It covers a significant portion of Luzon's eastern coastline, making it a key geographic feature in the country.
Unique Flora and Fauna
The Sierra Madre mountain range is a biodiversity hotspot, home to numerous unique species of plants and animals. Its diverse ecosystems range from tropical rainforests to pine-oak forests, supporting rich flora and fauna.
The region hosts endemic species like the Philippine eagle and the Sierra Madre forest mouse. Rare plants such as the waling-waling orchid thrive in its habitats. Conservation efforts focus on protecting these irreplaceable natural treasures from deforestation and habitat loss.
Indigenous Peoples & Cultures
The Sierra Madre mountain range, stretching across the Philippines, is home to diverse indigenous groups with rich cultural traditions. These communities maintain ancestral practices that contribute to the region's unique heritage and ecological stewardship.
- Igorot Peoples - The Igorot are one of the prominent indigenous groups inhabiting the highlands of the Sierra Madre, known for their rice terrace farming and vibrant rituals.
- Tagbanua Community - The Tagbanua live in the Sierra Madre lowlands and coastal areas, preserving distinct languages and spiritual customs connected to nature.
- Traditional Ecological Knowledge - Indigenous groups in the Sierra Madre apply ancestral knowledge for sustainable forest management and biodiversity conservation.
Key Ecotourism Destinations
| Ecotourism Destination | Highlights |
|---|---|
| Mount Sierra Madre Range | Rich biodiversity, endemic species, hiking trails, birdwatching spots |
| Calaguas Islands | Pristine beaches, marine wildlife, snorkeling, island hopping tours |
| Dupax del Sur Forest | Ancient trees, wildlife sanctuary, guided nature walks, cultural sites |
| Nagtipunan River | White-water rafting, scenic riverbanks, freshwater ecosystems |
| Casecnan Protected Landscape | Waterfalls, diverse flora and fauna, eco-lodges, conservation projects |
Threats to Sierra Madre's Ecosystem
What are the main threats to the Sierra Madre's ecosystem?
Deforestation caused by logging and agricultural expansion significantly endangers the Sierra Madre's biodiversity. Poaching and illegal wildlife trade also contribute to the decline of native animal species.
How does climate change impact the Sierra Madre region?
Rising temperatures and altered rainfall patterns disrupt habitats, affecting endemic species. These changes increase the vulnerability of the ecosystem to invasive species and forest fires.
Why is mining a concern for the Sierra Madre environment?
Mining activities lead to habitat destruction and contamination of soil and waterways. These pollutants harm aquatic life and reduce the availability of clean water for wildlife and local communities.
What role does human settlement play in threatening the Sierra Madre?
Expanding human settlements cause habitat fragmentation, isolating wildlife populations. Infrastructure development such as roads facilitates easier access for illegal activities.
How do conservation efforts address threats to Sierra Madre's ecosystem?
Protected areas and reforestation projects aim to restore natural habitats and increase biodiversity resilience. Community-based conservation encourages sustainable resource management and reduces environmental damage.
Conservation Efforts & Initiatives
The Sierra Madre mountain range hosts diverse ecosystems that are crucial for biodiversity conservation. Conservation efforts focus on protecting endemic species and preserving natural habitats.
Organizations collaborate on reforestation projects and wildlife monitoring to combat deforestation and habitat loss. Sustainable tourism initiatives promote environmental awareness while supporting local communities.
Economic Importance & Resources
The Sierra Madre mountain range is rich in natural resources, contributing significantly to the local and national economy. It supports mining activities with abundant deposits of gold, copper, and other minerals. The forests provide timber and non-timber products, while the fertile soils support agriculture and livestock farming.
Landmark Sites & Natural Wonders
The Sierra Madre mountain range stretches across the Philippines, offering breathtaking landscapes and rich biodiversity. It is home to several landmark sites and natural wonders that attract adventurers and nature lovers alike.
- Mount Canlaon - An active stratovolcano and the highest peak in the range, known for its lush forests and volcanic activity.
- Callao Cave - A limestone cave system featuring impressive chambers and prehistoric archaeological finds.
- Dupinga Falls - A picturesque waterfall surrounded by verdant foliage, providing a serene escape for visitors.
- The Northern Sierra Madre Natural Park - The largest protected area in the Philippines, recognized for its exceptional biodiversity and pristine ecosystems.
- Absolon Rock Formation - Unique rock formations shaped by natural erosion, offering striking geological views.
