Proper garbage disposal plays a crucial role in maintaining clean environments and reducing pollution. Infographics provide a clear and visually engaging way to understand waste management practices and their impact. Effective waste segregation and disposal methods help conserve resources and protect ecosystems.
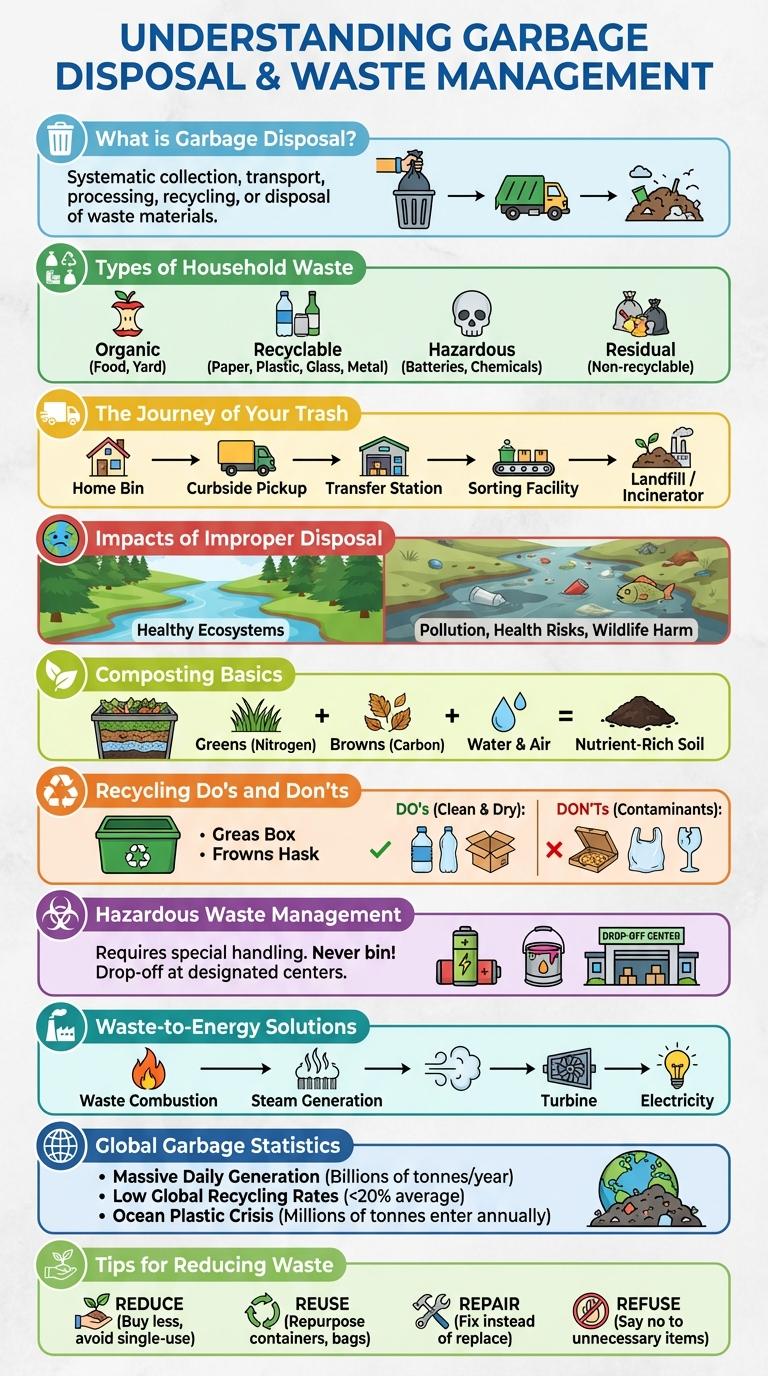
What is Garbage Disposal?
Garbage disposal is a device installed under kitchen sinks that shreds food waste into small pieces, allowing it to pass through plumbing easily. It helps reduce kitchen waste sent to landfills by breaking down organic material. This system promotes efficient waste management and minimizes unpleasant odors in the kitchen.
Types of Household Waste
Household waste consists of various materials that require proper disposal to minimize environmental impact. Understanding the different types helps in effective recycling and waste management.
Common types include organic waste, recyclable materials, hazardous waste, electronic waste, and general trash. Each type demands specific handling to ensure safety and sustainability.
The Journey of Your Trash
Your trash undergoes a complex journey from your home to final disposal. Understanding this process highlights the importance of responsible waste management.
- Collection - Waste is gathered from households and businesses by sanitation trucks on scheduled days.
- Sorting - At processing facilities, recyclable materials are separated from landfill waste and hazardous items.
- Final Disposal - Non-recyclable trash is either compacted in landfills or processed through incineration to reduce volume.
Impacts of Improper Disposal
Improper garbage disposal leads to environmental pollution, contaminating soil, water, and air. Toxic substances from waste harm wildlife and disrupt ecosystems. Human health risks increase due to exposure to hazardous materials and disease vectors.
Composting Basics
What is composting and why is it important for waste management? Composting is the natural process of recycling organic matter, such as food scraps and yard waste, into nutrient-rich soil. This process reduces landfill waste and enriches soil health, promoting sustainable gardening and farming.
How can you start composting at home? Begin by collecting organic waste like vegetable peels, coffee grounds, and grass clippings in a compost bin. Maintain a balance of green materials (nitrogen) and brown materials (carbon) to optimize decomposition.
What materials should not be included in compost? Avoid adding meat, dairy, oils, and diseased plants as they can attract pests and slow down decomposition. Proper segregation ensures safe and efficient composting.
What are the environmental benefits of composting? Composting decreases methane emissions from landfills and reduces the need for chemical fertilizers. It conserves water by improving soil's moisture retention and enhances biodiversity.
| Compost Material | Category |
|---|---|
| Vegetable scraps | Green (Nitrogen) |
| Dry leaves | Brown (Carbon) |
| Coffee grounds | Green (Nitrogen) |
| Shredded newspaper | Brown (Carbon) |
| Grass clippings | Green (Nitrogen) |
Recycling Do's and Don'ts
Proper recycling helps reduce landfill waste and conserves natural resources. Understanding what can and cannot be recycled is essential for effective waste management.
Do rinse containers before recycling to prevent contamination. Don't place plastic bags or food-soiled items in recycling bins, as they can disrupt the process.
Hazardous Waste Management
Proper hazardous waste management is essential to protect human health and the environment from toxic substances. Effective disposal methods minimize the risks associated with hazardous materials.
- Identification - Hazardous waste must be accurately identified to prevent improper handling and disposal.
- Segregation - Hazardous waste is separated from non-hazardous waste to avoid contamination and facilitate safe processing.
- Treatment and Disposal - Specialized treatments like incineration or chemical neutralization are applied before final disposal to reduce toxicity.
Waste-to-Energy Solutions
Waste-to-energy (WTE) solutions convert municipal solid waste into usable energy forms such as electricity and heat. This approach reduces landfill dependency and helps manage growing waste volumes effectively.
Waste is processed through combustion, anaerobic digestion, or gasification to generate energy. Advanced technologies improve emissions control, ensuring environmental compliance. WTE plants contribute to circular economy goals by recovering value from waste materials.
Global Garbage Statistics
Global garbage generation has reached alarming levels, impacting ecosystems and human health worldwide. Efficient garbage disposal methods are critical to managing waste sustainably and reducing environmental harm.
- Amount of Waste Generated - The world produces over 2 billion tons of municipal solid waste annually, with projections rising by 70% by 2050.
- Waste Composition - Organic waste constitutes nearly 44% of global municipal waste, followed by plastics at 17%, challenging disposal and recycling efforts.
- Recycling Rates - Only about 30% of global waste is recycled or composted, while the majority ends up in landfills or is incinerated.
Innovative waste management solutions and increased global cooperation are essential to reversing the trend of escalating garbage statistics.
