Deforestation dramatically alters ecosystems by removing vast areas of forest, resulting in loss of biodiversity and disruption of carbon cycles. This infographic highlights key statistics, causes, and environmental impacts associated with deforestation worldwide. Visual representations clarify complex data, emphasizing the urgent need for sustainable forest management.
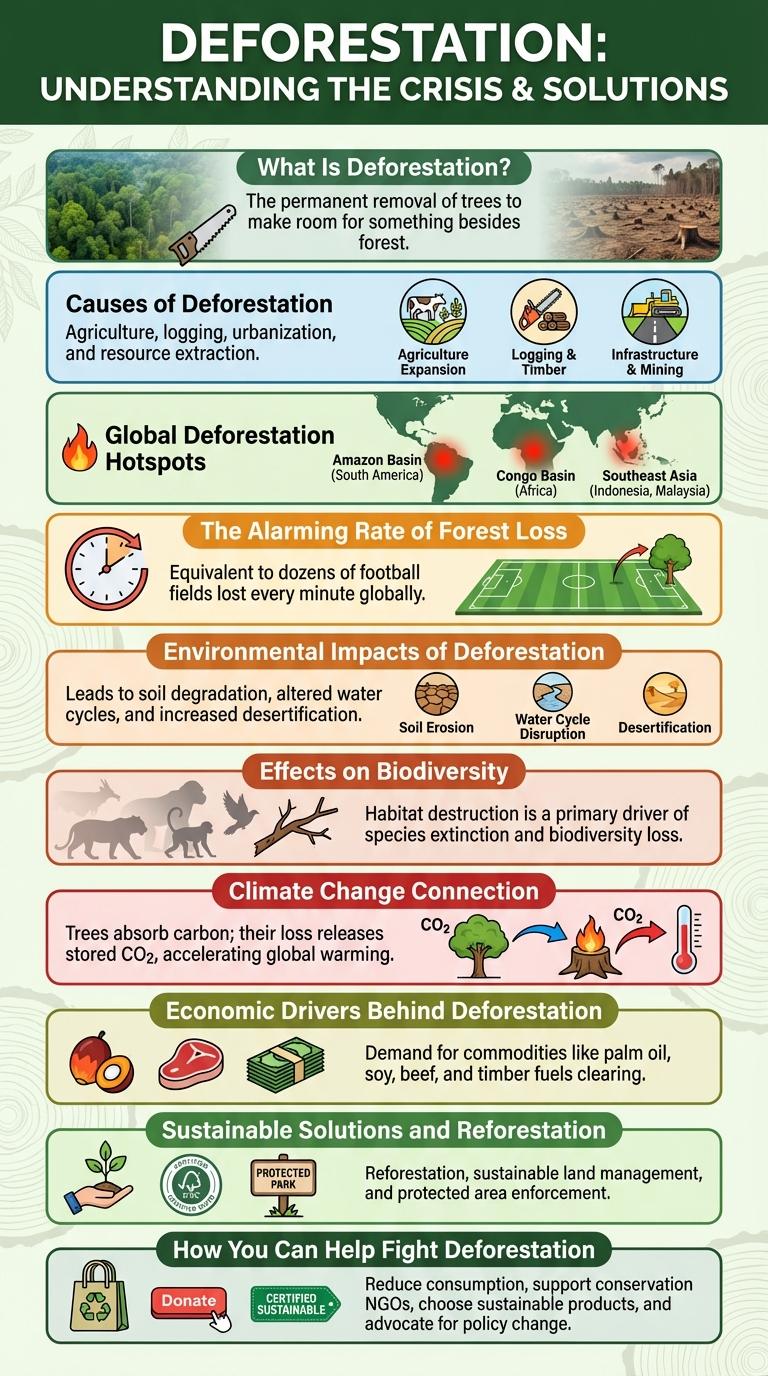
What Is Deforestation?
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Deforestation refers to the large-scale removal of forest cover, transforming forested land into non-forested areas. |
| Causes | Agricultural expansion, logging, infrastructure development, and mining activities are primary drivers of deforestation. |
| Impacts | Loss of biodiversity, disruption of water cycles, increased greenhouse gas emissions, and soil erosion are major consequences. |
| Global Extent | Approximately 10 million hectares of forest are lost annually worldwide, with tropical rainforests being the most affected. |
| Significance | Forests cover about 31% of Earth's land area and play a crucial role in carbon sequestration and climate regulation. |
Causes of Deforestation
Deforestation primarily results from agricultural expansion, where forests are cleared to create farmland and pastures. Logging for timber and paper products significantly reduces forest cover worldwide. Infrastructure development, including roads and urban construction, also contributes to the ongoing loss of vital forest ecosystems.
Global Deforestation Hotspots
Global deforestation hotspots represent regions experiencing the fastest loss of forest cover, significantly impacting biodiversity and climate. These areas face intense pressures from agriculture, logging, and urban expansion.
- Amazon Basin - The Amazon rainforest suffers from extensive illegal logging and farmland conversion, causing massive habitat loss.
- Congo Basin - Central Africa's Congo Basin faces deforestation due to charcoal production and commercial logging activities.
- Southeast Asia - Indonesia and Malaysia experience rapid forest clearing driven by palm oil plantations and timber extraction.
Protecting these global deforestation hotspots is essential for maintaining ecological balance and combating climate change.
The Alarming Rate of Forest Loss
Deforestation is occurring at an unprecedented rate, with an estimated 10 million hectares of forest lost globally each year. Tropical rainforests, which house over 50% of the world's terrestrial species, are disappearing rapidly due to logging, agriculture, and urban expansion. This accelerating forest loss threatens biodiversity, disrupts carbon cycles, and exacerbates climate change impacts worldwide.
Environmental Impacts of Deforestation
Deforestation causes significant environmental damage by disrupting natural ecosystems and reducing biodiversity. The loss of forests accelerates climate change by increasing greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere.
- Loss of Habitat - Deforestation eliminates the homes of countless plant and animal species, leading to population declines and extinction risks.
- Soil Degradation - Tree removal exposes soil to erosion, reducing fertility and increasing the likelihood of landslides and desertification.
- Carbon Emissions - Cutting down forests releases stored carbon dioxide, contributing significantly to global warming and climate instability.
Effects on Biodiversity
Deforestation severely disrupts ecosystems by destroying habitats critical to countless species. The loss of trees reduces biodiversity, leading to the extinction of vulnerable plants and animals.
- Habitat Loss - Removal of forests eliminates shelter and food sources for wildlife, causing population declines.
- Species Extinction - Many species face extinction due to shrinking habitats and fragmented ecosystems.
- Reduced Genetic Diversity - Fragmented habitats decrease gene flow, weakening species' adaptability to environmental changes.
Climate Change Connection
Deforestation significantly accelerates climate change by releasing stored carbon dioxide when trees are cut down. Forests act as major carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 and regulating global temperatures.
The loss of forest cover reduces the Earth's ability to capture greenhouse gases, intensifying global warming. This disruption alters local climates, reduces rainfall, and increases the frequency of extreme weather events. Preserving forests is essential to mitigate climate change and protect biodiversity.
Economic Drivers Behind Deforestation
What are the main economic drivers behind deforestation?
Deforestation is primarily driven by the expansion of agriculture, logging, and infrastructure development. These activities provide essential resources and economic growth but often lead to significant environmental degradation.
Sustainable Solutions and Reforestation
Deforestation significantly impacts global biodiversity and climate stability. Sustainable solutions aim to balance economic needs with environmental preservation.
Reforestation restores degraded land by planting native tree species. These efforts enhance carbon sequestration and support wildlife habitats.
