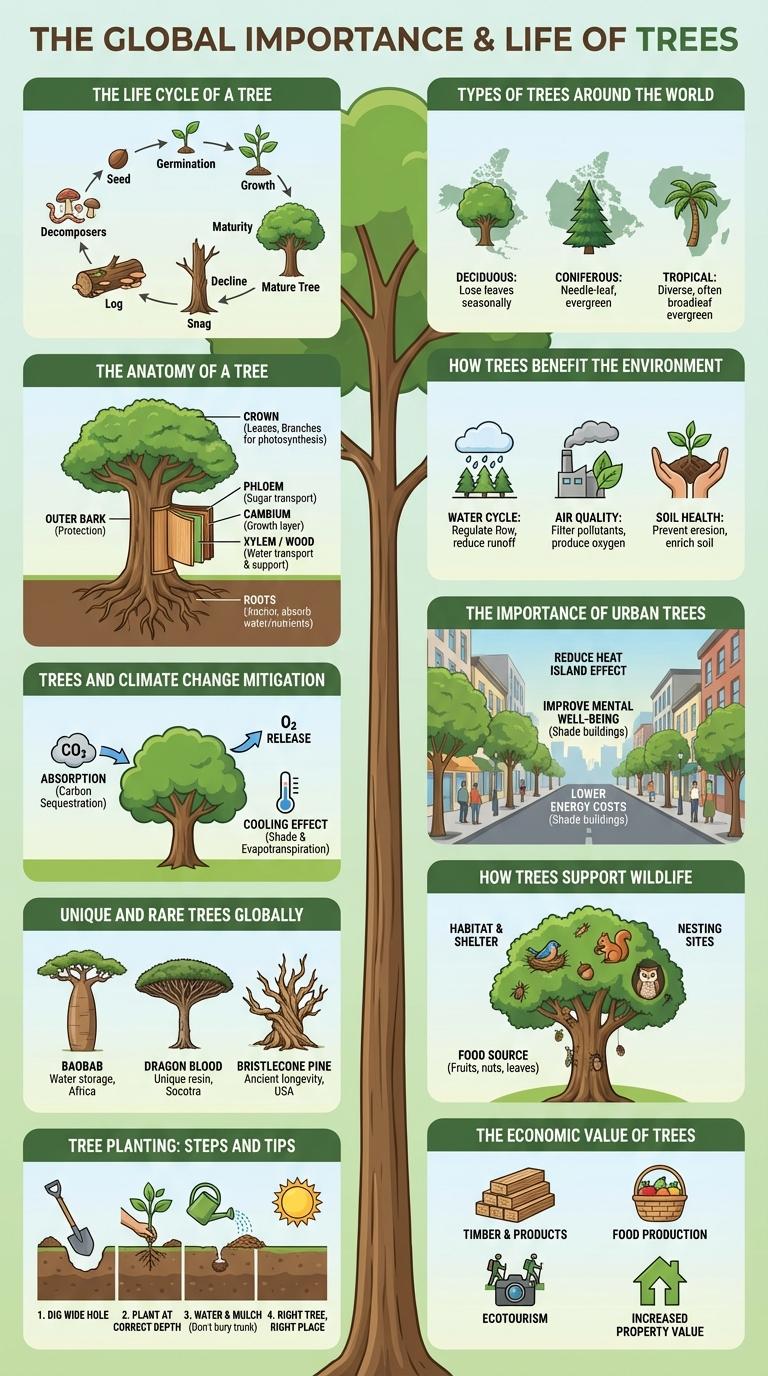
Infographics about trees visually represent essential information on tree species, growth patterns, and environmental benefits. They highlight the role trees play in air purification, carbon sequestration, and providing habitats for wildlife. These visual tools enhance understanding of tree conservation and the importance of urban forestry.
The Life Cycle of a Tree
Trees begin their life cycle as seeds containing the embryo of a future giant. Germination marks the start of growth when the seed absorbs water and nutrients from the soil.
Seedlings emerge and develop roots, stems, and leaves, enabling photosynthesis to provide energy. Mature trees reproduce through flowers or cones, producing new seeds to continue the cycle.
Types of Trees Around the World
Trees play a crucial role in global ecosystems, supporting biodiversity and regulating climate. Different types of trees are adapted to various environments around the world, showcasing diverse forms and functions.
- Deciduous Trees - These trees shed their leaves annually and are commonly found in temperate regions with distinct seasons.
- Coniferous Trees - Known for their needle-like leaves and cones, conifers dominate boreal forests across the Northern Hemisphere.
- Tropical Trees - Thriving in warm climates, tropical trees such as mahogany and kapok contribute to dense rainforests with high biodiversity.
The Anatomy of a Tree
Trees are complex living organisms with distinct parts that each play a vital role in their growth and survival. Understanding the anatomy of a tree helps reveal how it supports life and maintains ecosystems.
- Roots - Anchor the tree and absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
- Trunk - Provides structural support and transports nutrients through the xylem and phloem.
- Leaves - Conduct photosynthesis to produce food for the tree using sunlight and carbon dioxide.
The bark protects the tree from environmental damage and helps prevent water loss.
How Trees Benefit the Environment
Trees play a crucial role in improving air quality by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen through photosynthesis. They provide habitat for wildlife, supporting biodiversity and maintaining ecological balance. Trees also help reduce soil erosion and moderate urban temperatures by offering shade and cooling effects.
Trees and Climate Change Mitigation
Trees play a crucial role in climate change mitigation by absorbing carbon dioxide through photosynthesis, reducing greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere. Forests act as carbon sinks, storing approximately 30% of the world's terrestrial carbon. Protecting and expanding tree cover supports biodiversity, improves air quality, and stabilizes local climates, making it a vital strategy for combating climate change.
The Importance of Urban Trees
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Air Quality Improvement | Urban trees absorb pollutants such as carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, enhancing air quality. |
| Temperature Regulation | Shade from trees lowers urban heat island effect, reducing temperatures by up to 10degF in city environments. |
| Stormwater Management | Trees intercept and absorb rainfall, decreasing runoff and reducing the risk of urban flooding. |
| Biodiversity Support | Provide habitats for birds, insects, and other wildlife, contributing to urban ecosystem health. |
| Mental Health Benefits | Green spaces with trees lower stress levels and improve overall well-being for city residents. |
Unique and Rare Trees Globally
Trees are essential to global ecosystems, with some species standing out for their rarity and unique characteristics. These rare trees often hold significant ecological, cultural, and scientific value.
One example is the Wollemi Pine, discovered in Australia and considered a "living fossil" dating back 200 million years. Another rare species is the Dragon's Blood Tree in Yemen, known for its distinctive umbrella shape and red sap.
How Trees Support Wildlife
How do trees support wildlife in their natural habitats?
Trees provide shelter, food, and breeding grounds essential for many animal species. Their complex structures create diverse ecosystems that sustain birds, insects, mammals, and fungi.
Tree Planting: Steps and Tips
Tree planting is a simple yet impactful way to enhance the environment and support biodiversity. Proper steps ensure healthy growth and long-lasting benefits for urban and rural areas.
Choose a suitable tree species based on your local climate and soil conditions. Dig a hole twice the width of the root ball and plant the tree at the correct depth to promote root development. Water the tree regularly and mulch around the base to retain moisture and prevent weeds.
